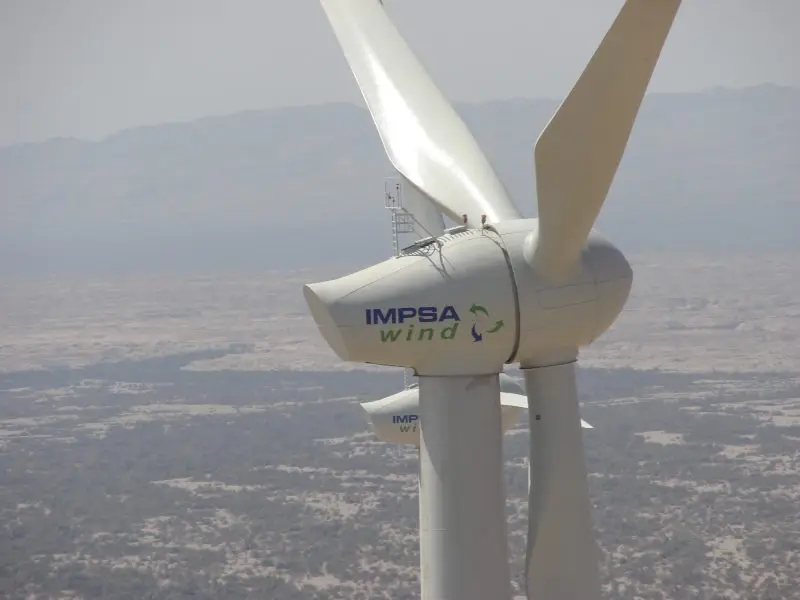
Composite
Materials
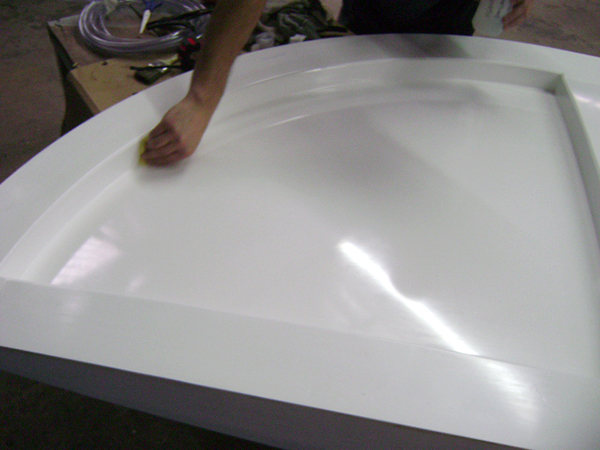
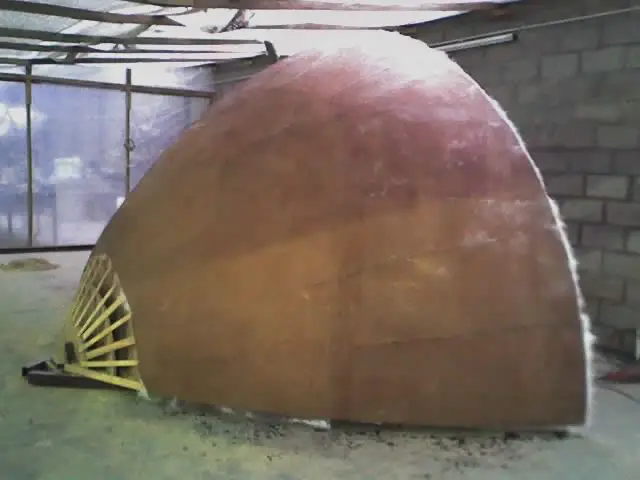
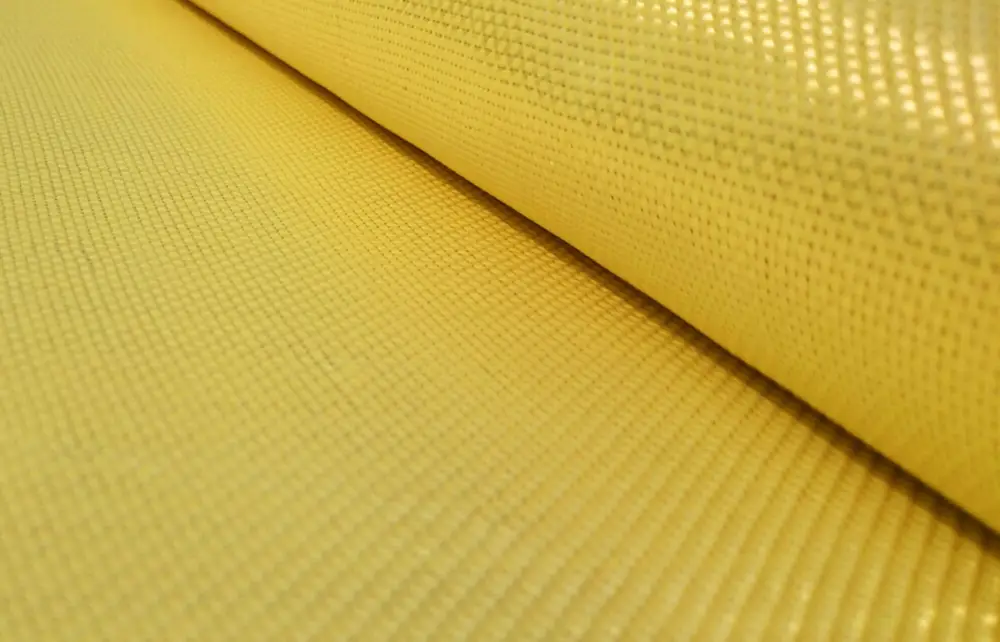
Composite materials, or Composites, are materials created by combining two or more different materials in such a way that the properties of the new material are superior to those of the individual materials used separately.
These composites have a primary requirement: to ensure the same mechanical and/or chemical resistance qualities as the original materials while also meeting various key objectives depending on the desired requirements. These objectives can include weight reduction, improved anti-corrosive properties, dielectricity, stiffness, performance at high temperatures, toughness, and more.

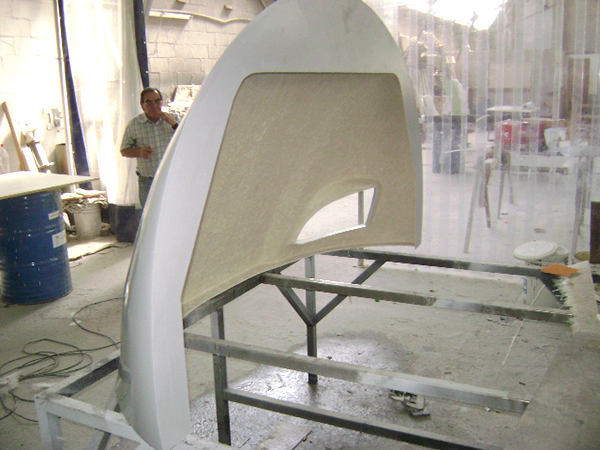
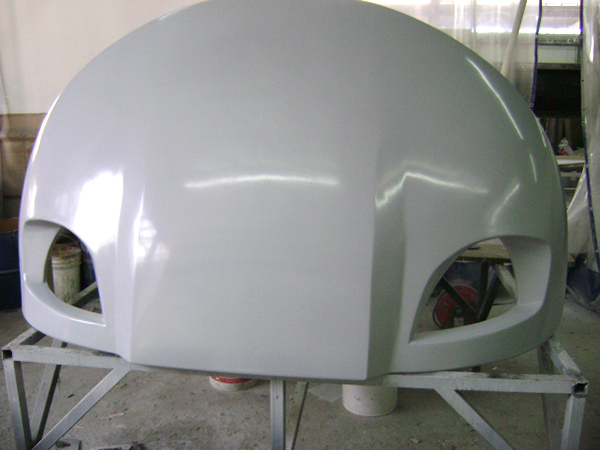
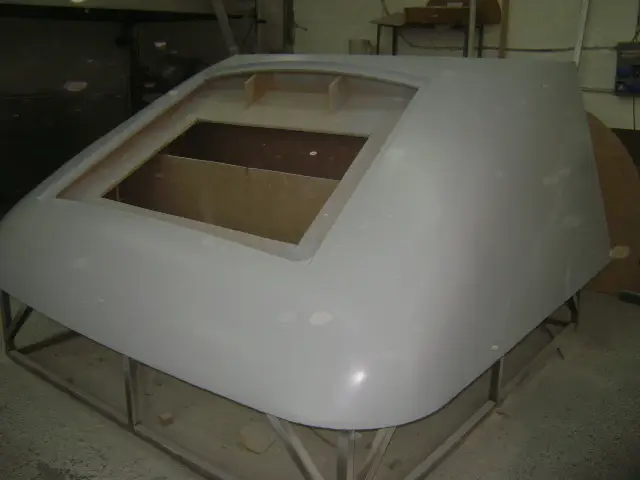
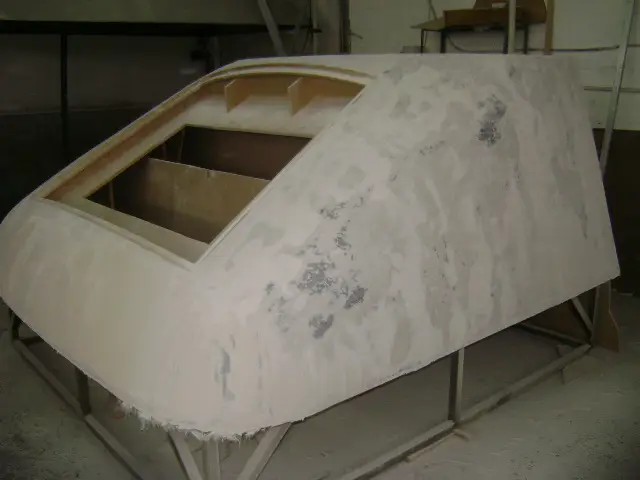
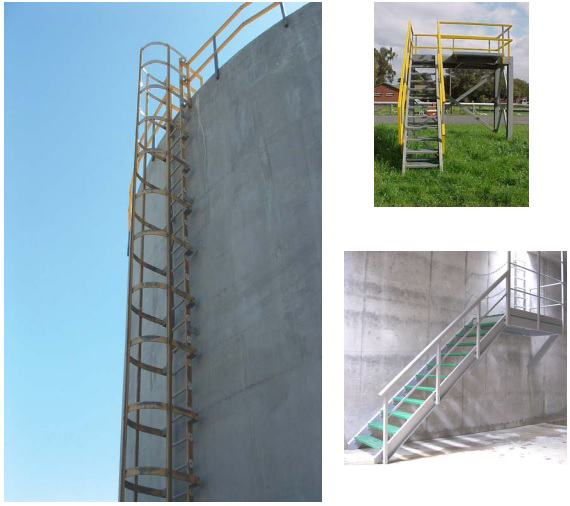
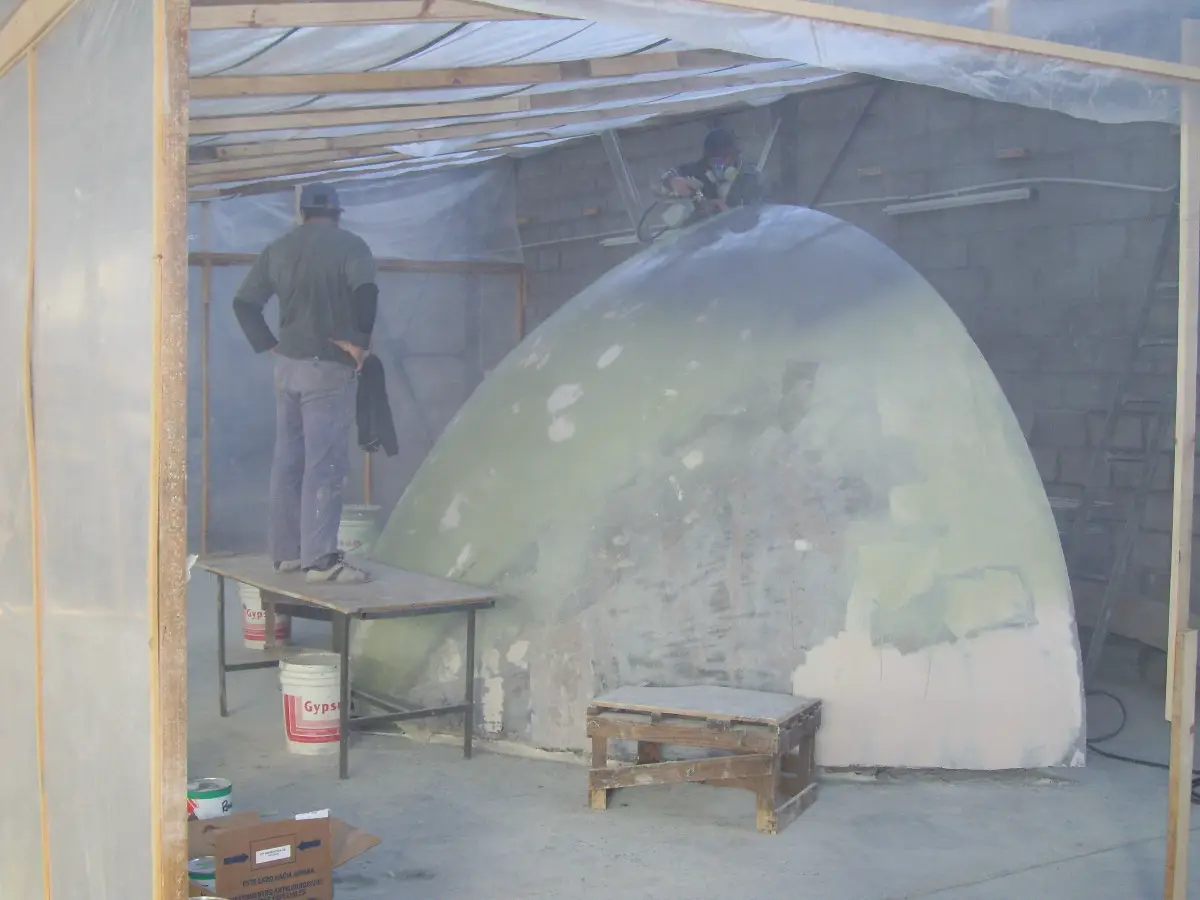
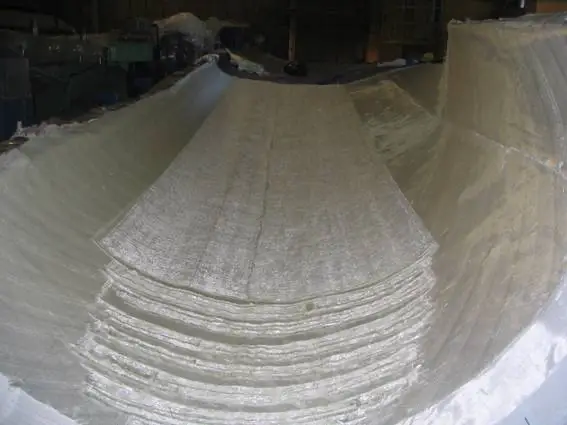
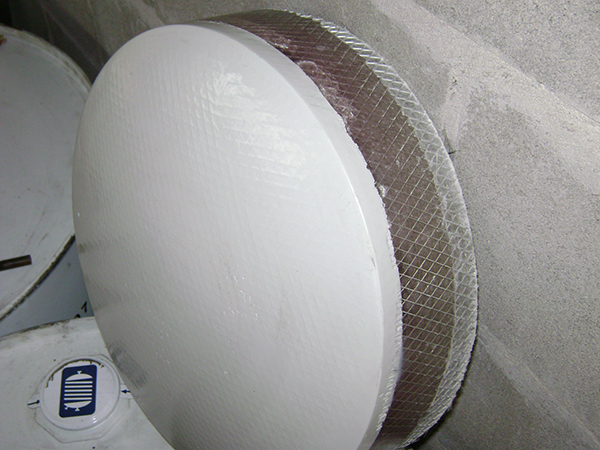
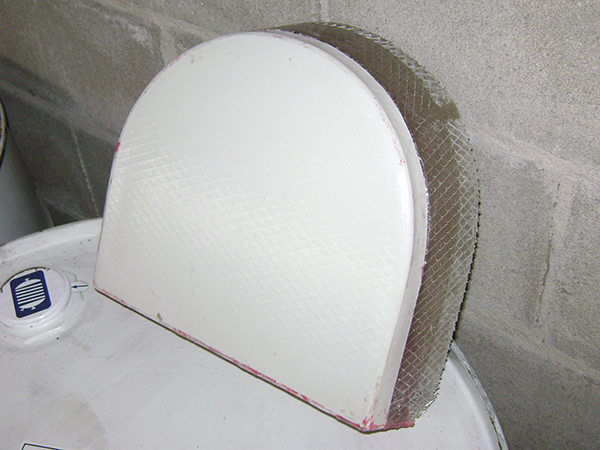
Hand lay-up
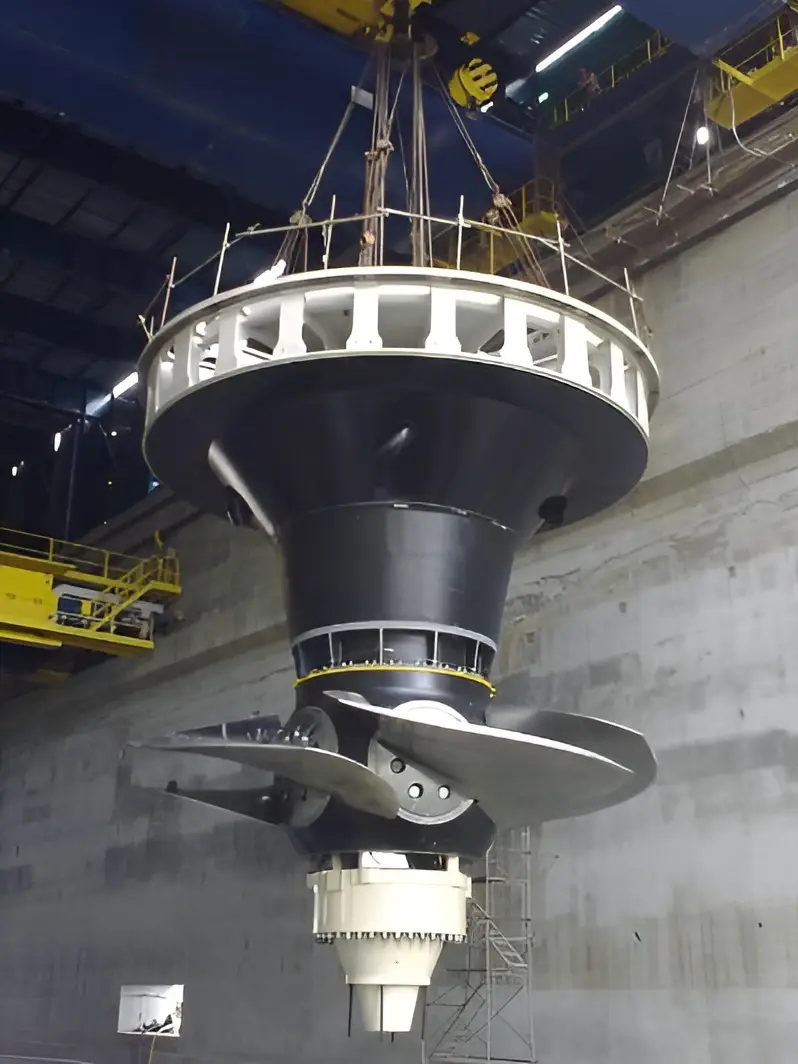
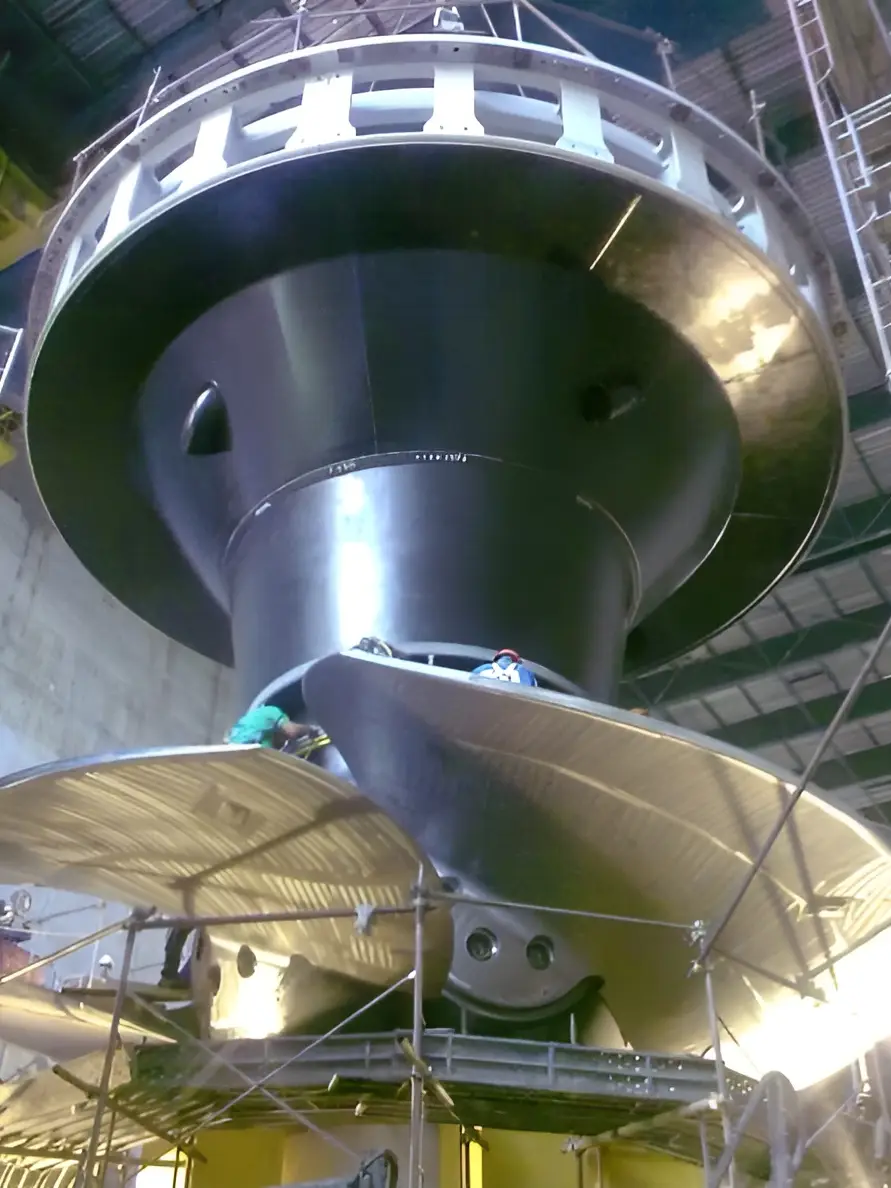
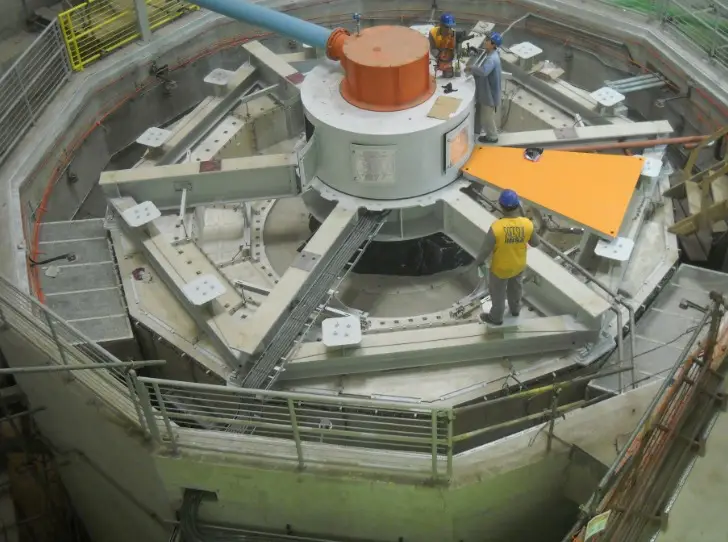
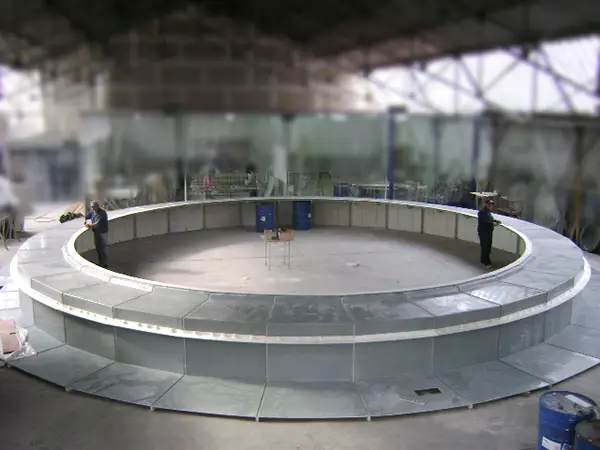
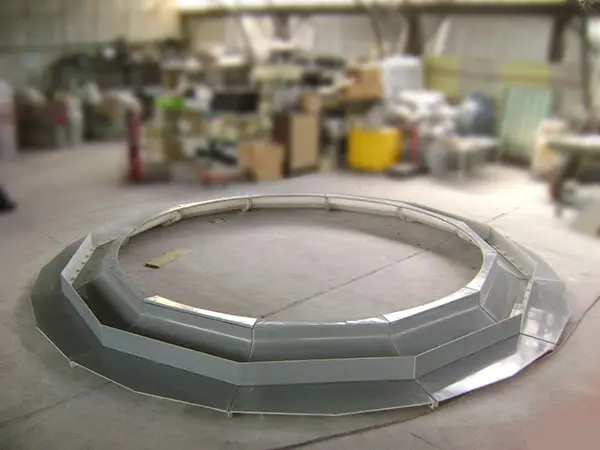
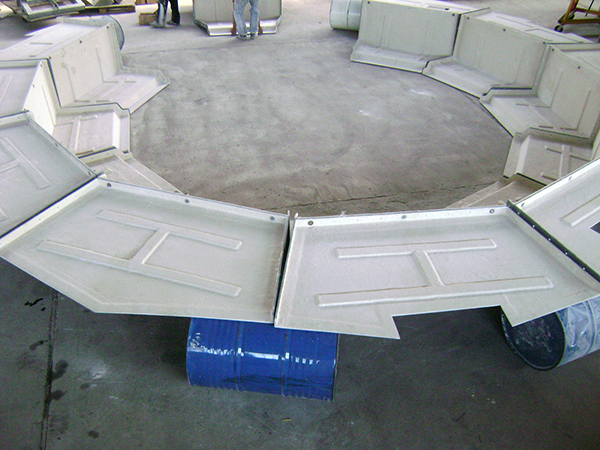
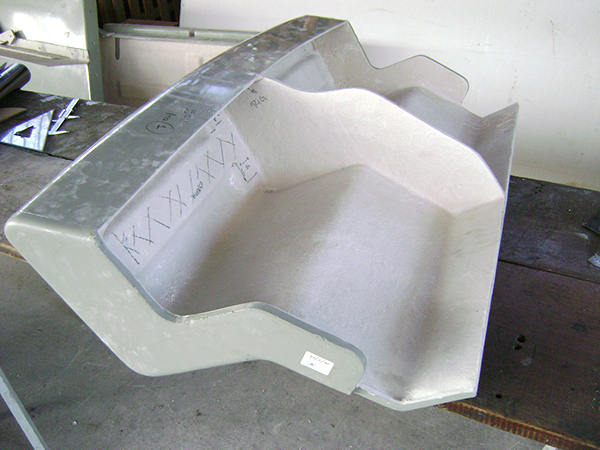
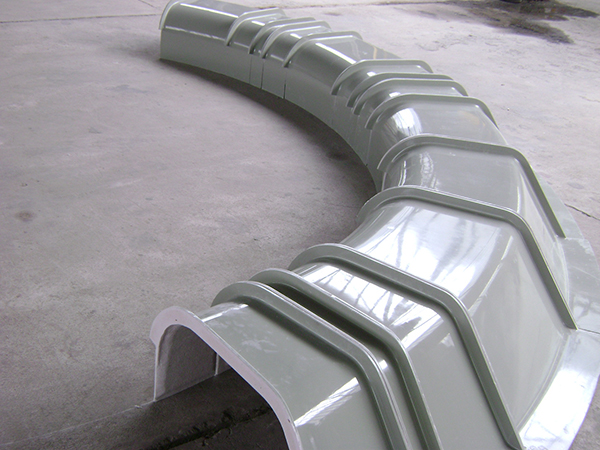
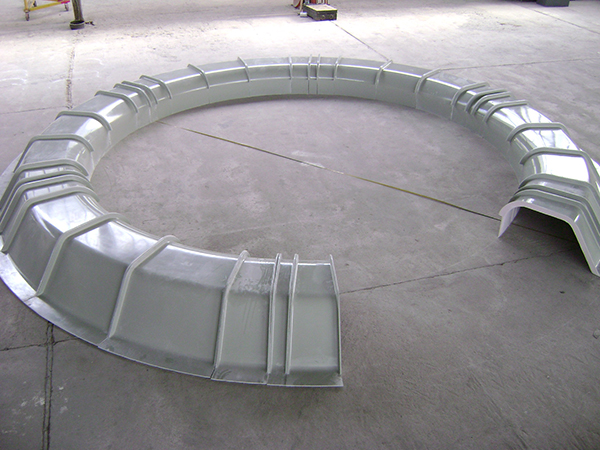
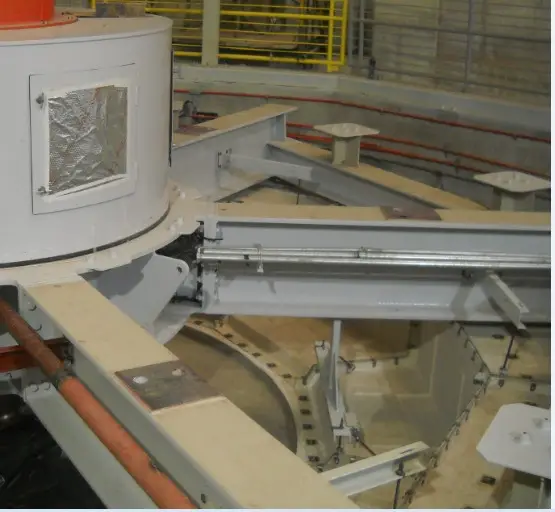
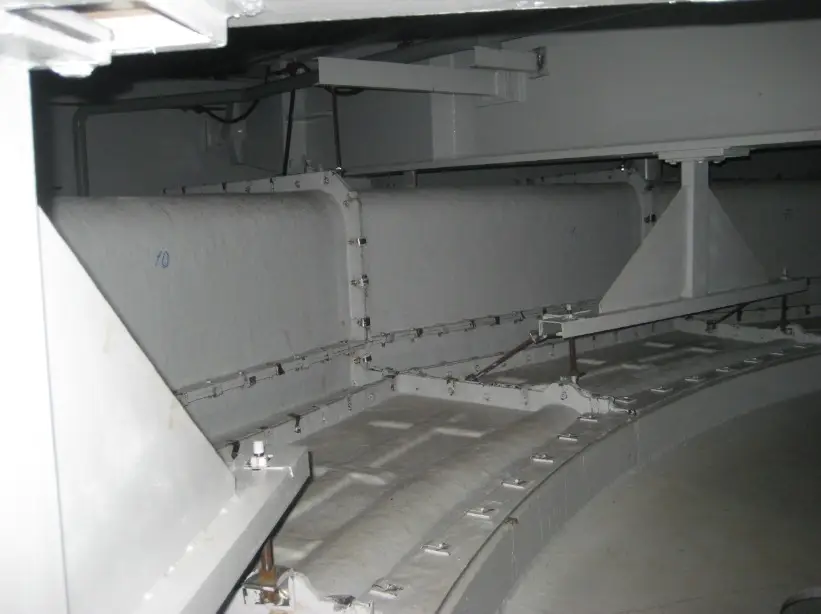
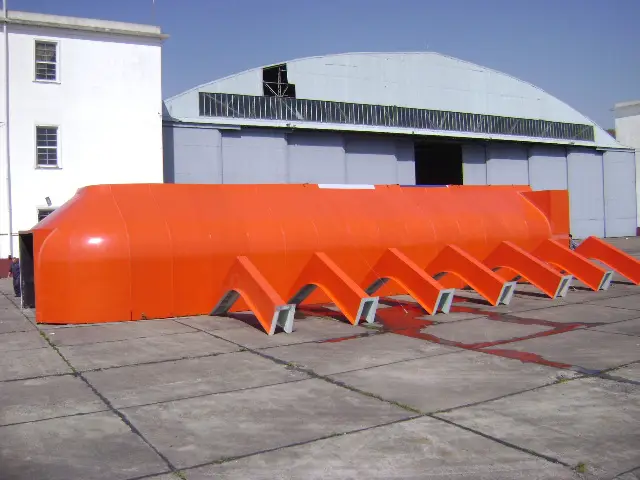
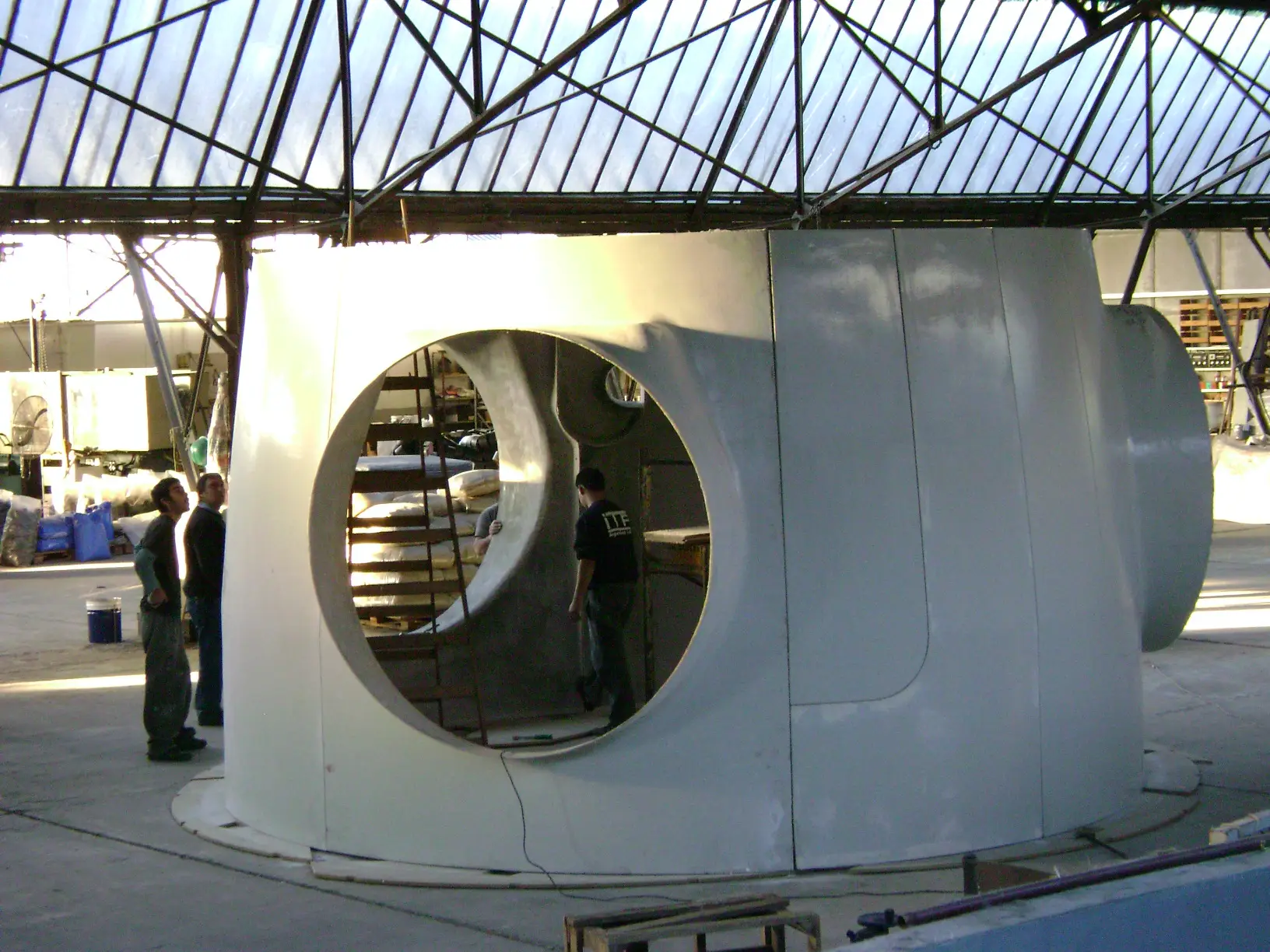
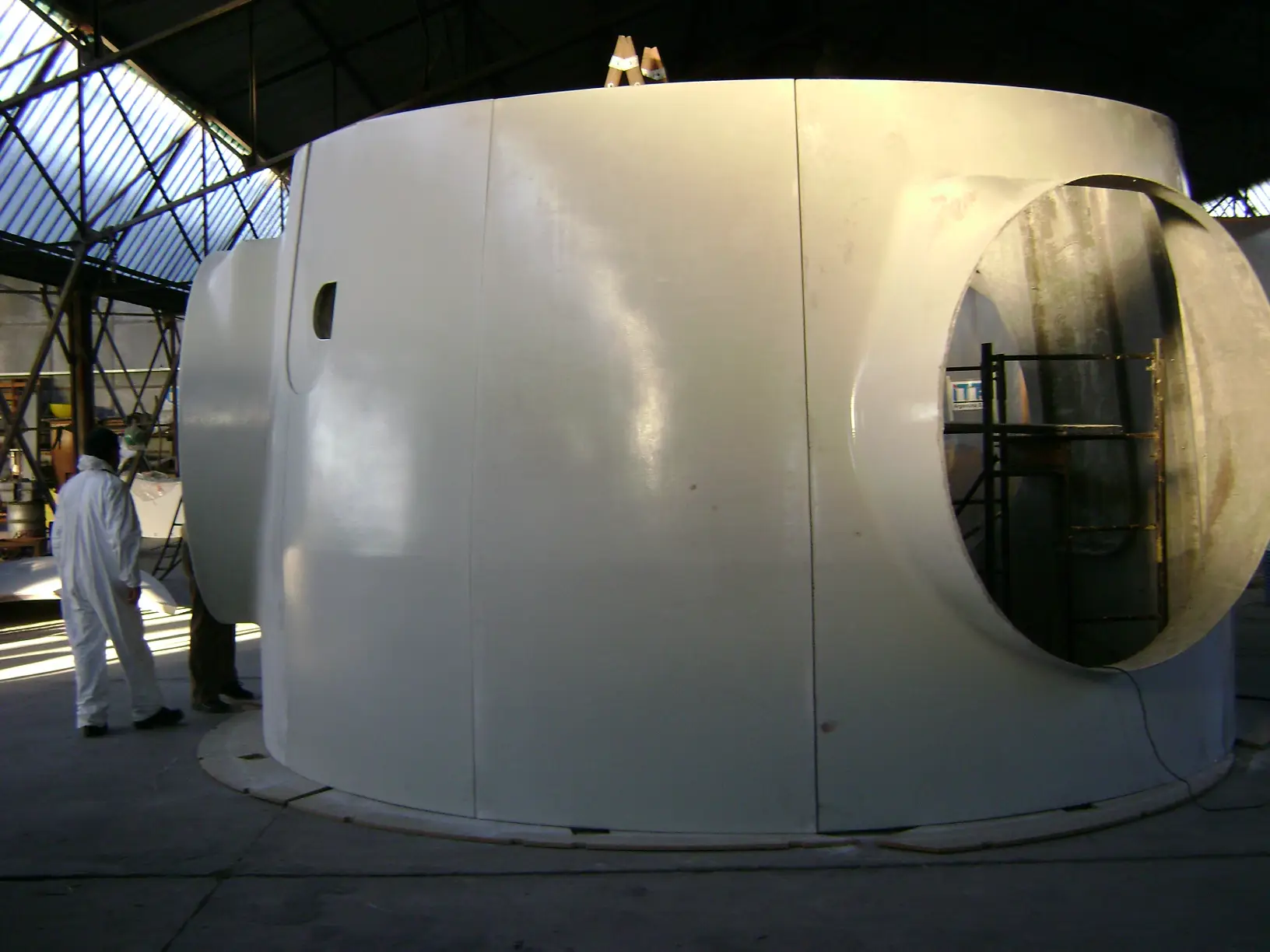
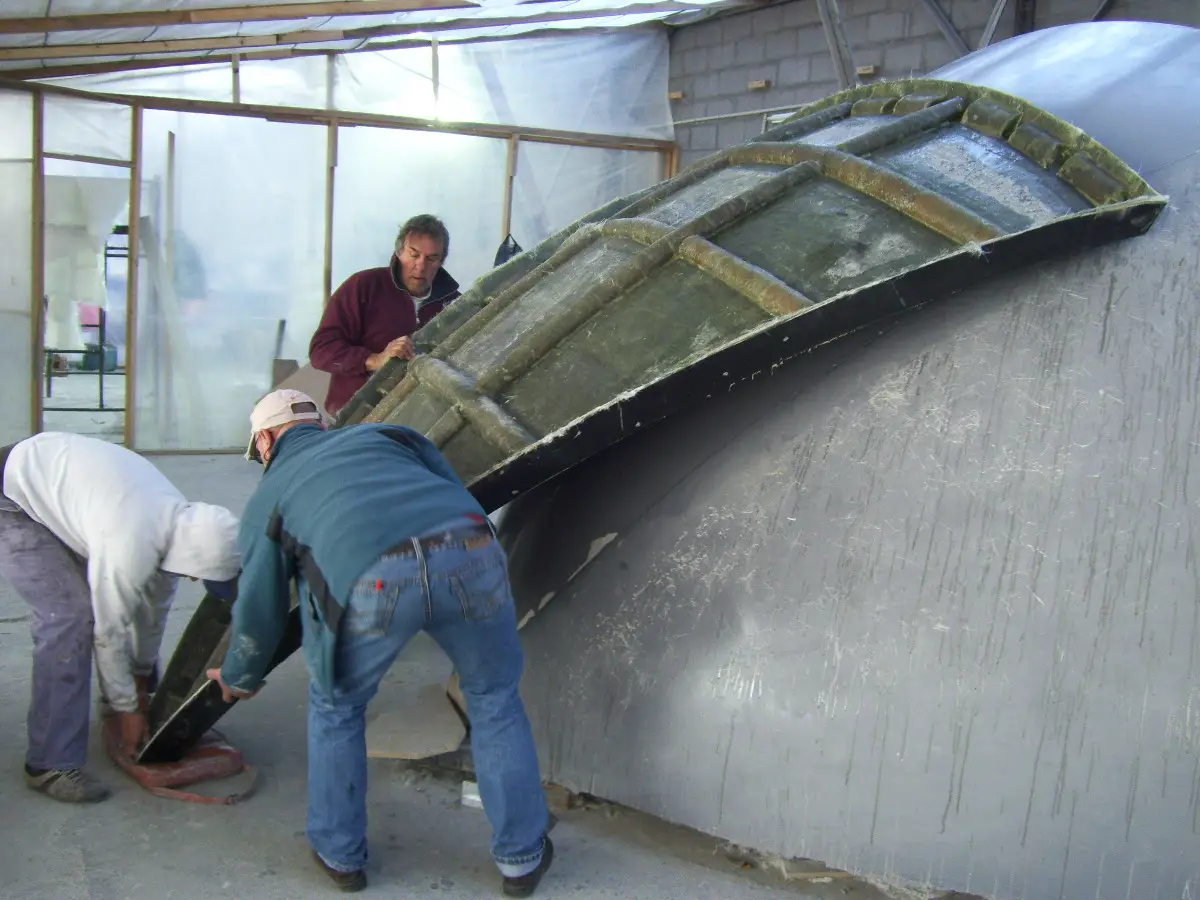
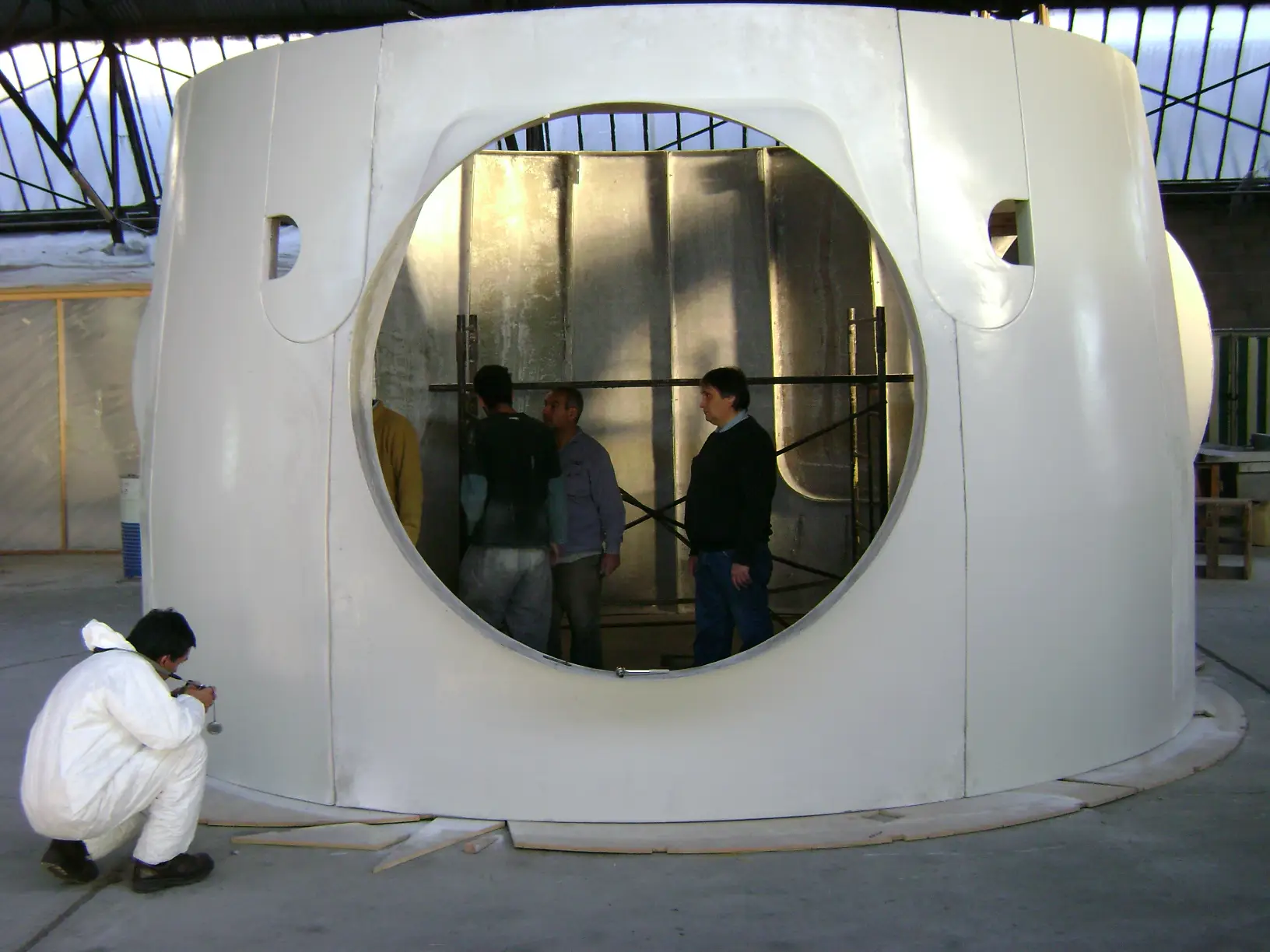
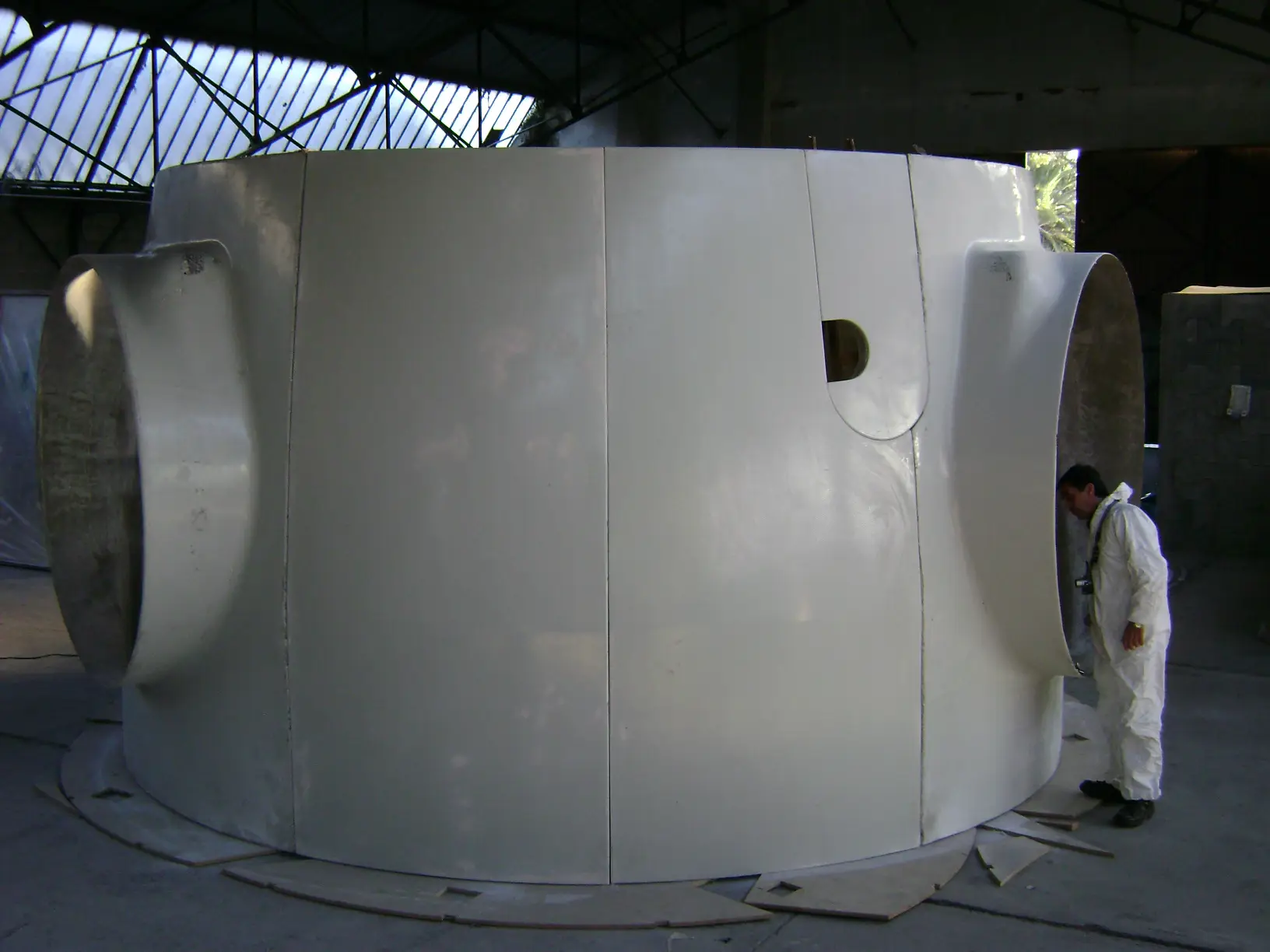
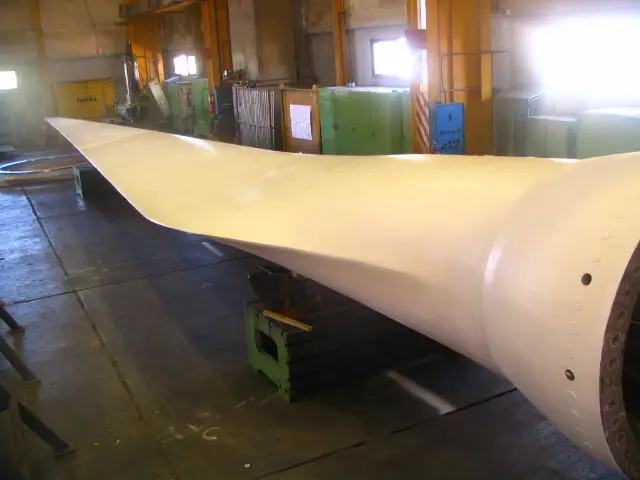
Air deflectors for hydroelectric turbines
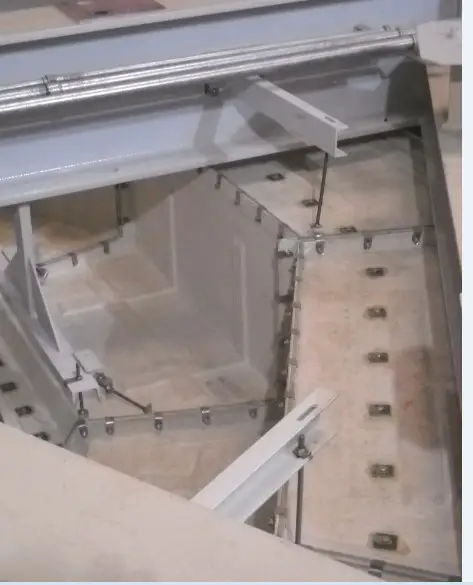
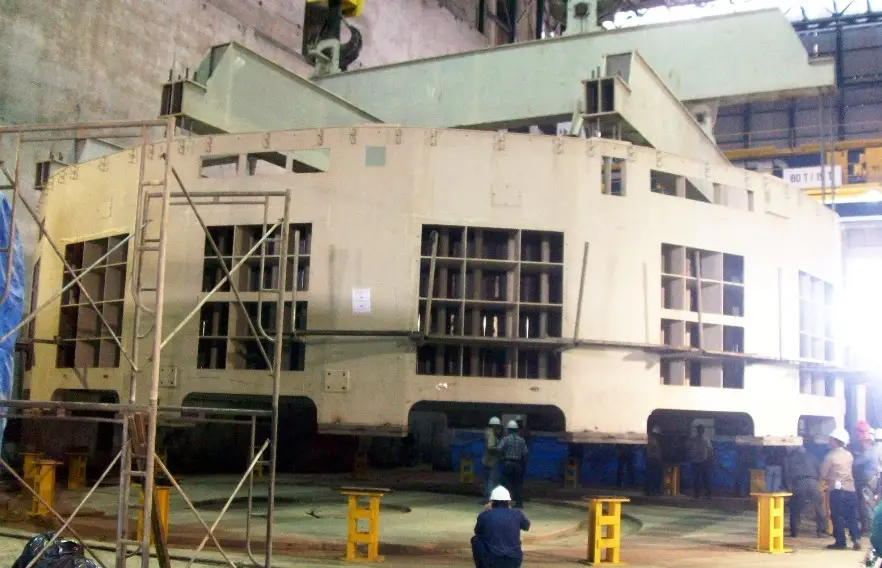
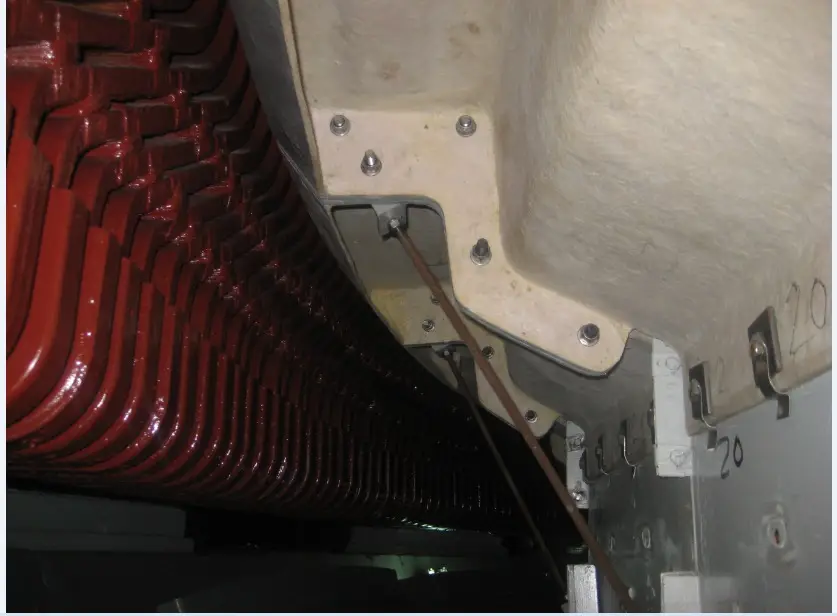
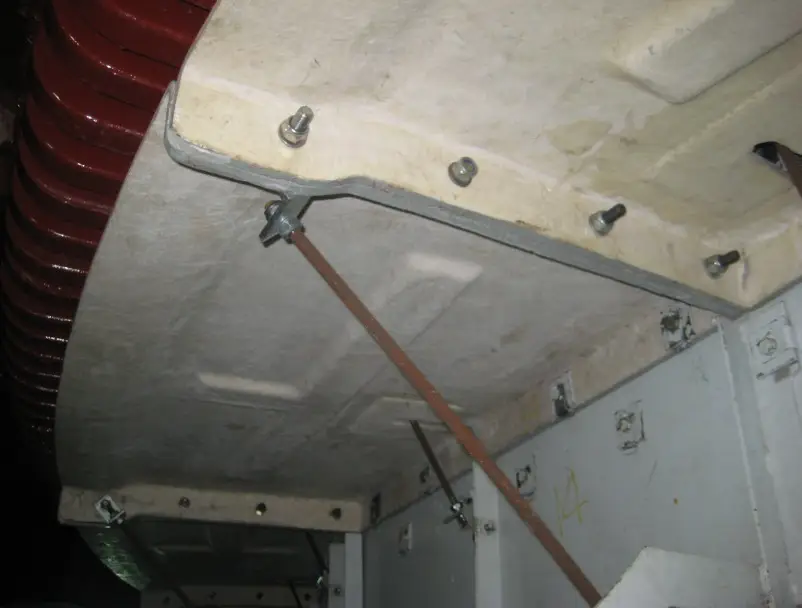
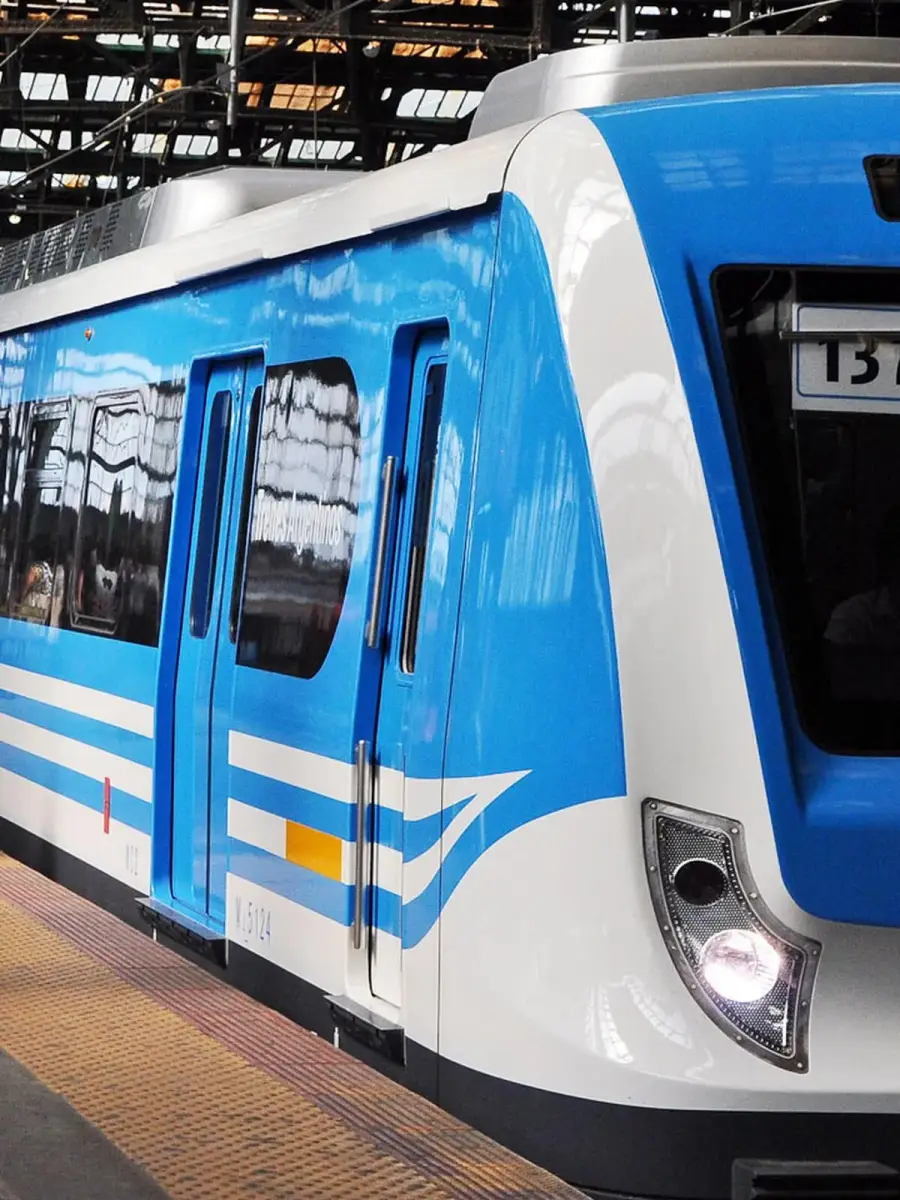
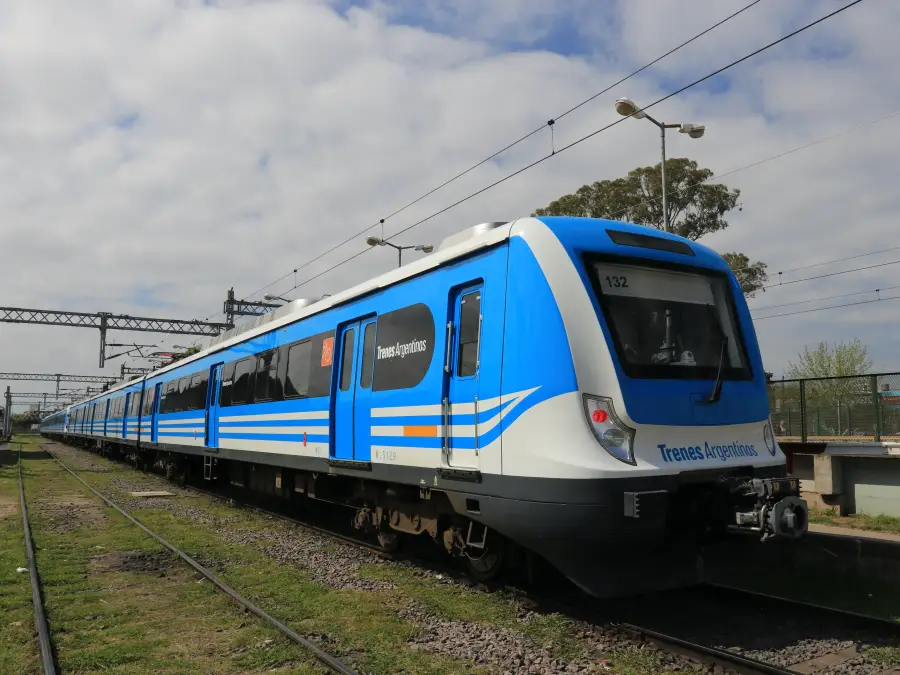
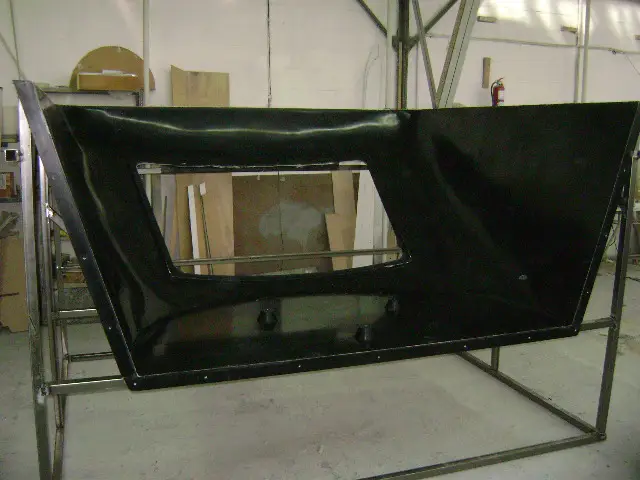
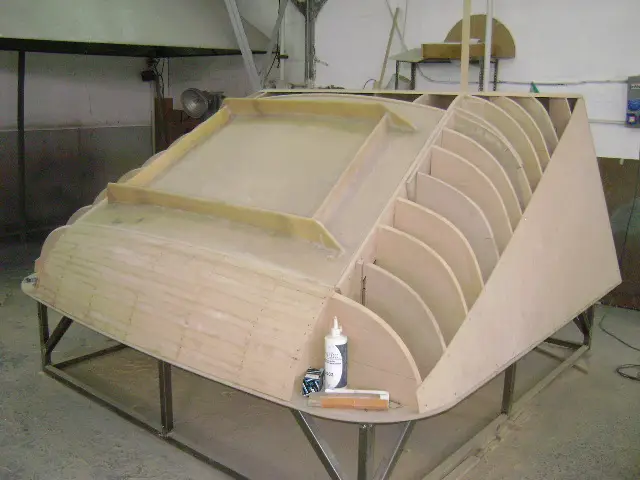
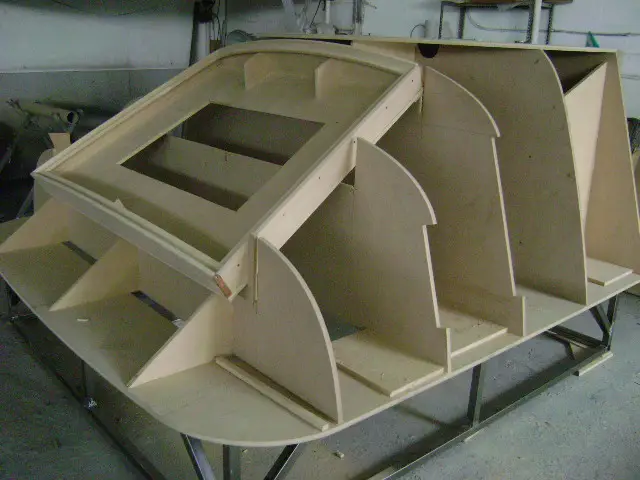
Train cabin
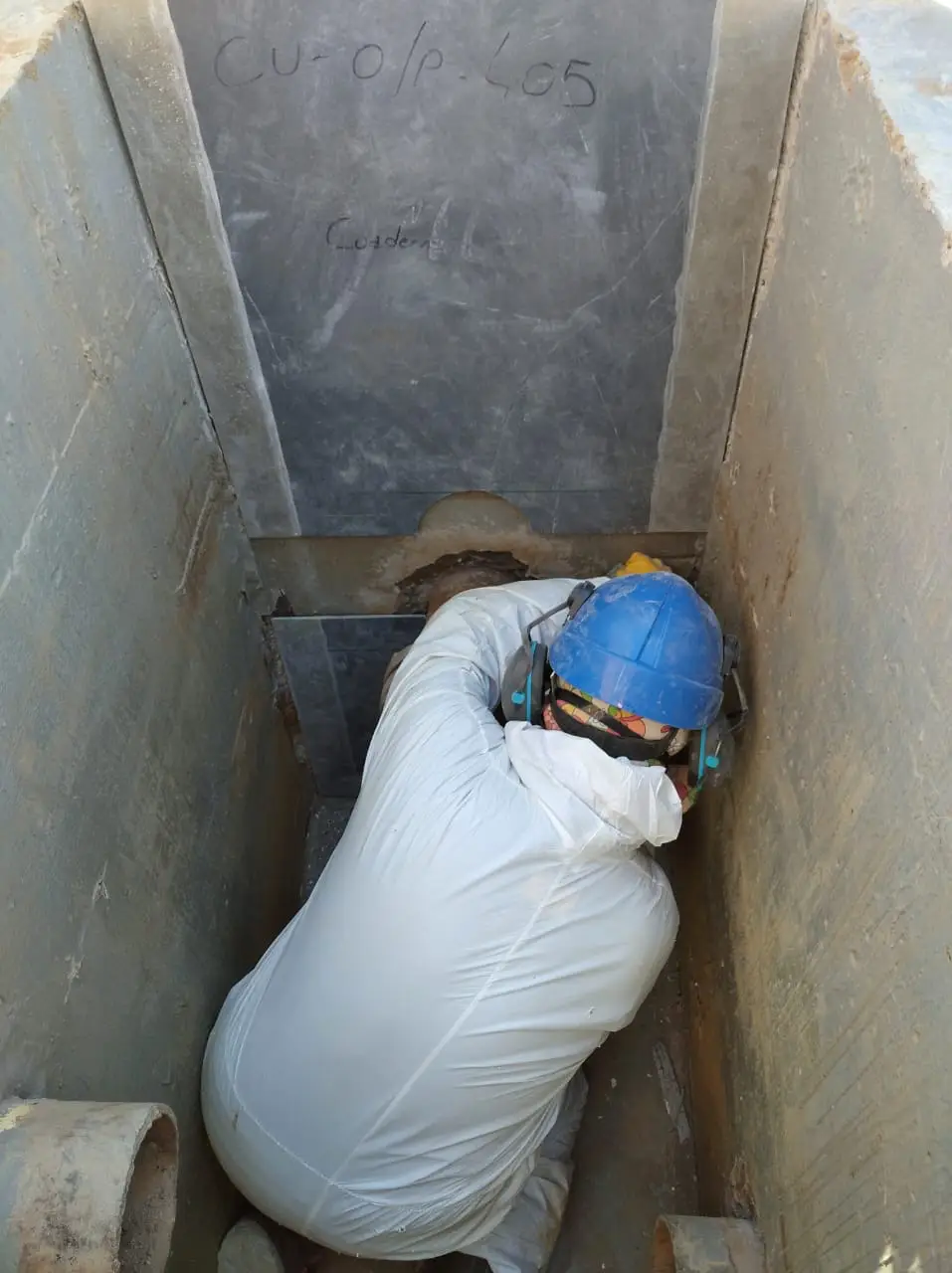
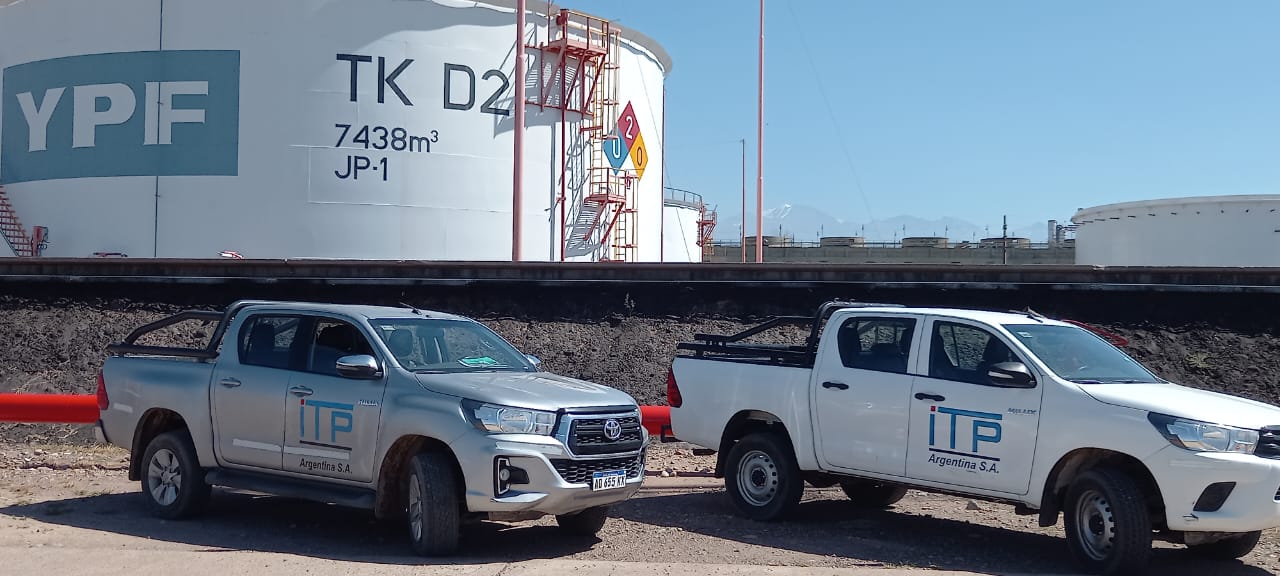
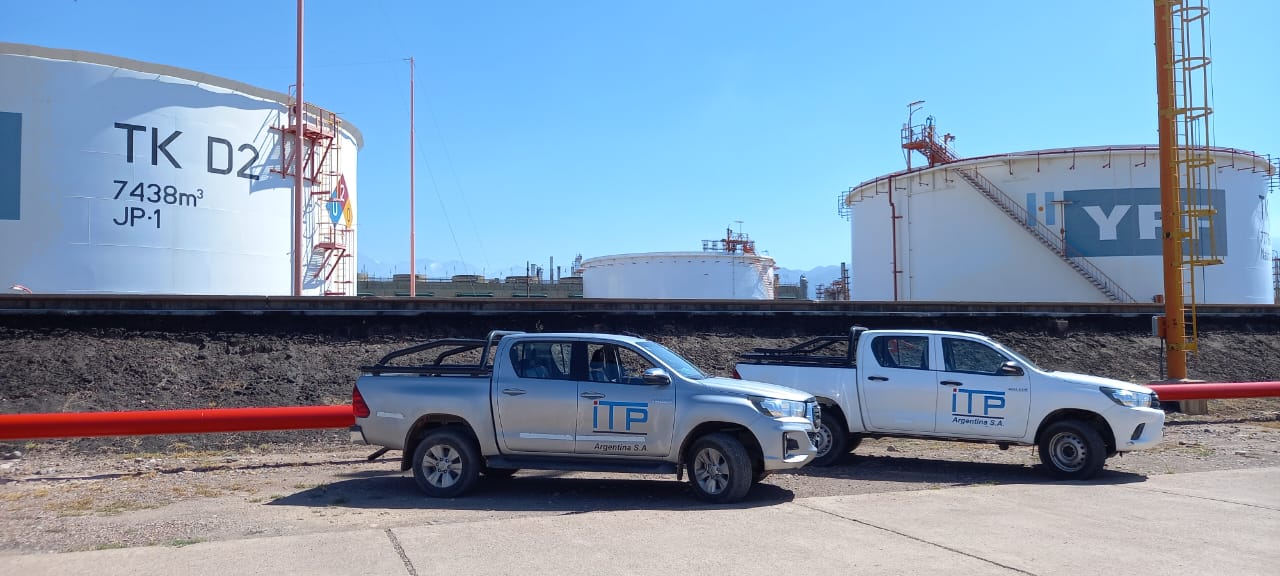
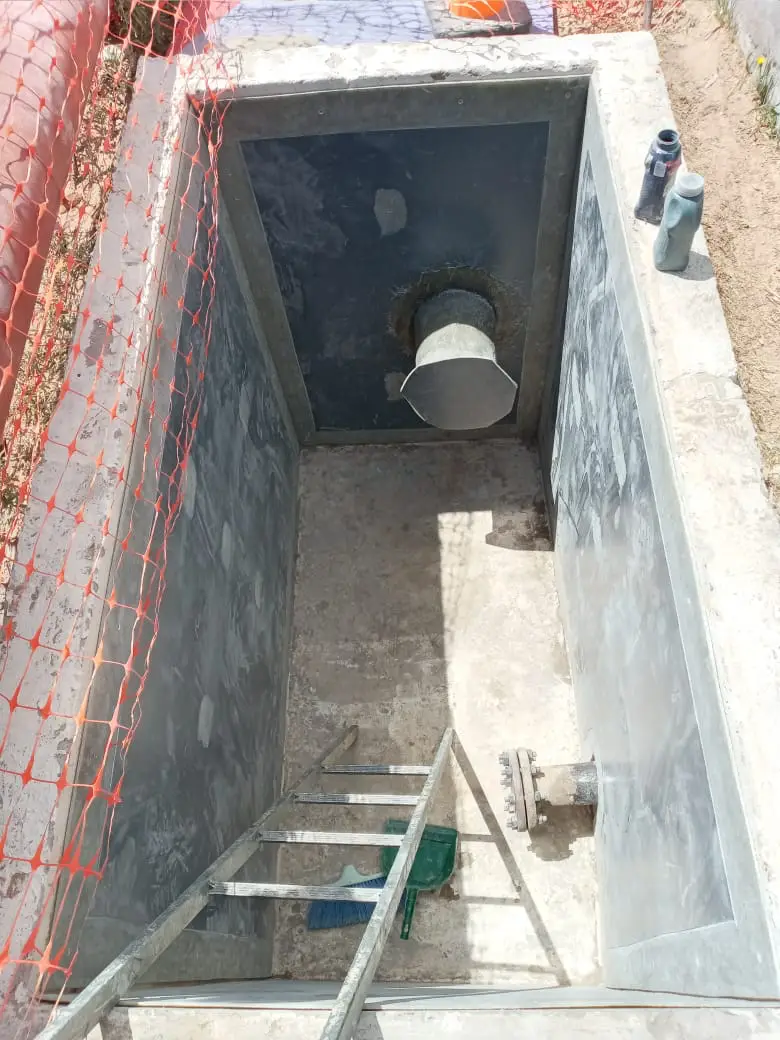
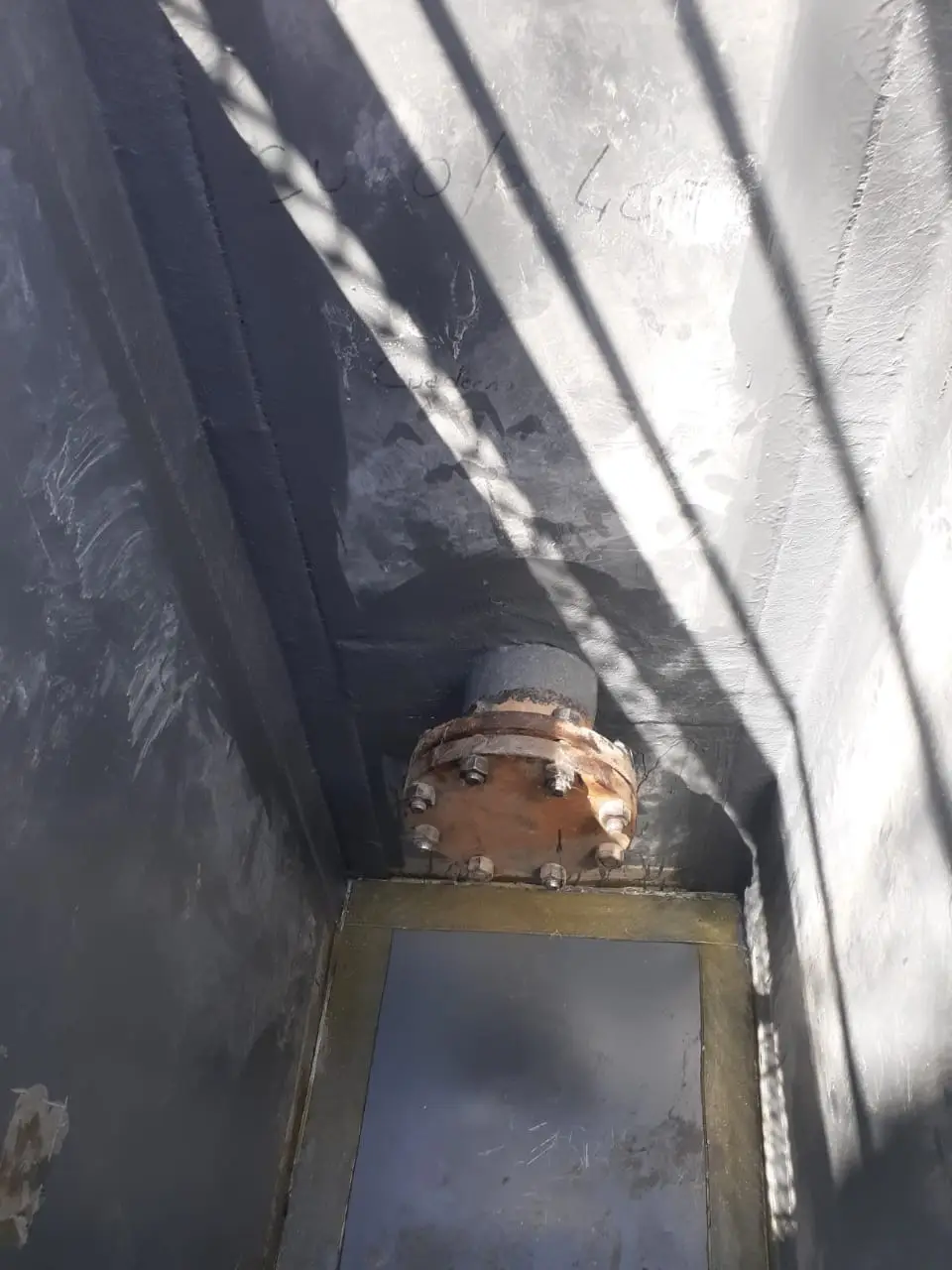
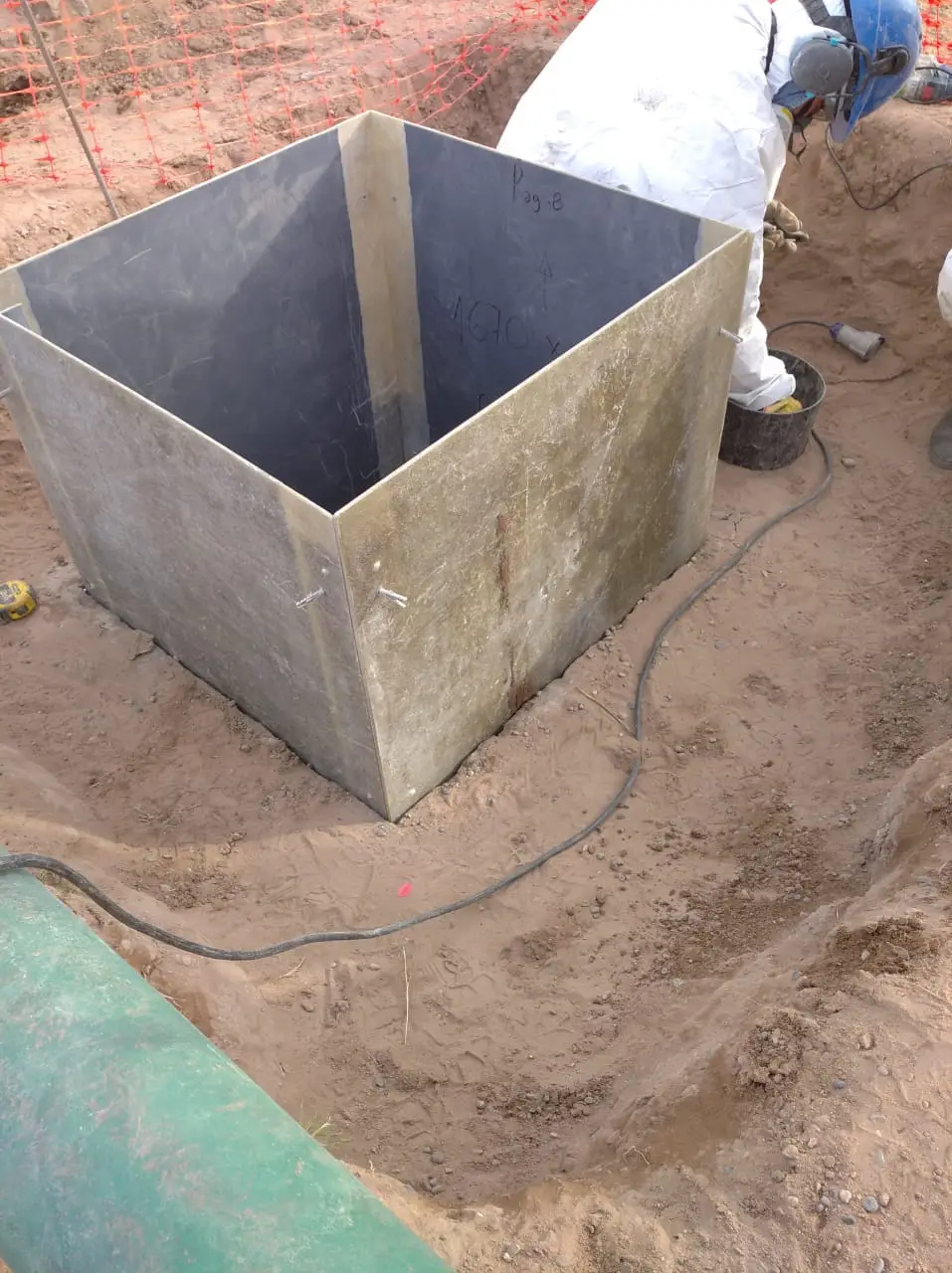
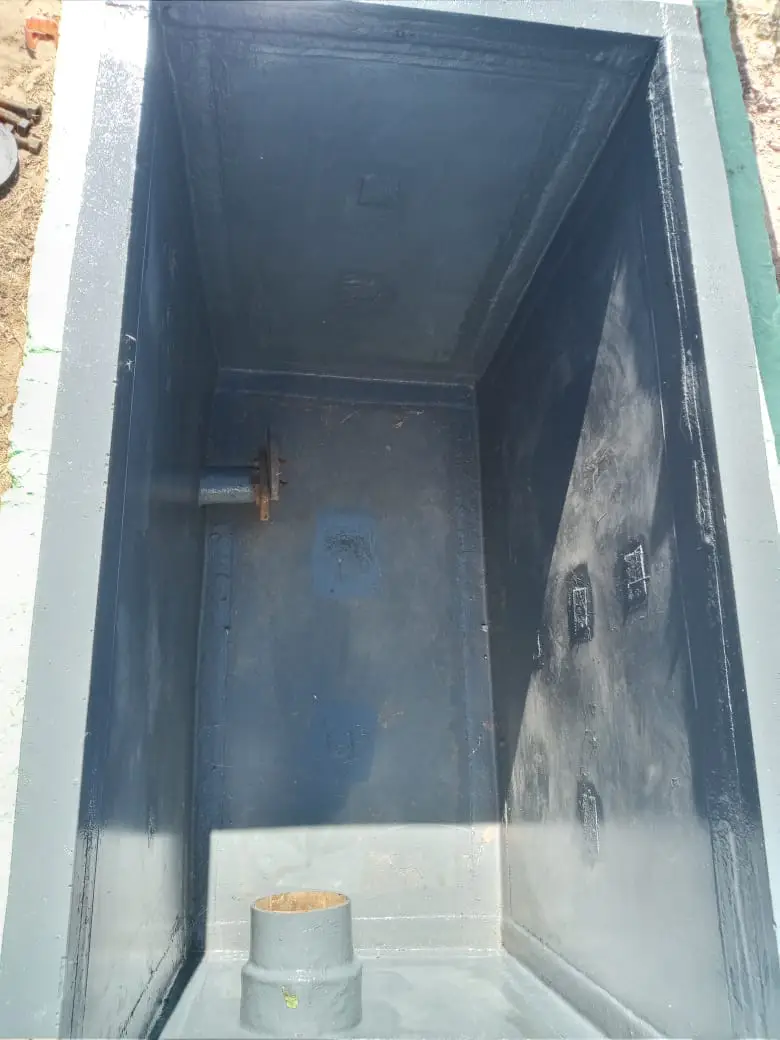
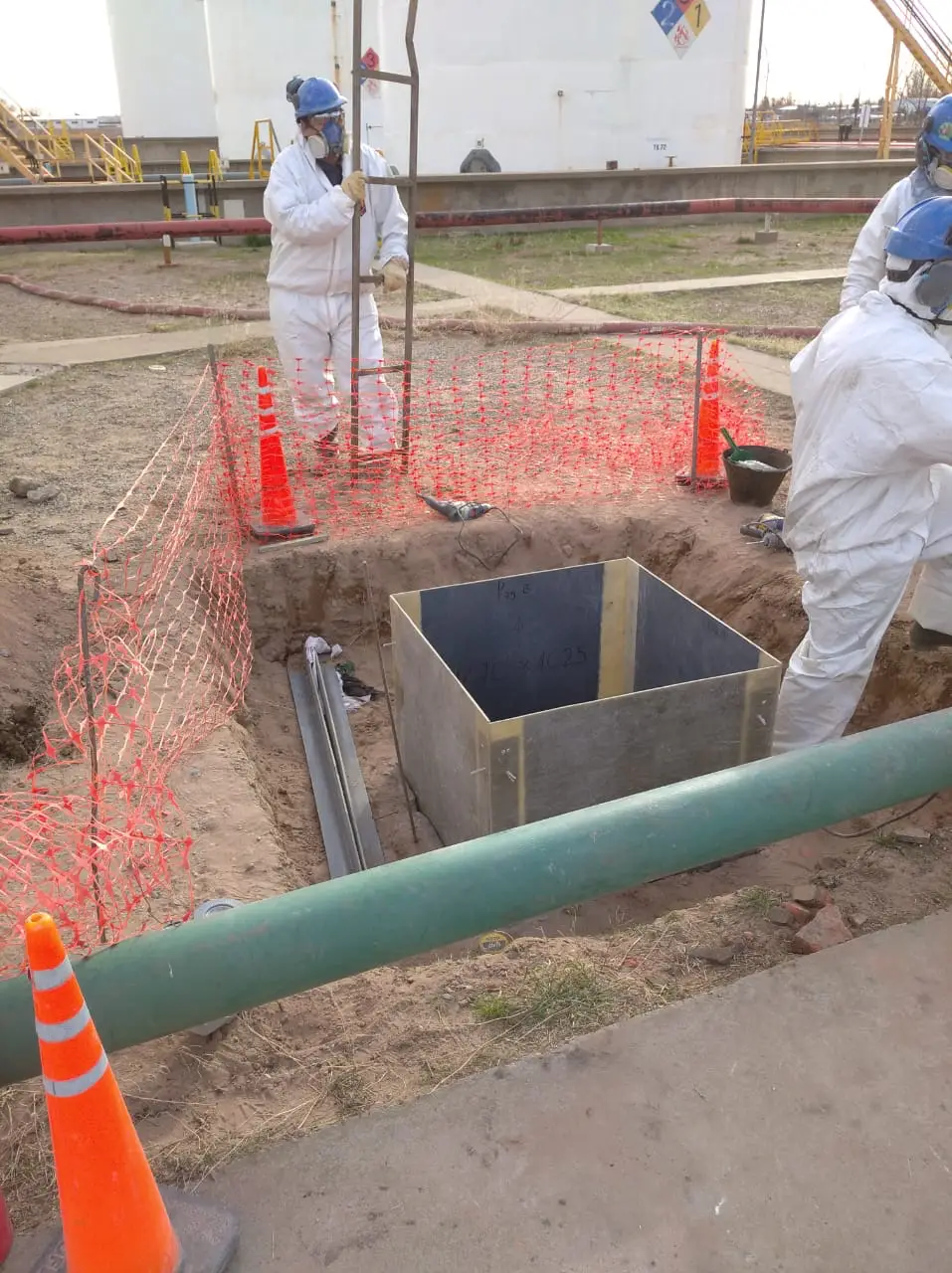
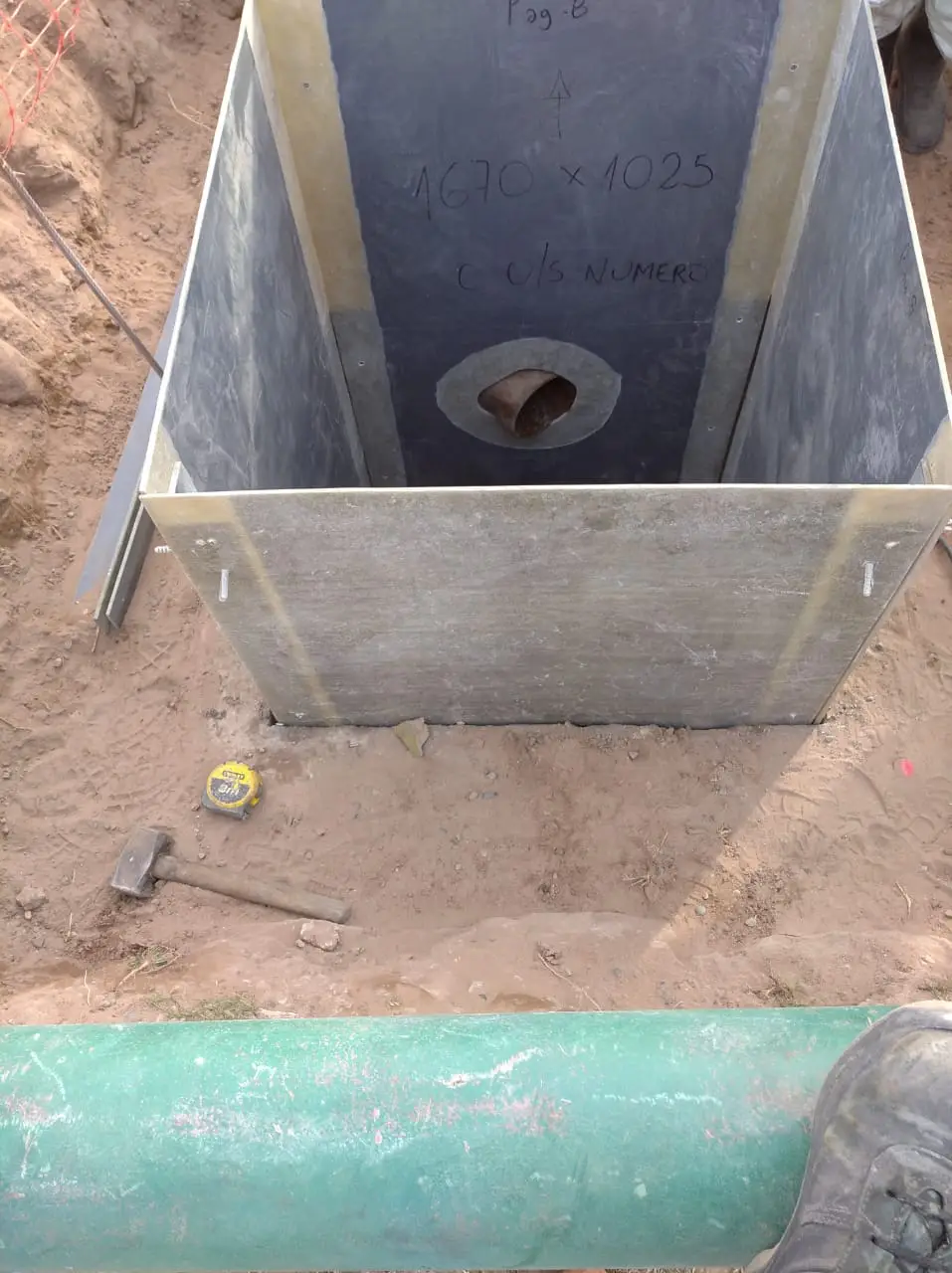
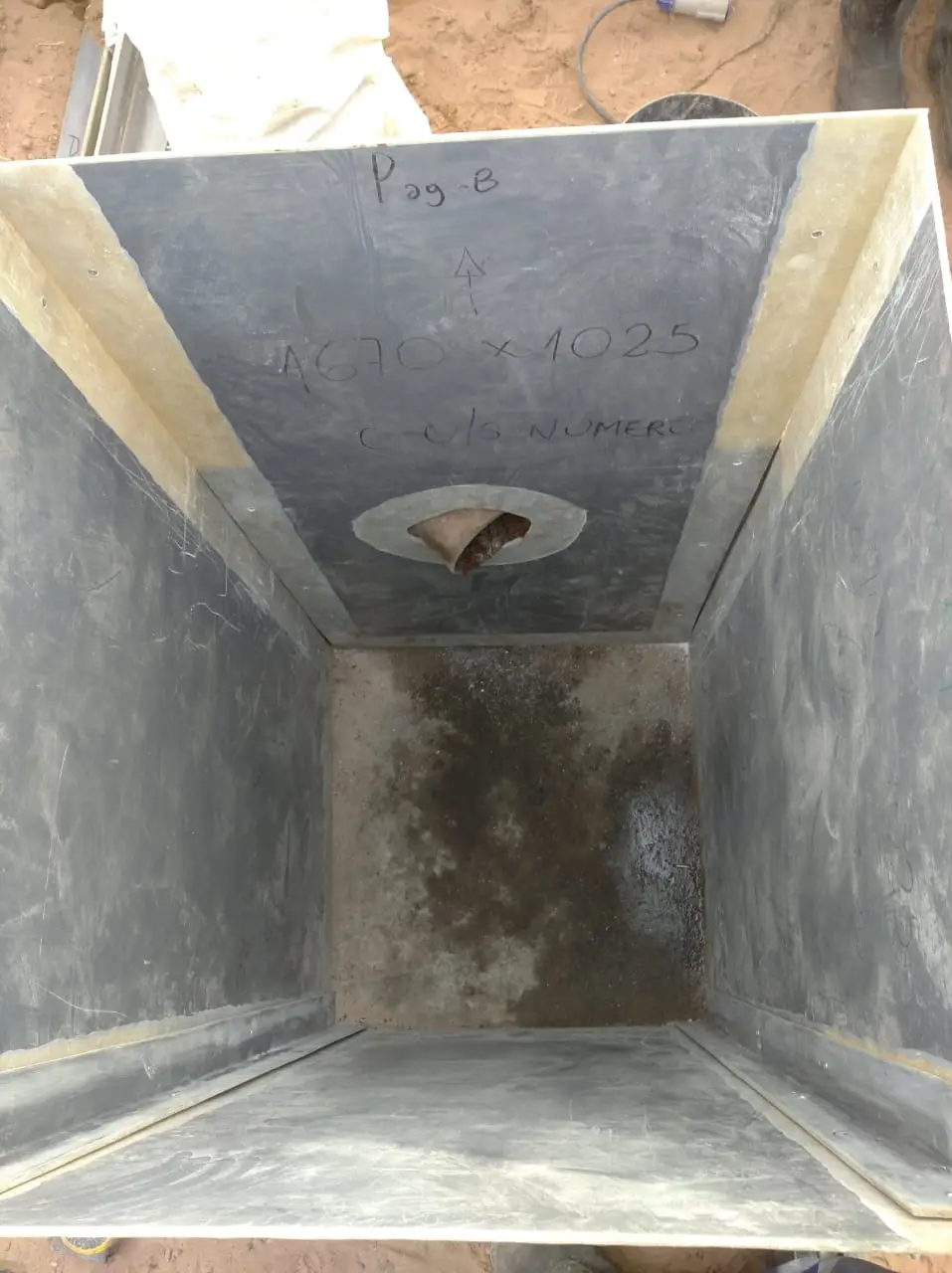
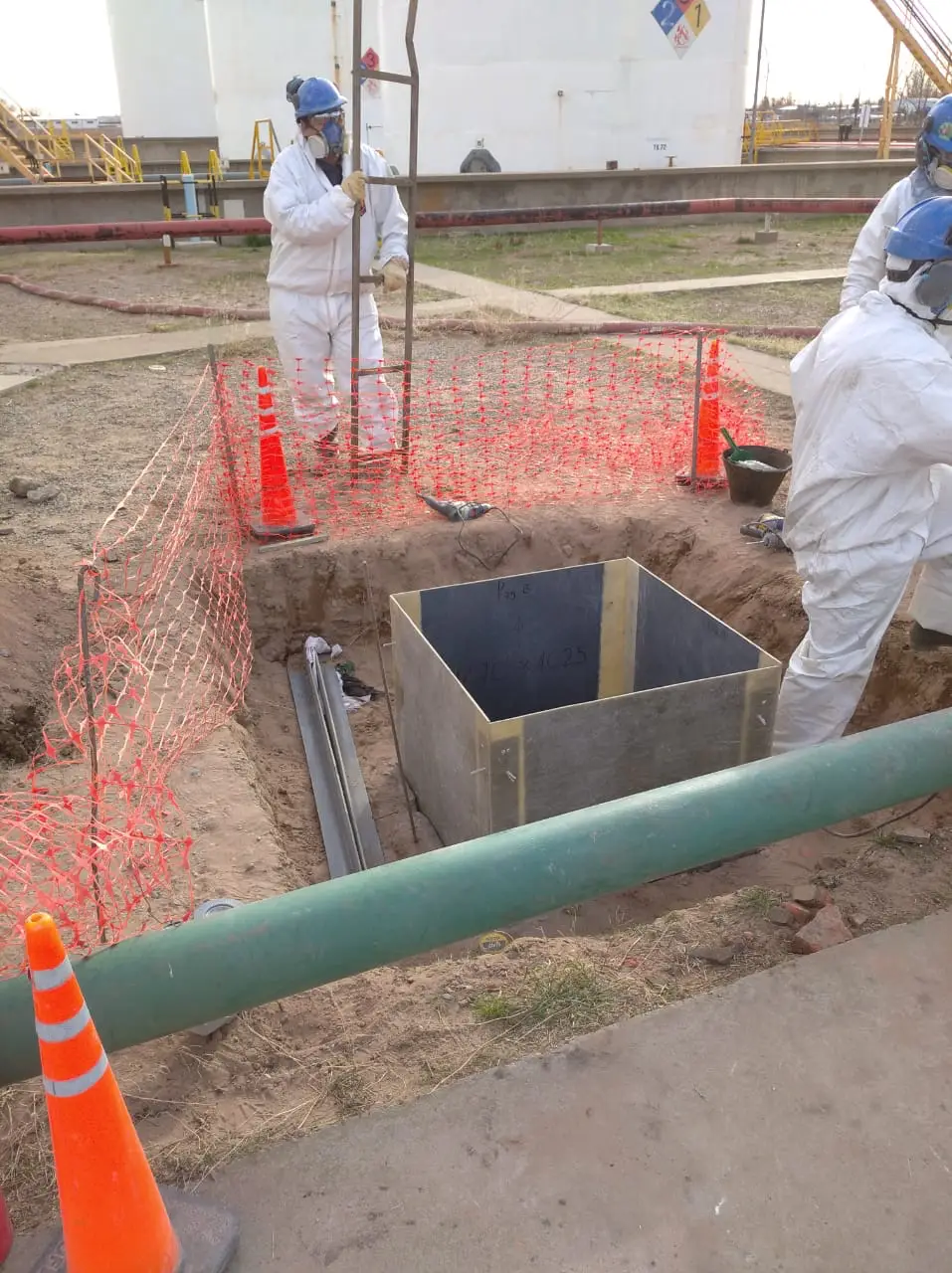
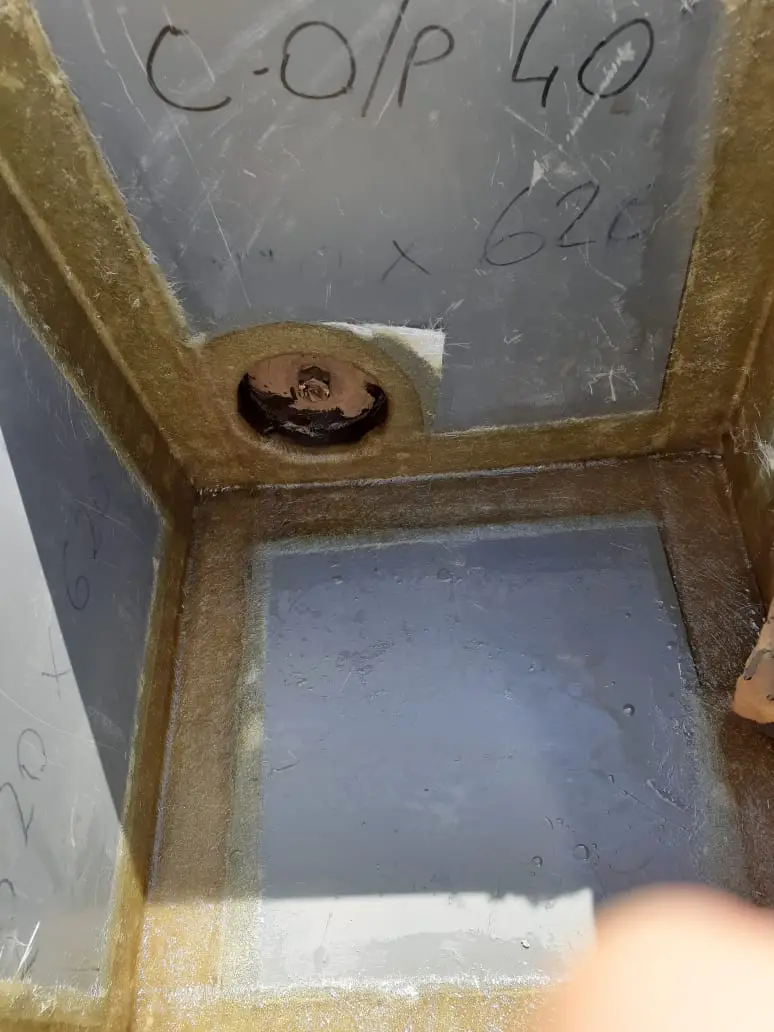
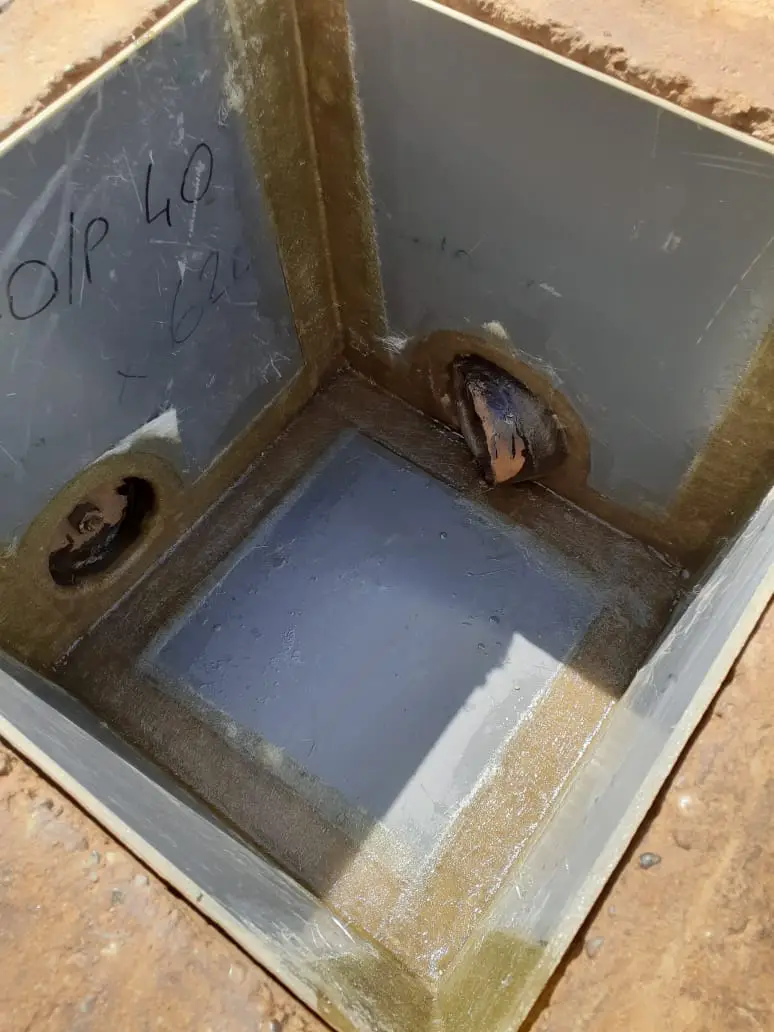
Waterproofing system for hydrocarbon effluent chambers for YPF
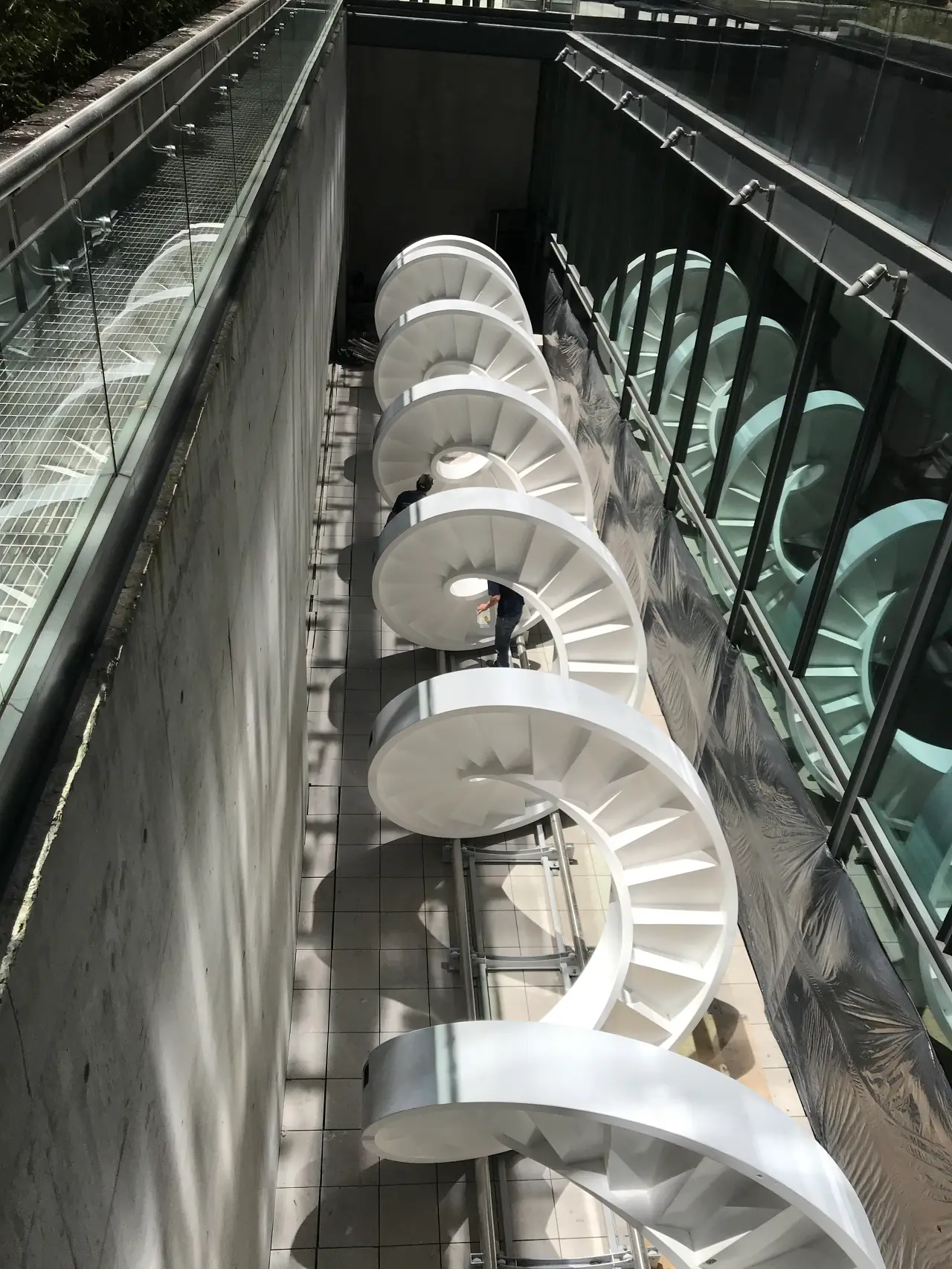
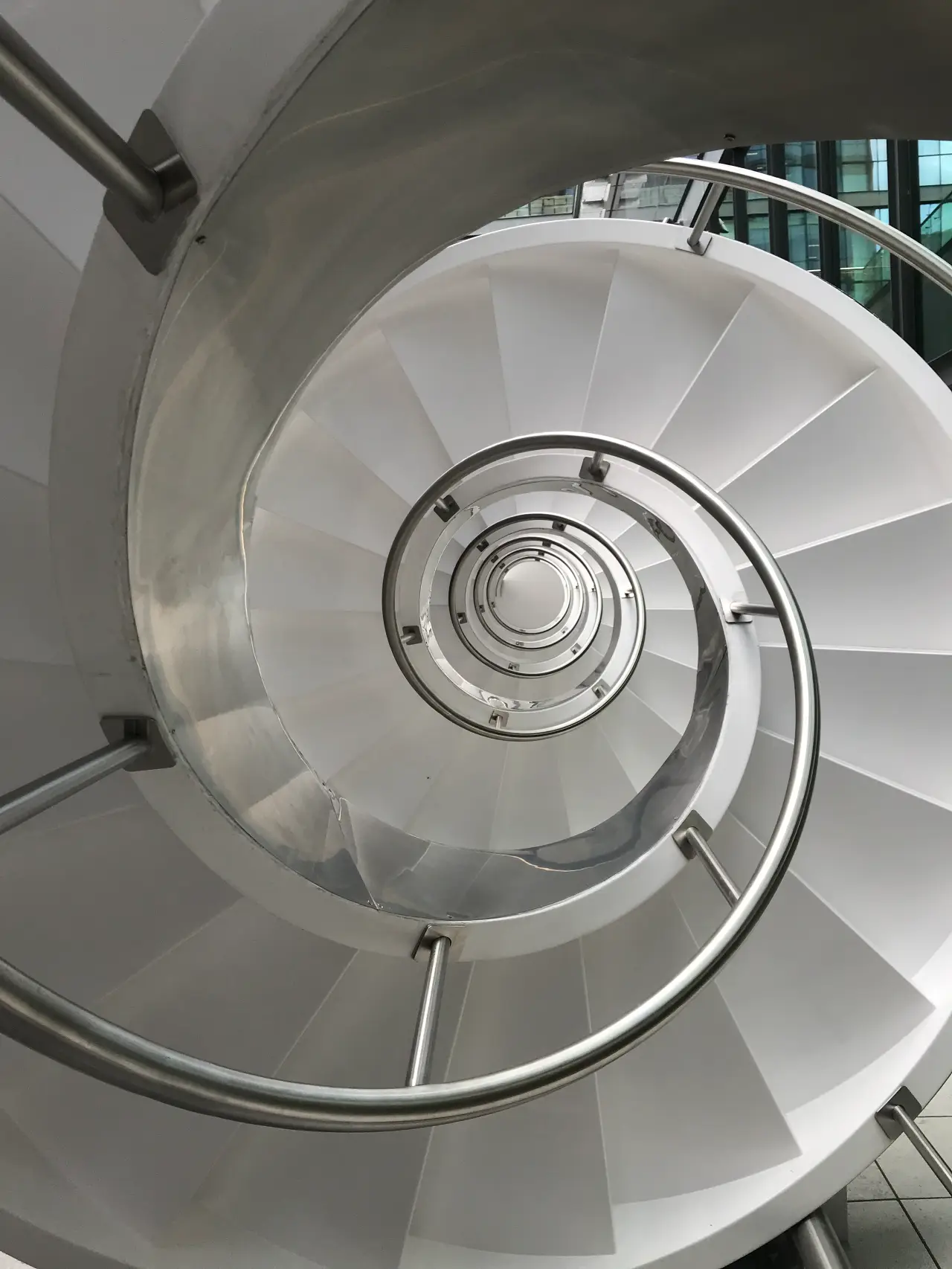
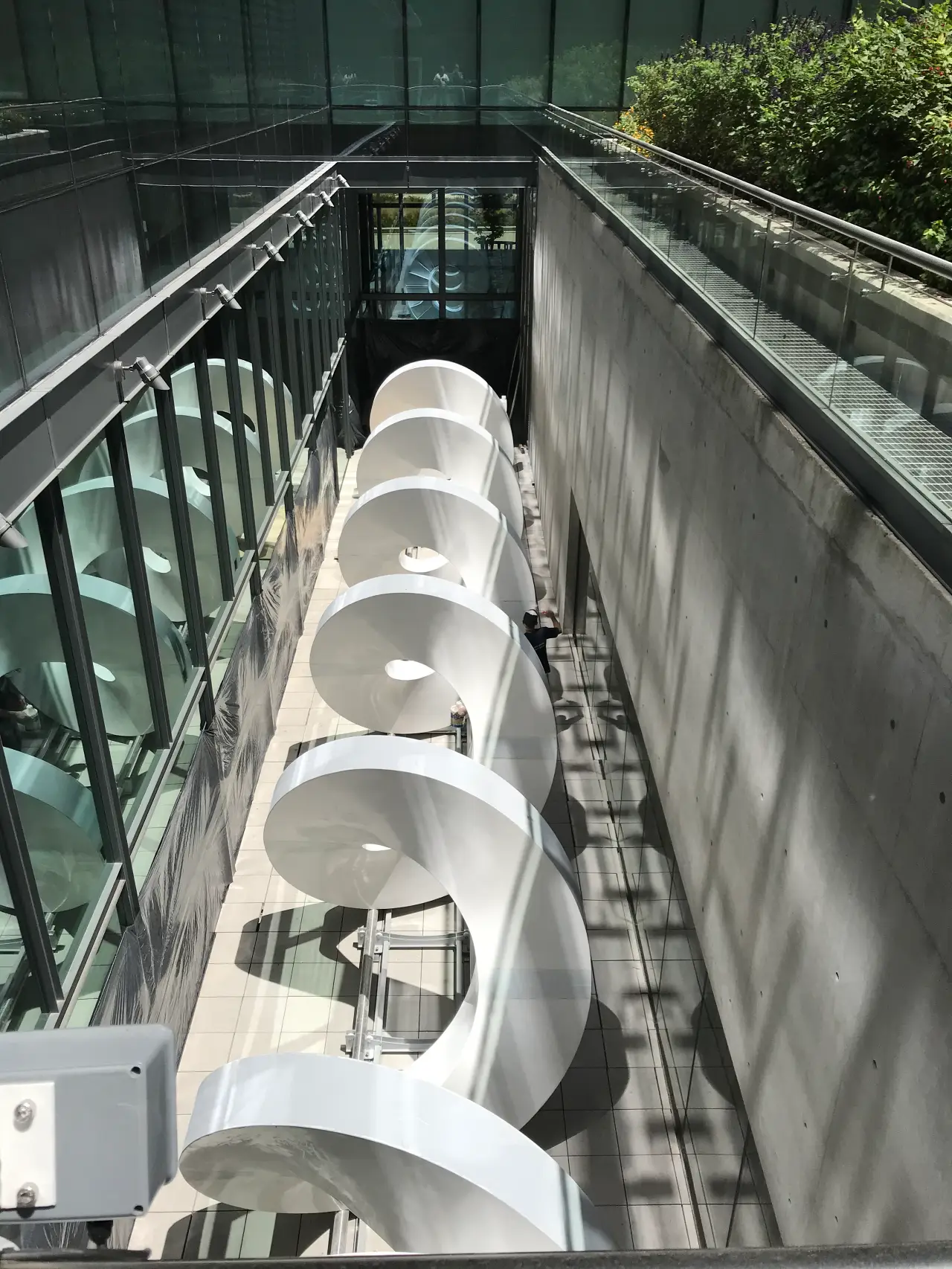
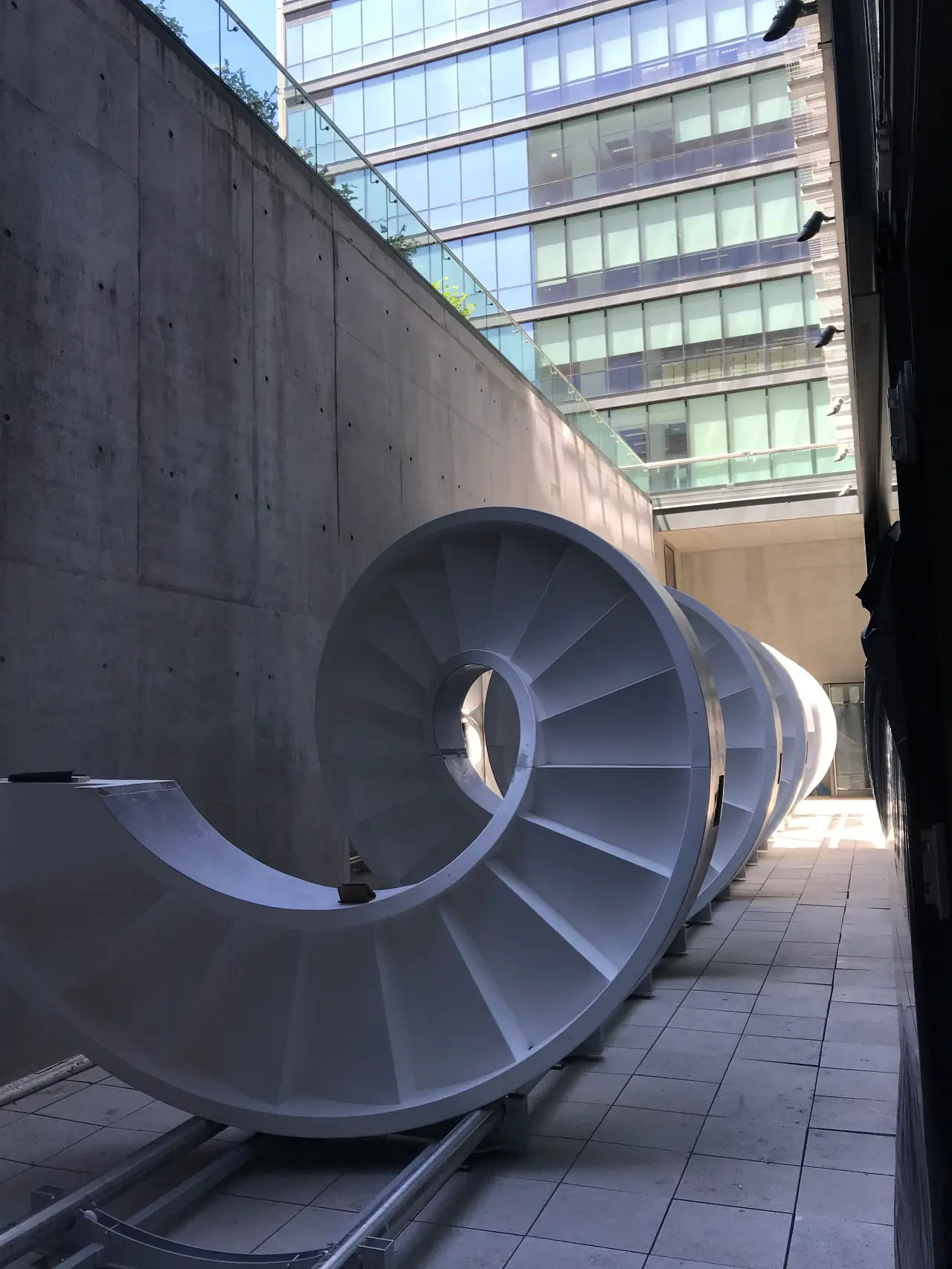
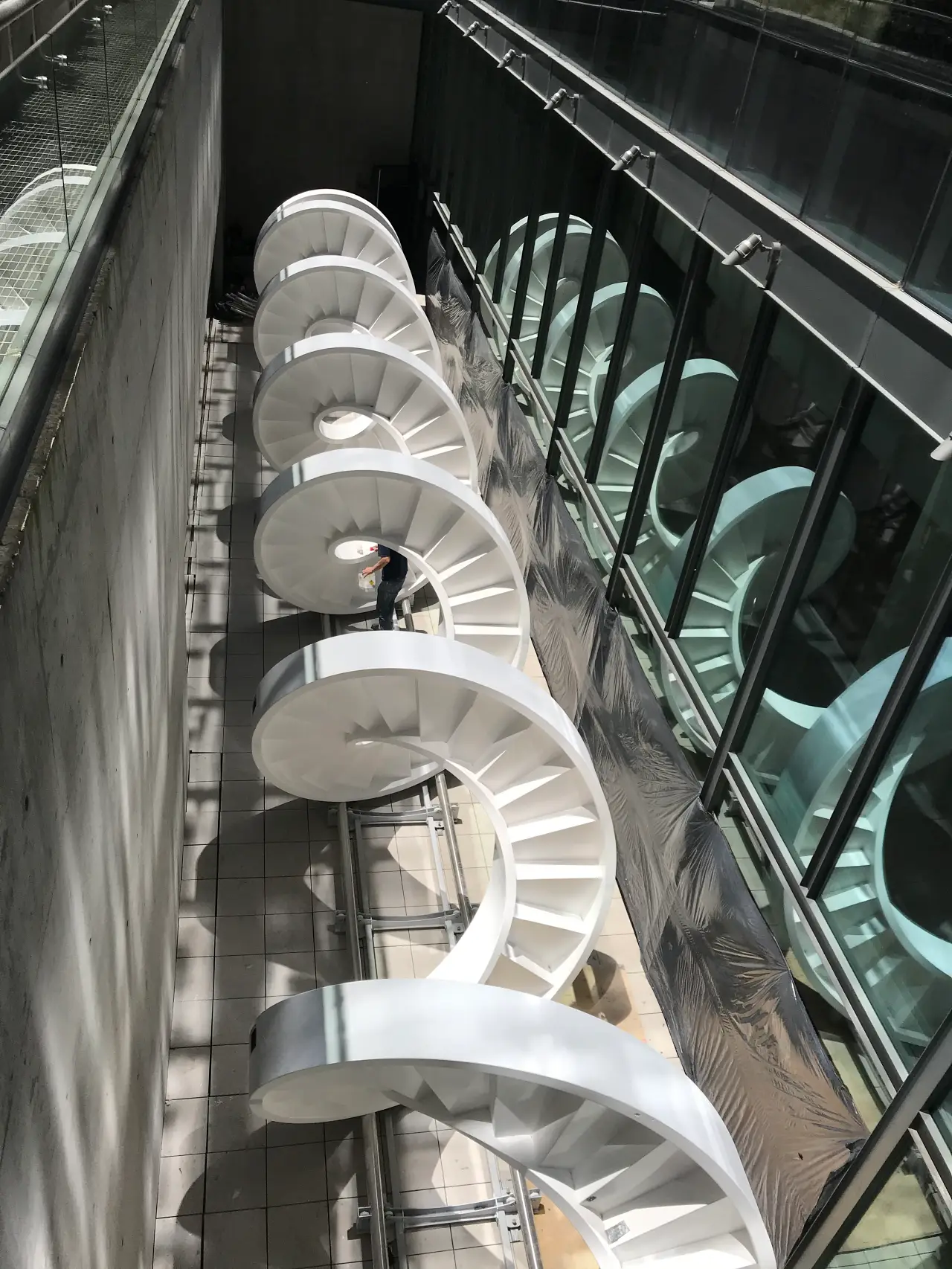
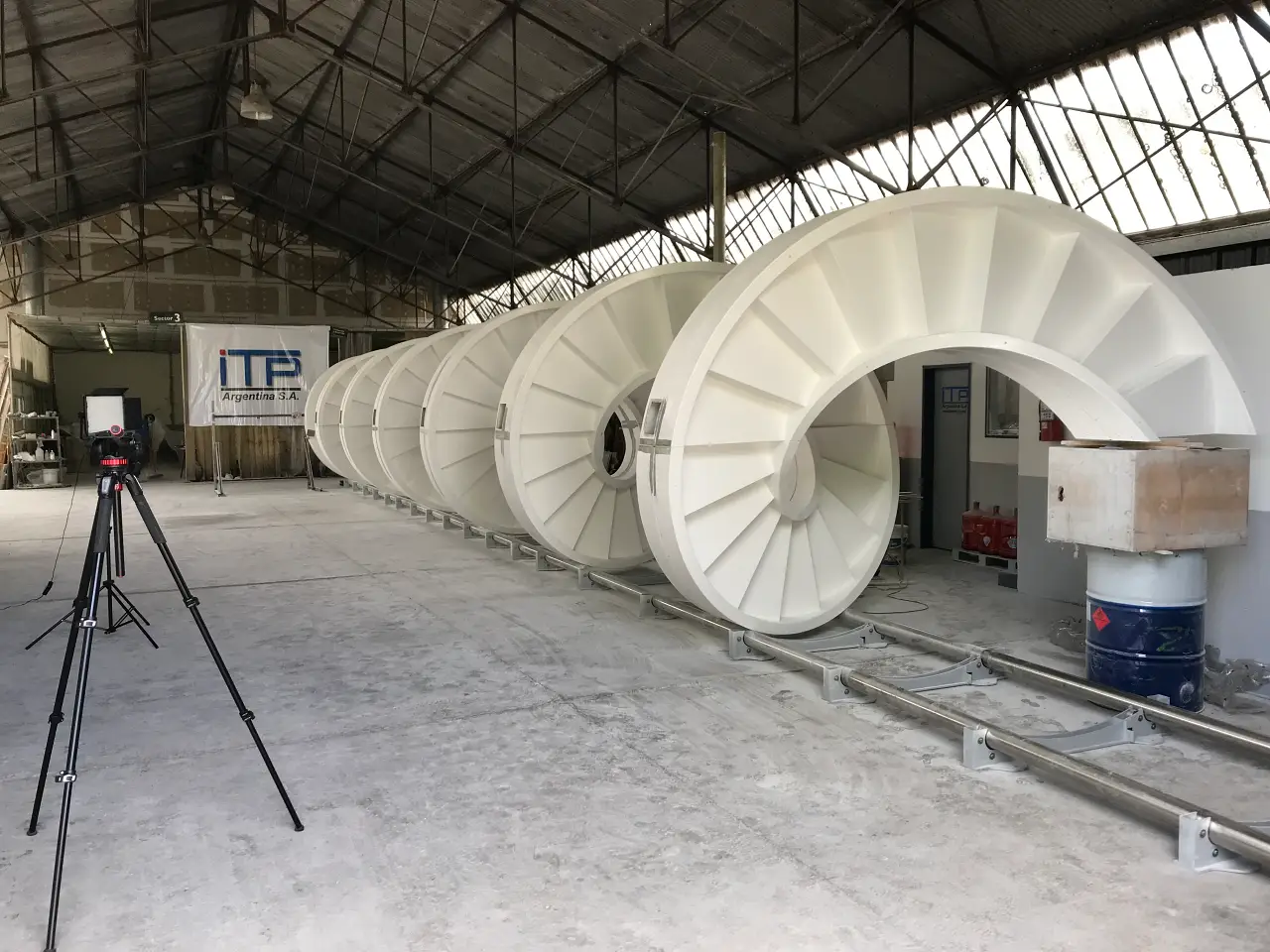
Helicoidal staircase
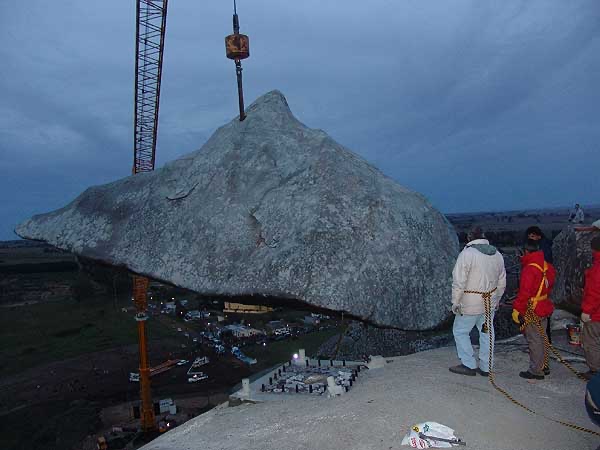
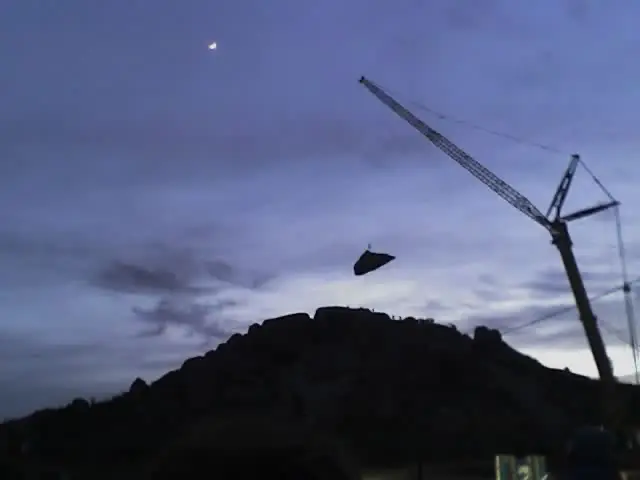
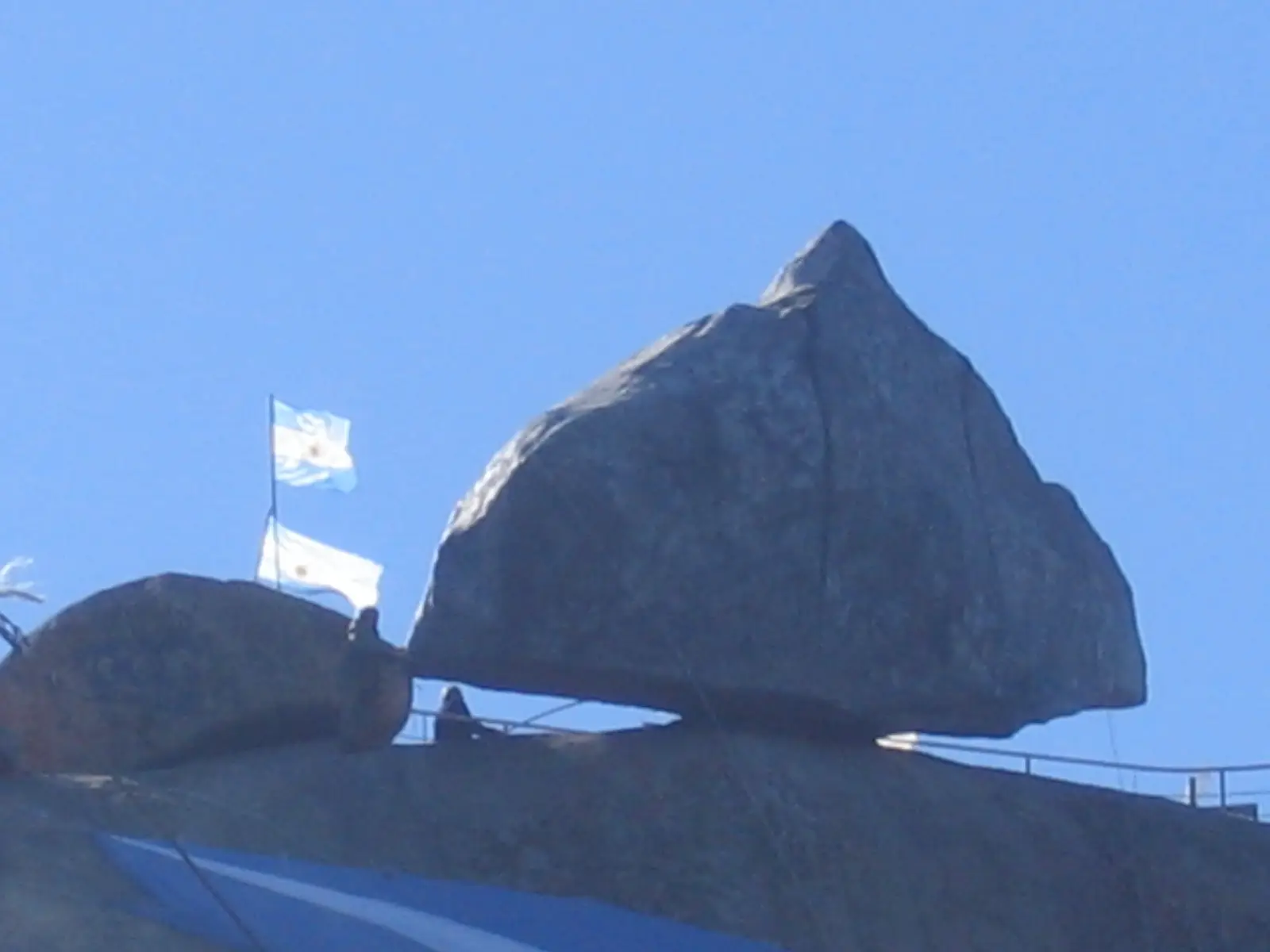
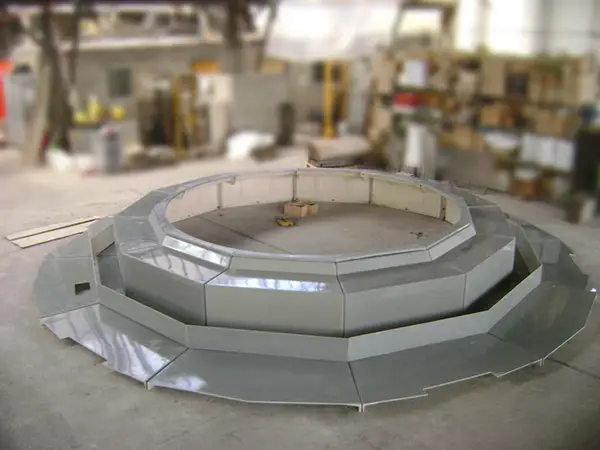
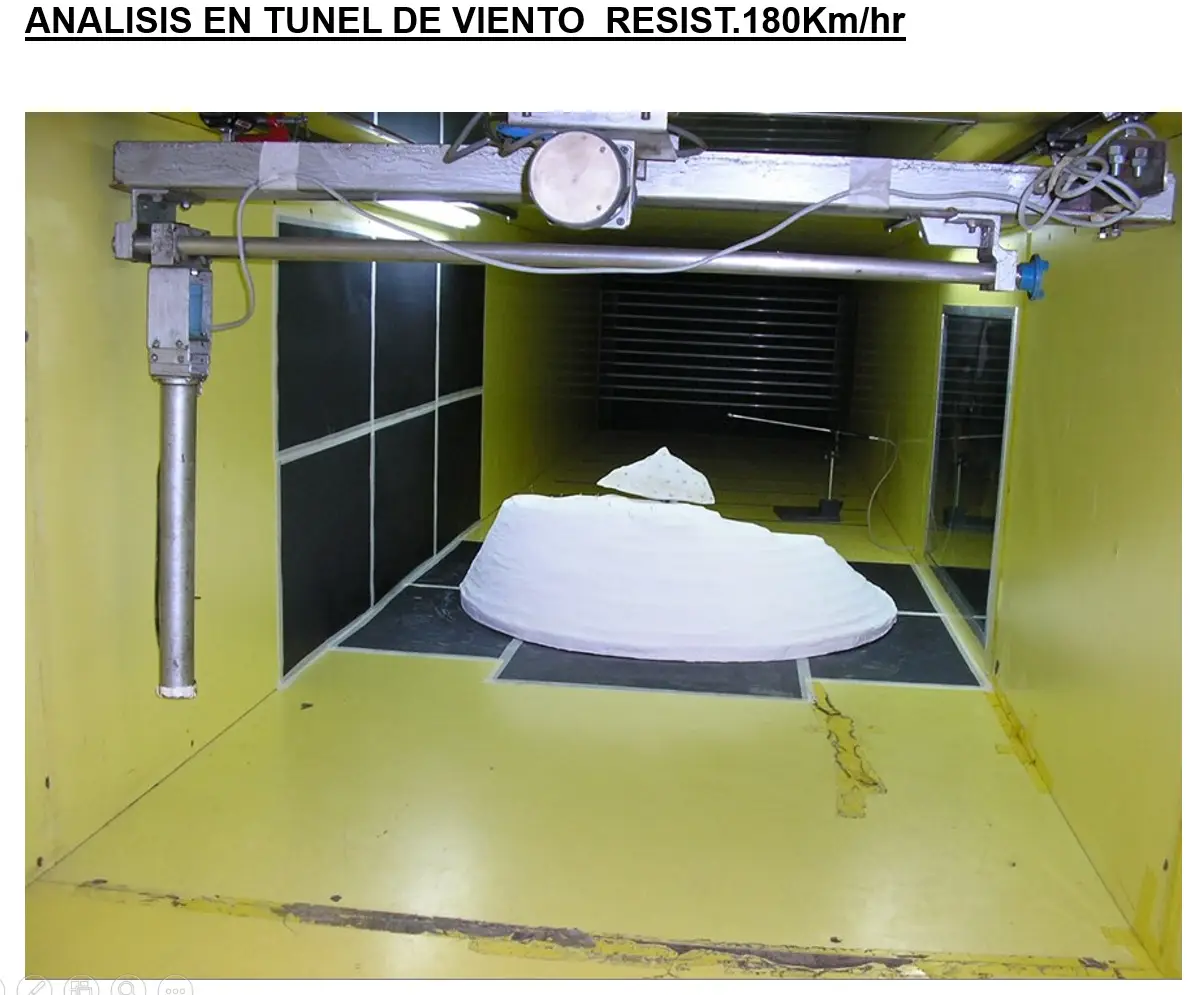
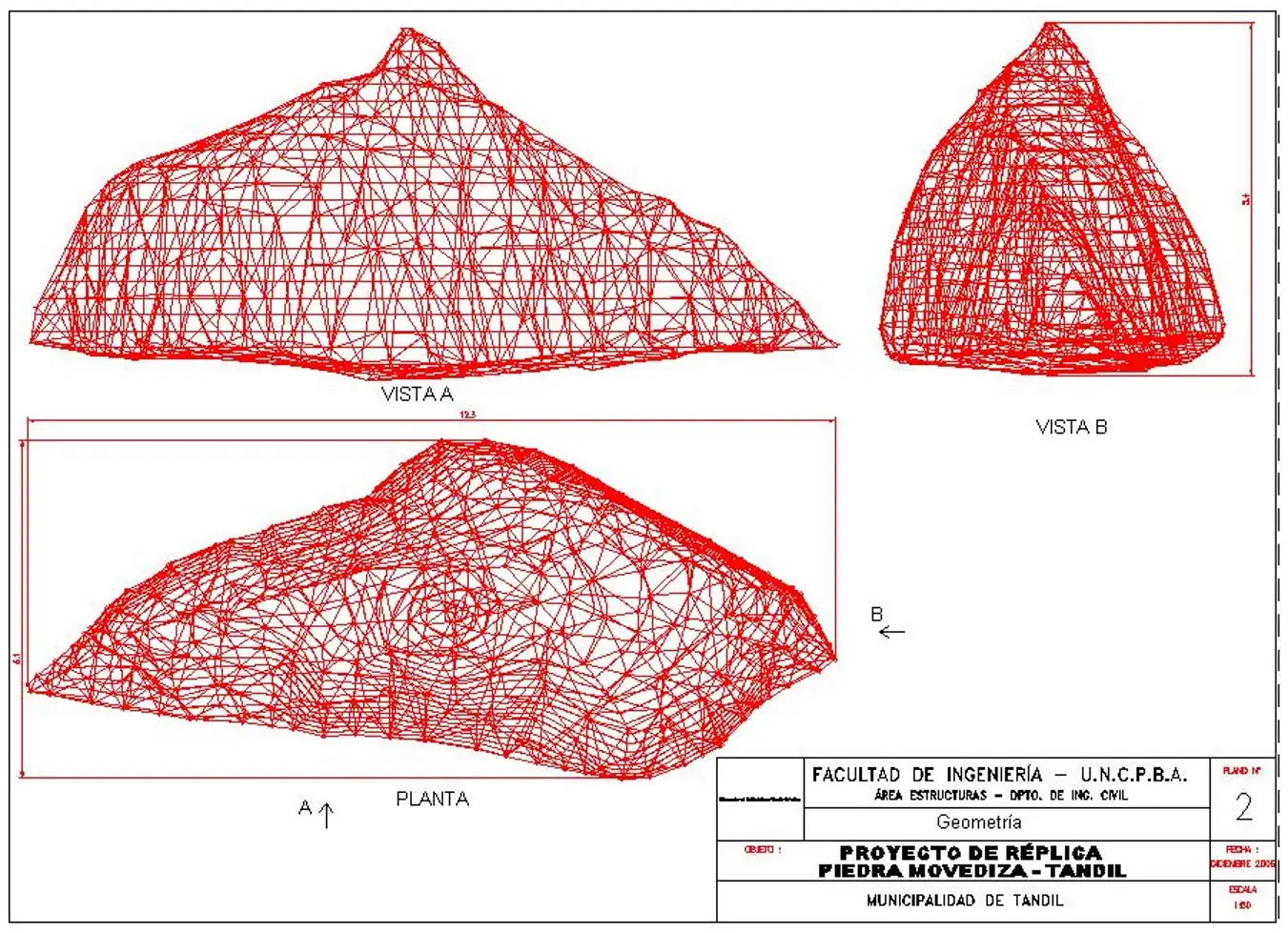
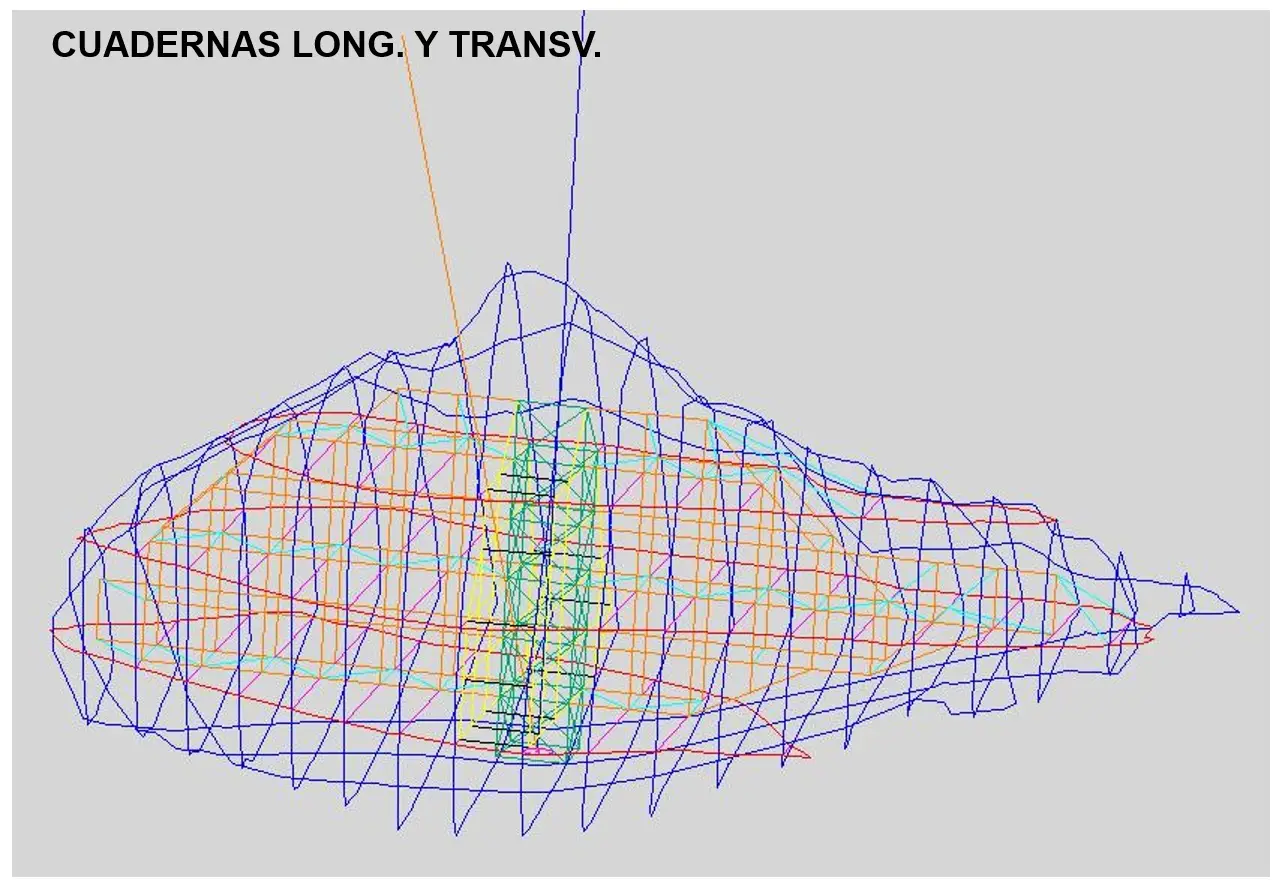
Tandil’s Moving Stone
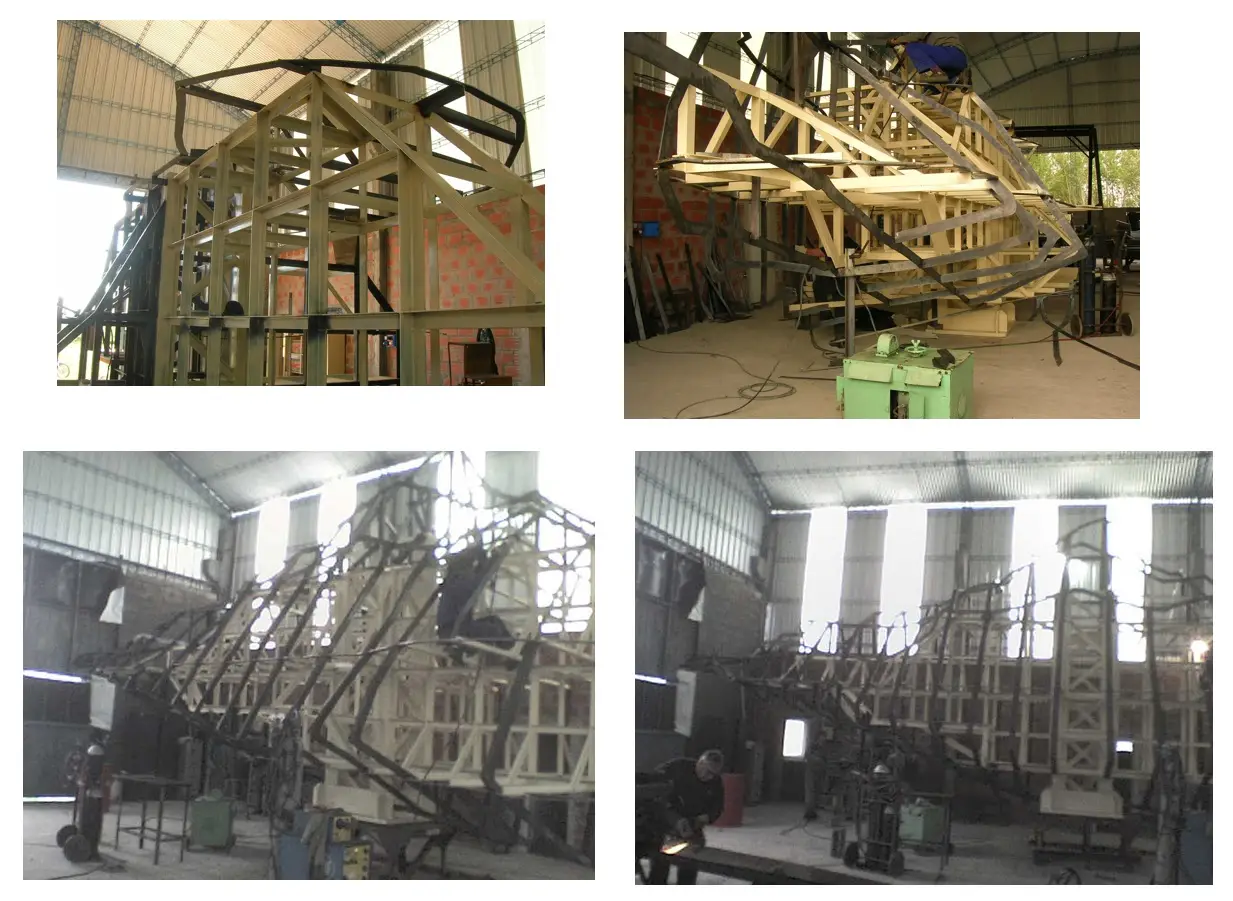
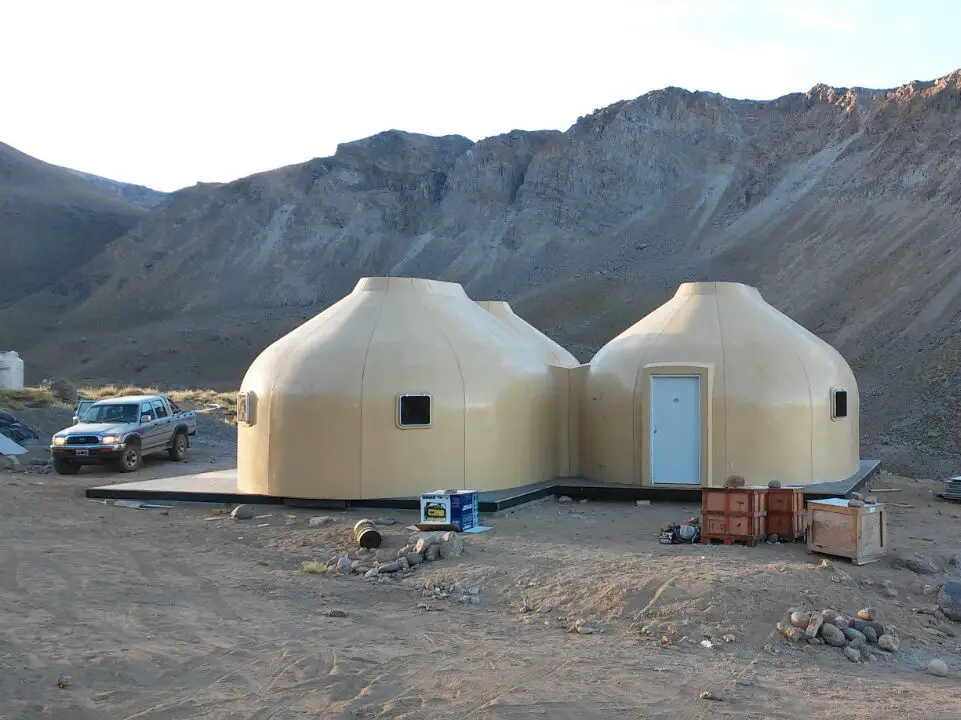
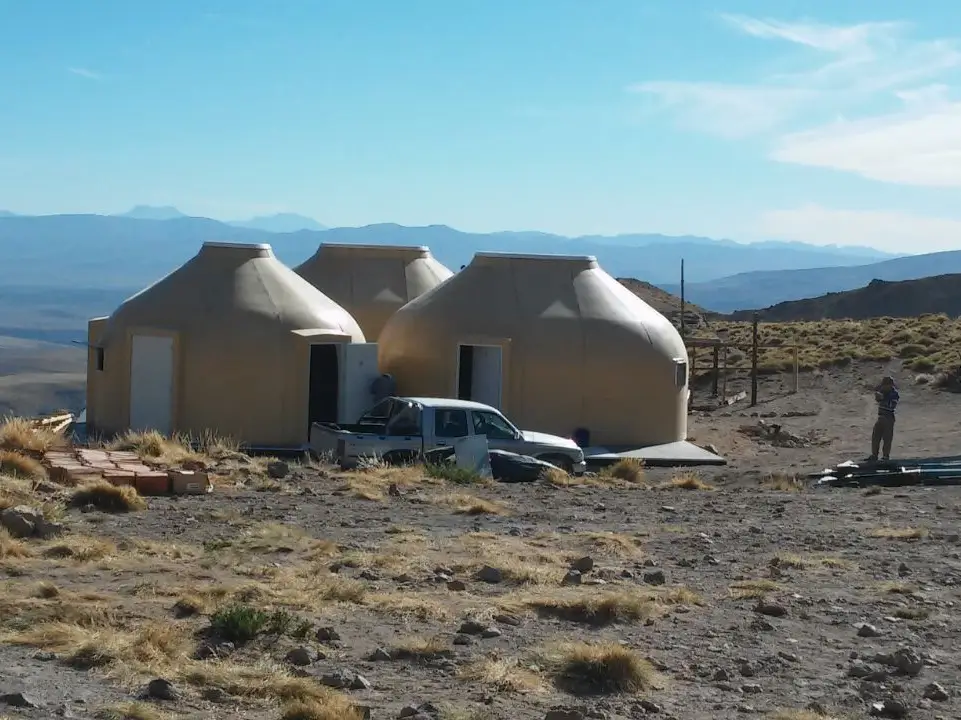
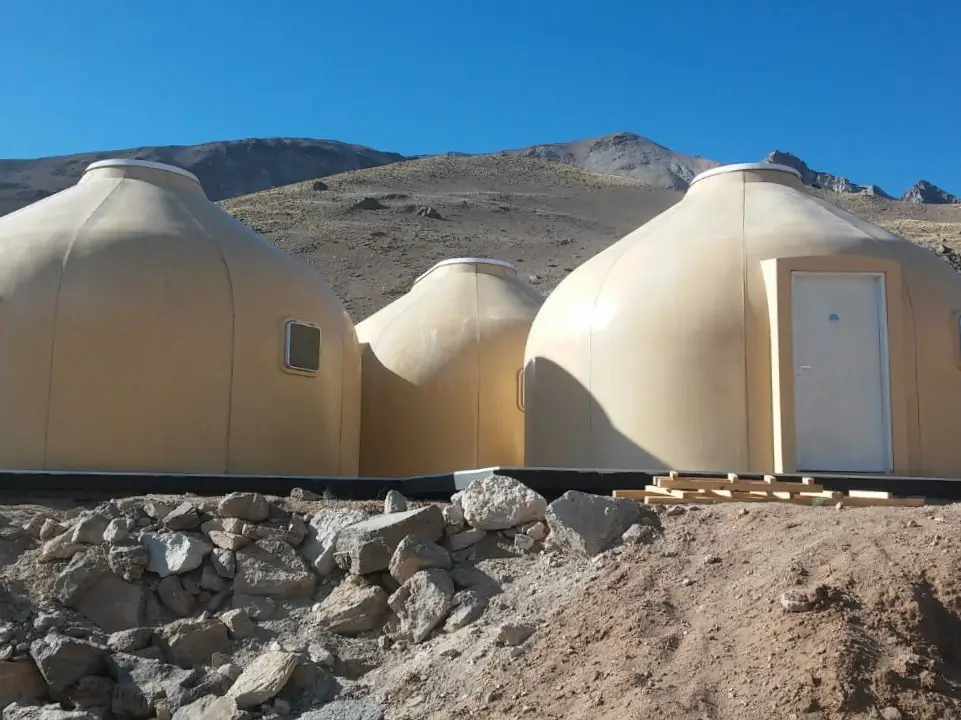
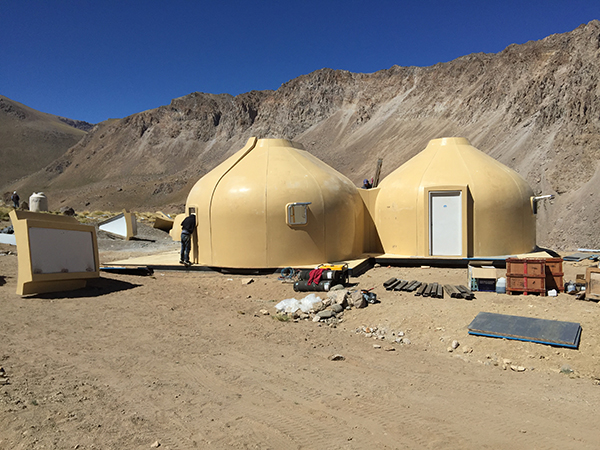
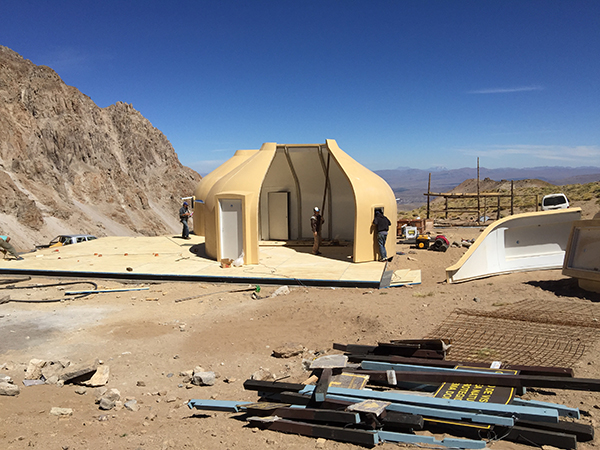
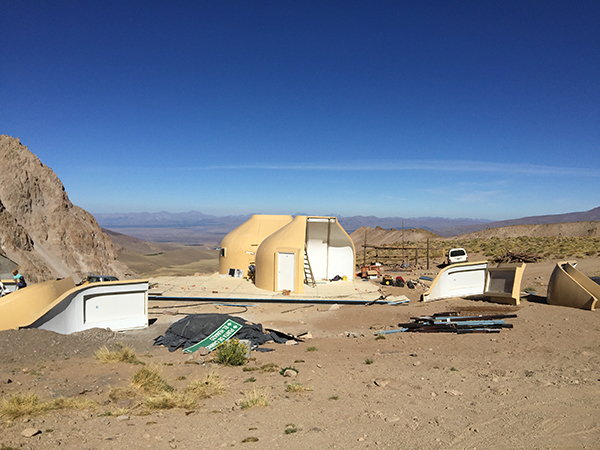
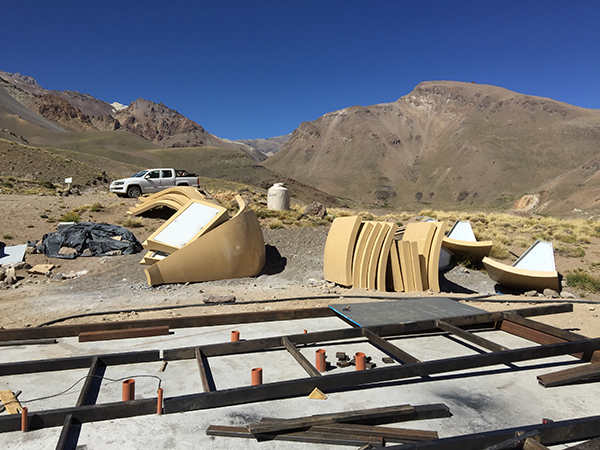
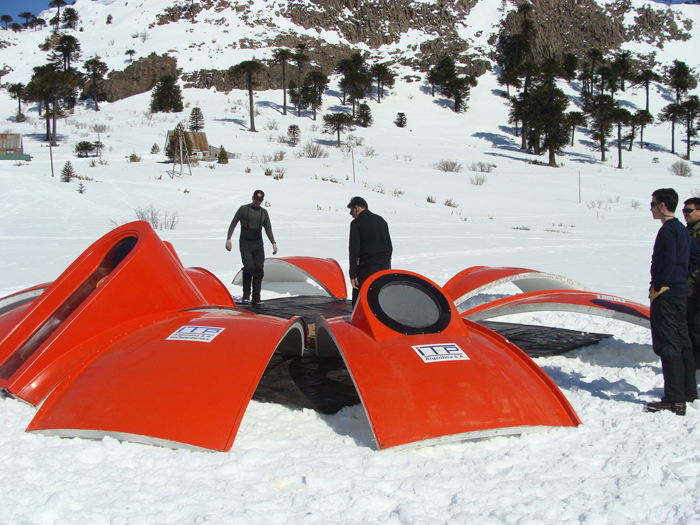
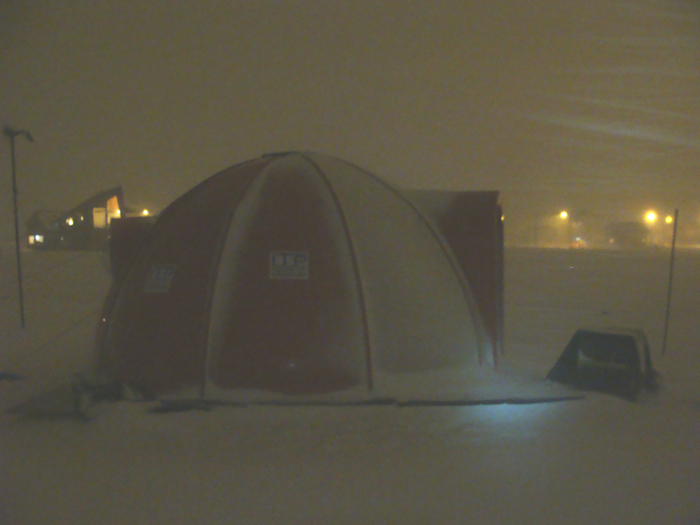
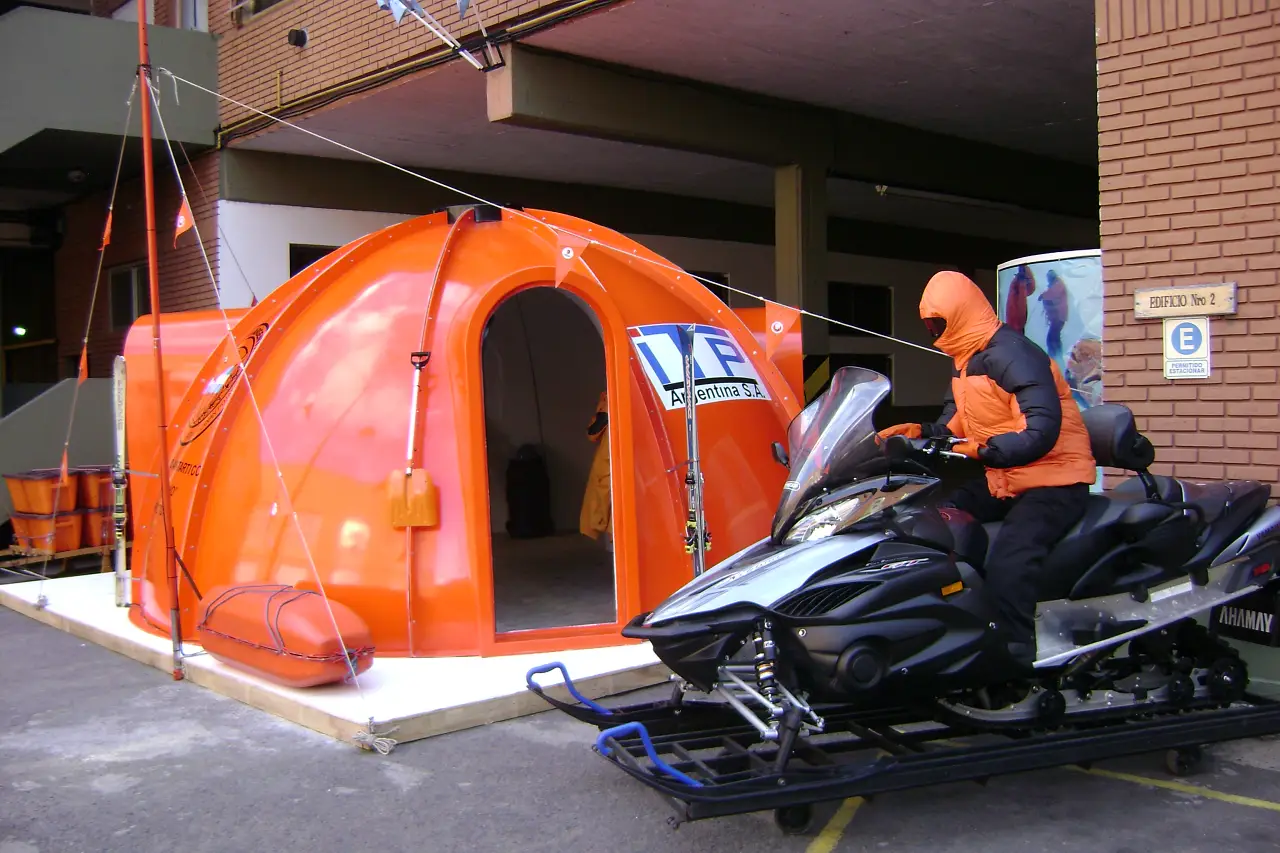
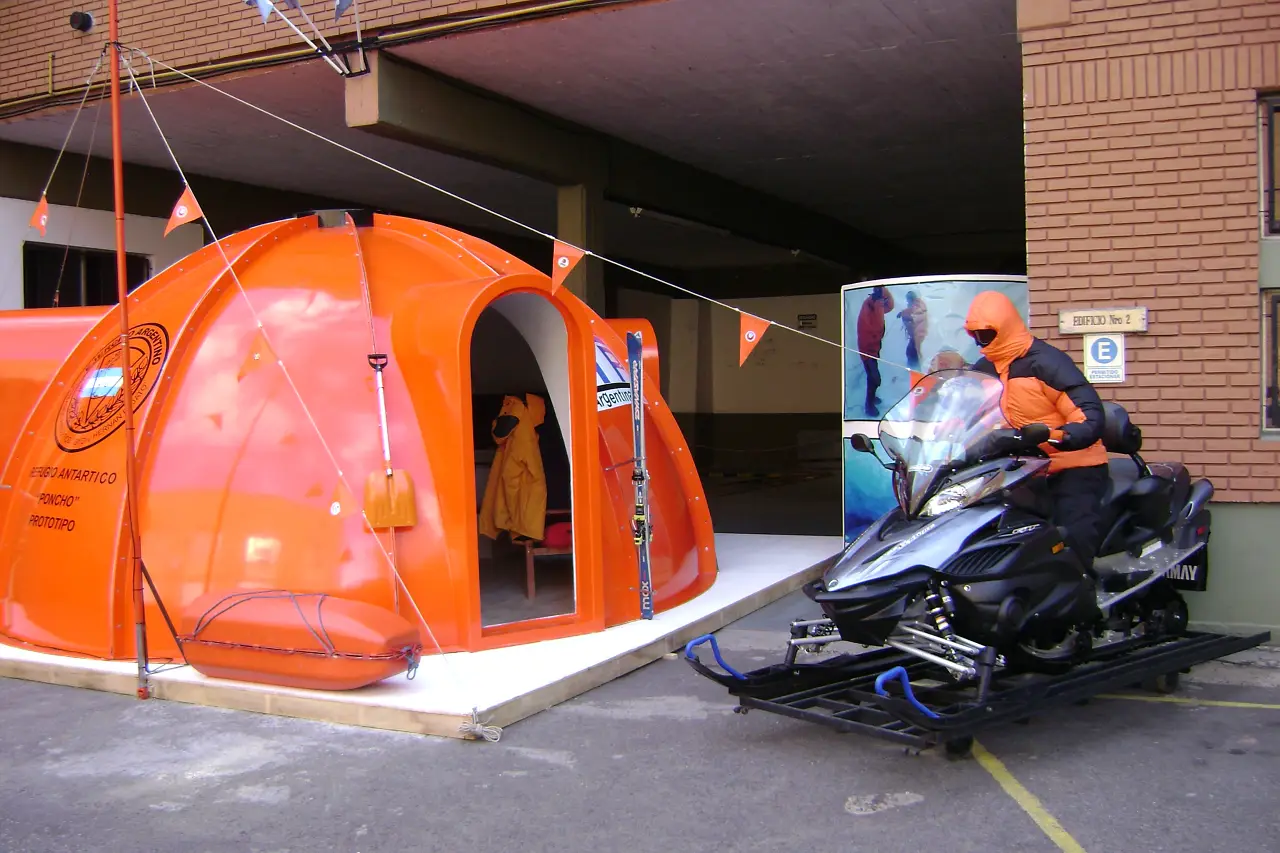
Mountain shelter
Military Developments
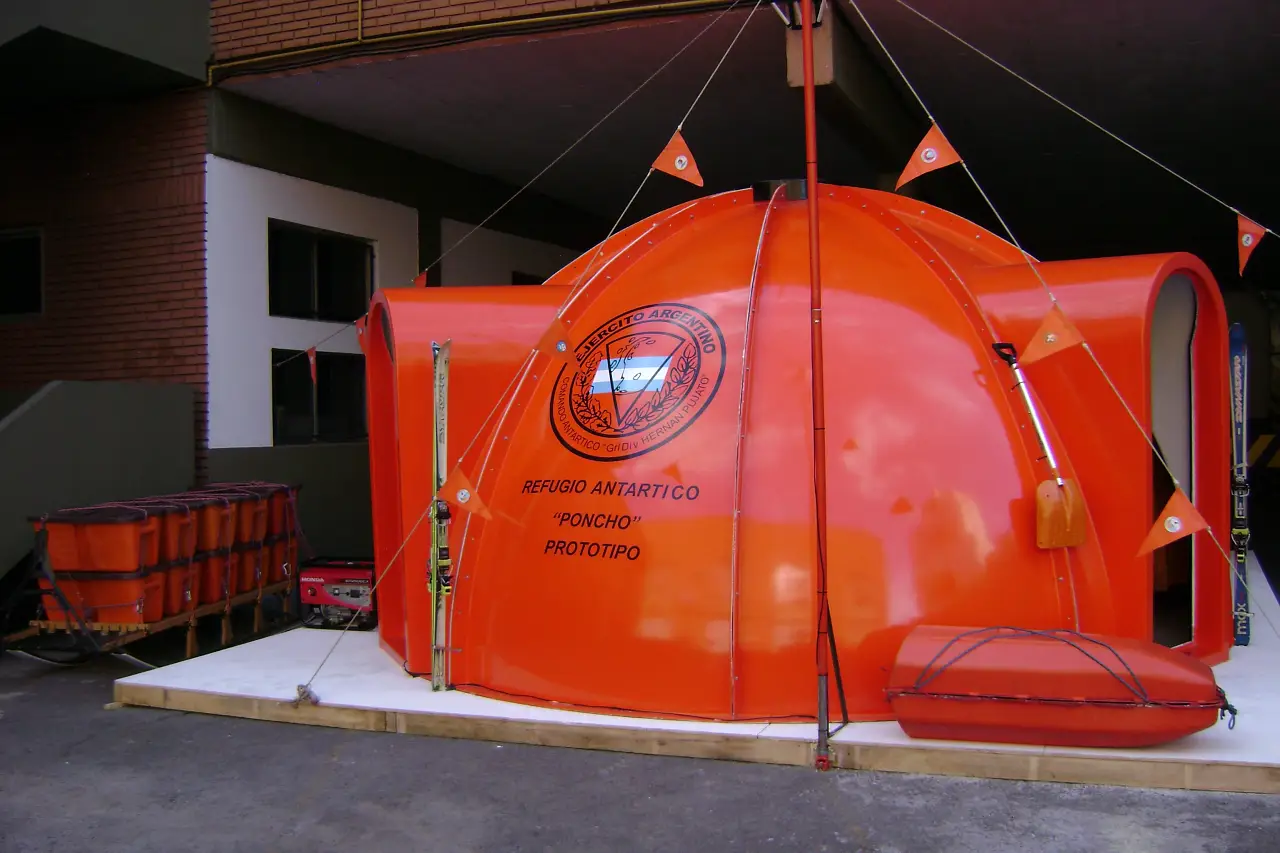
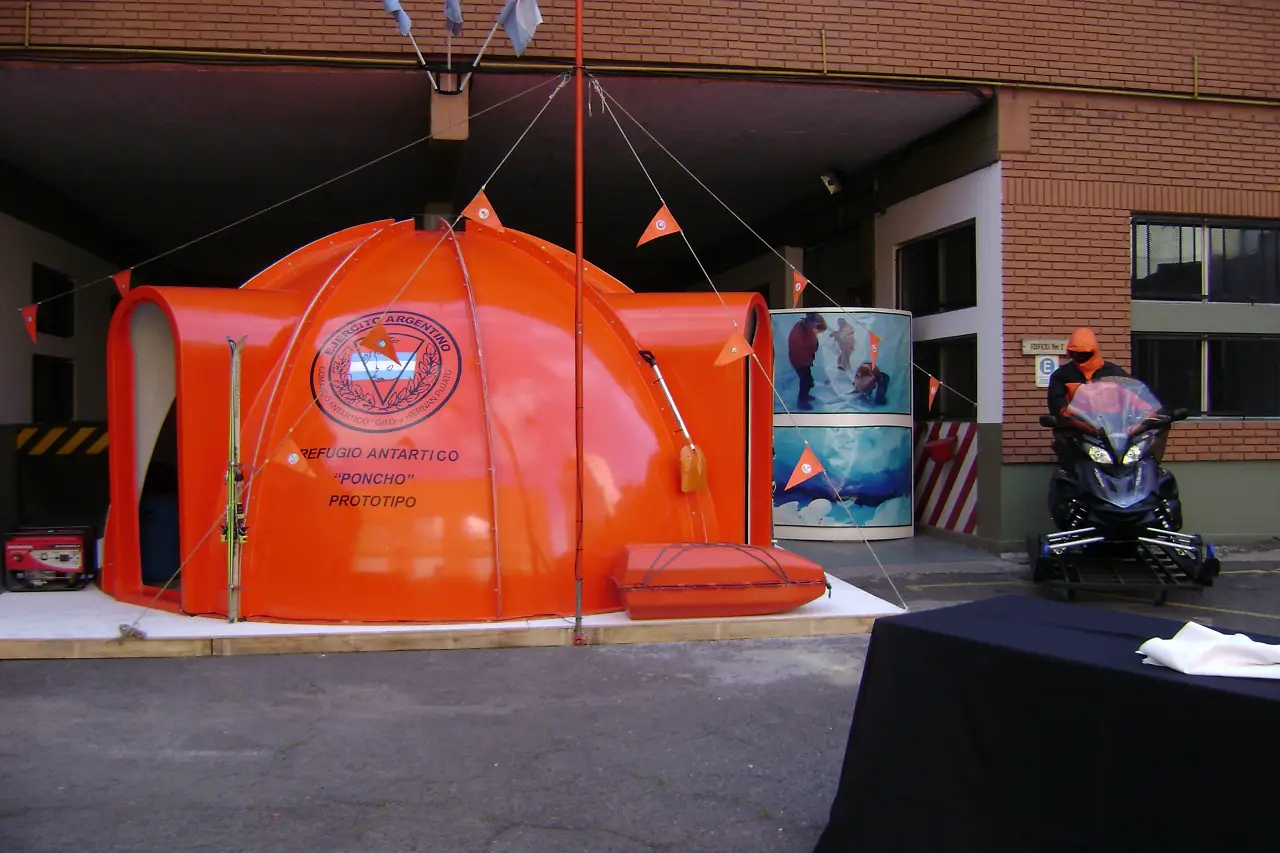
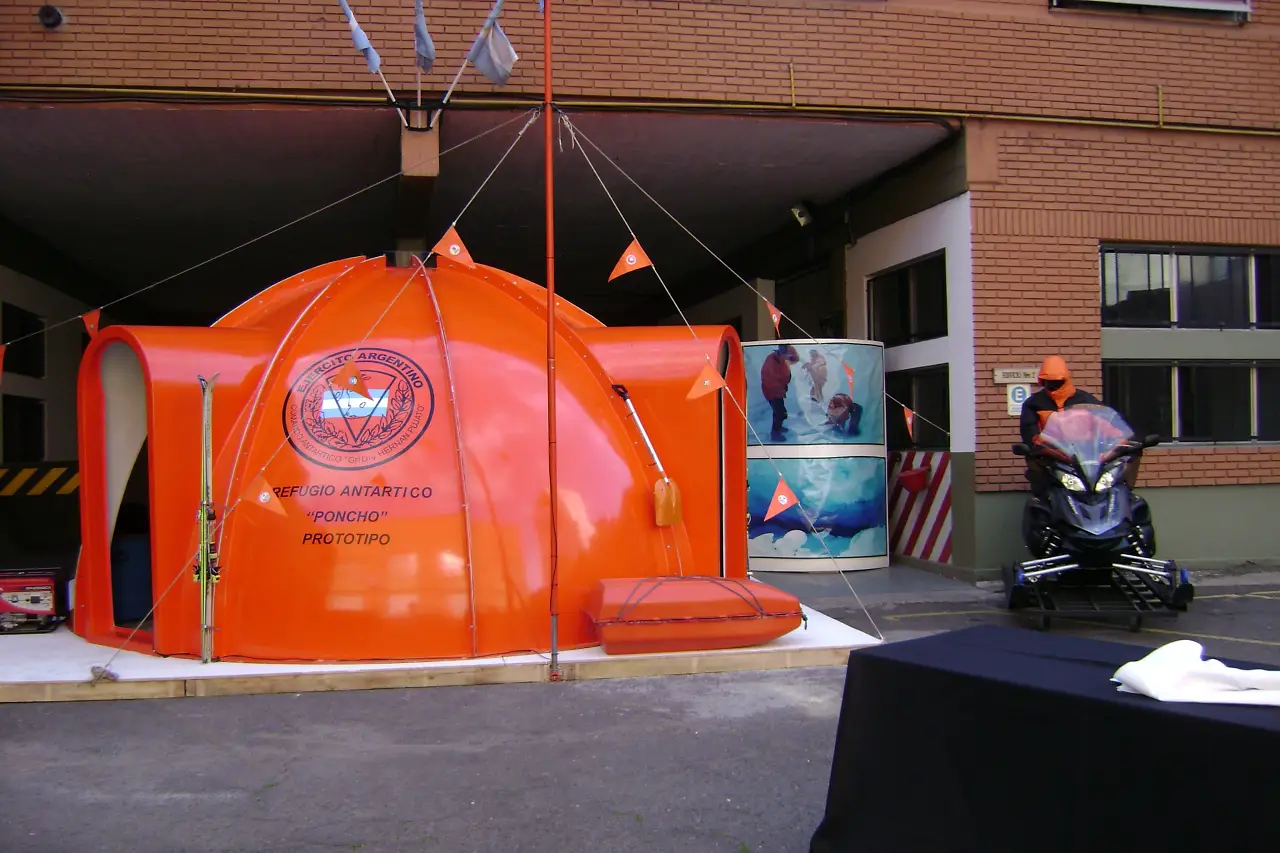
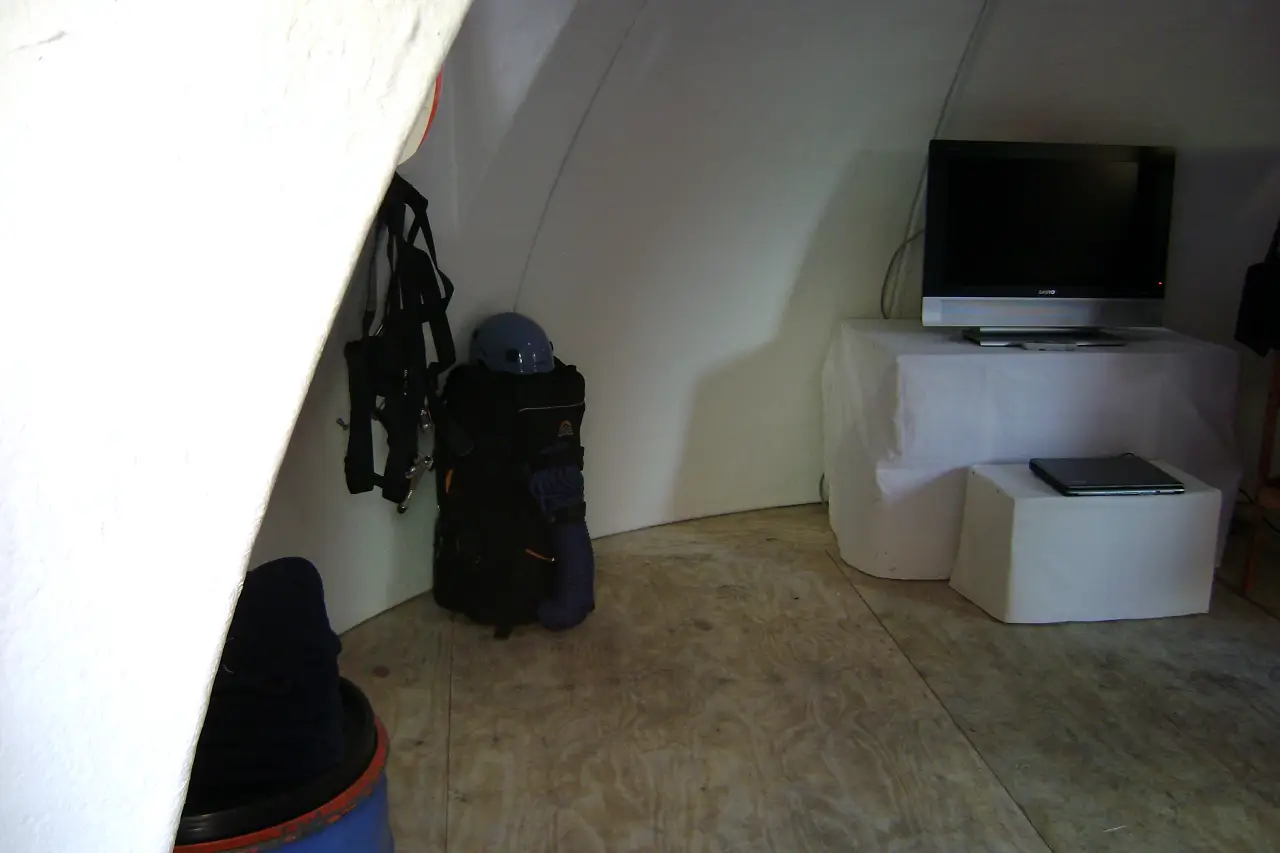
Relocatable Poncho shelter
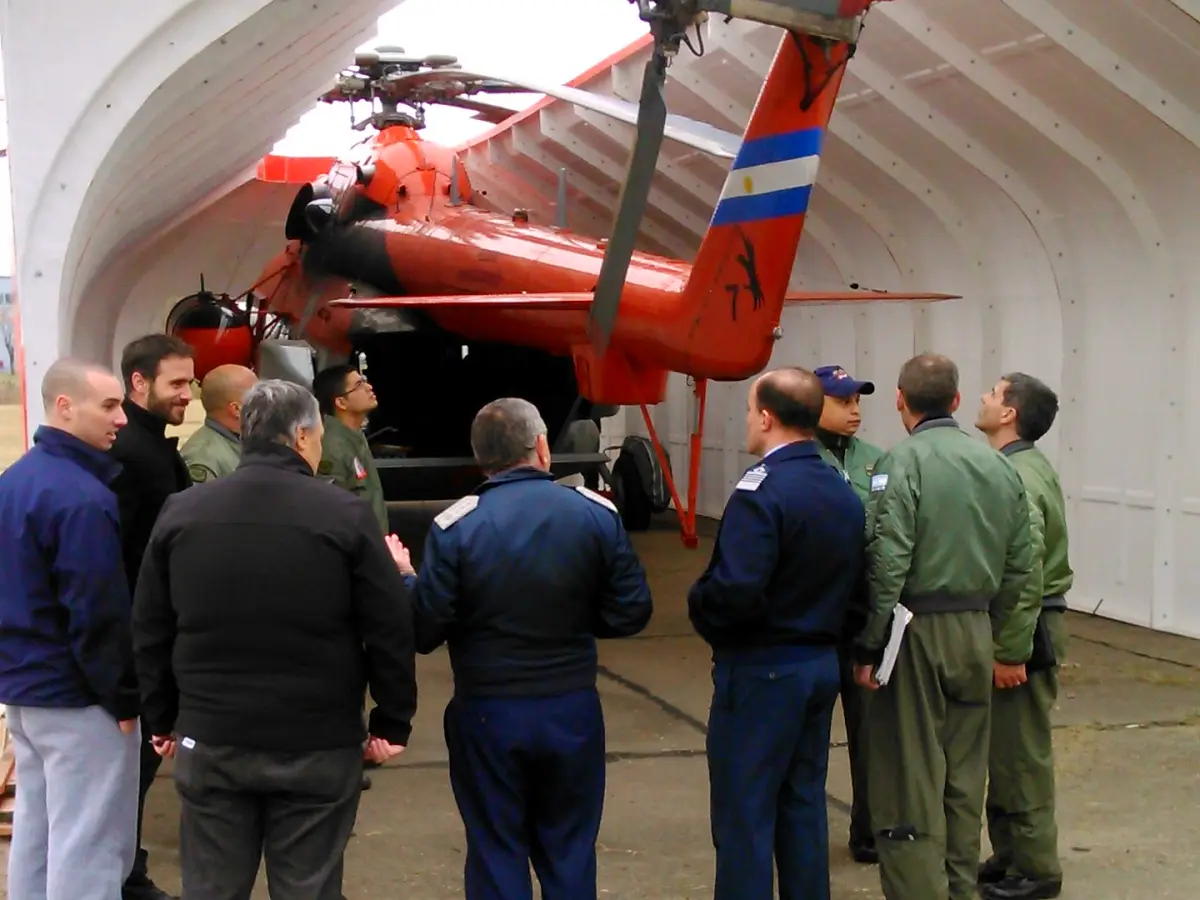
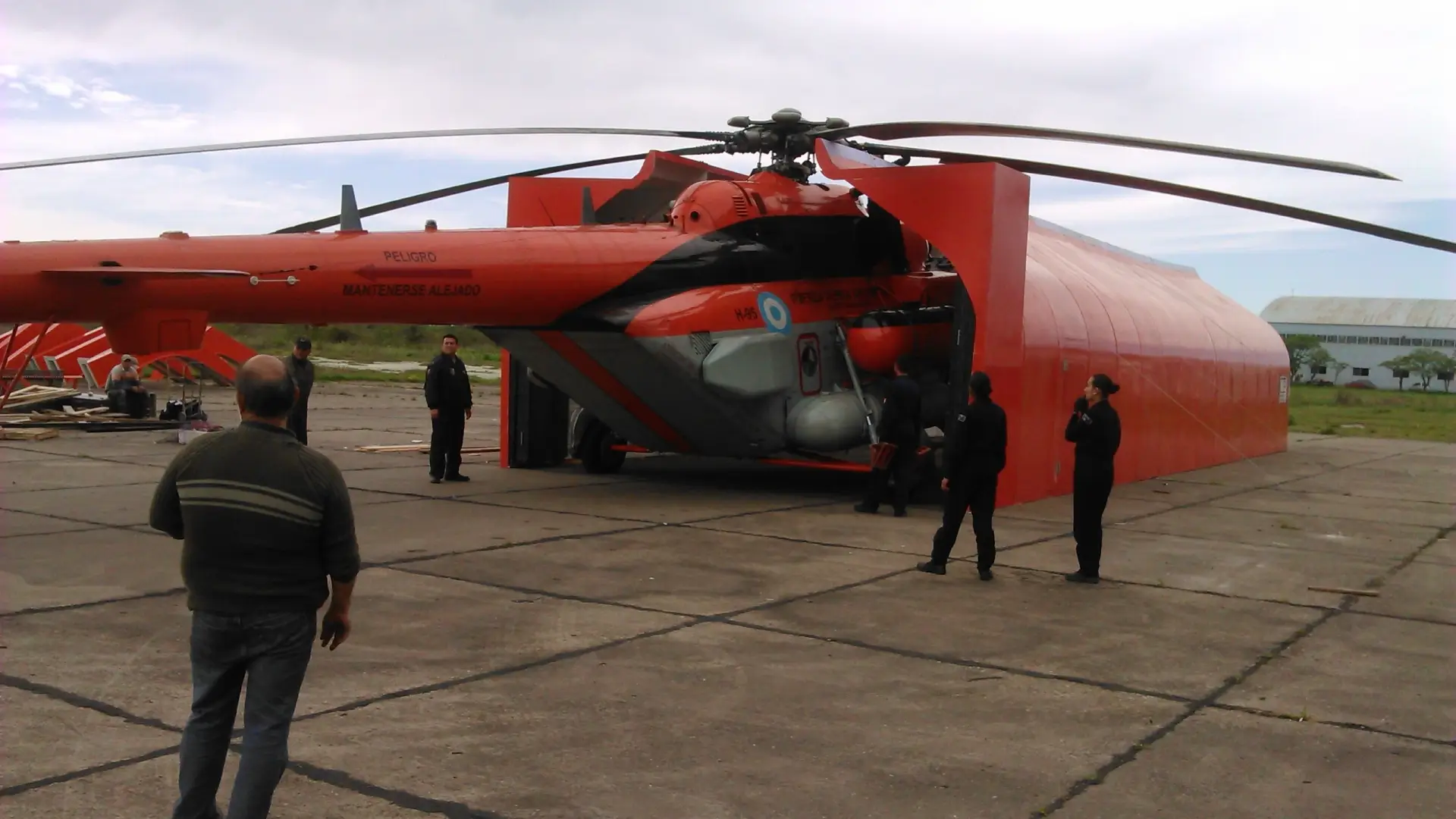
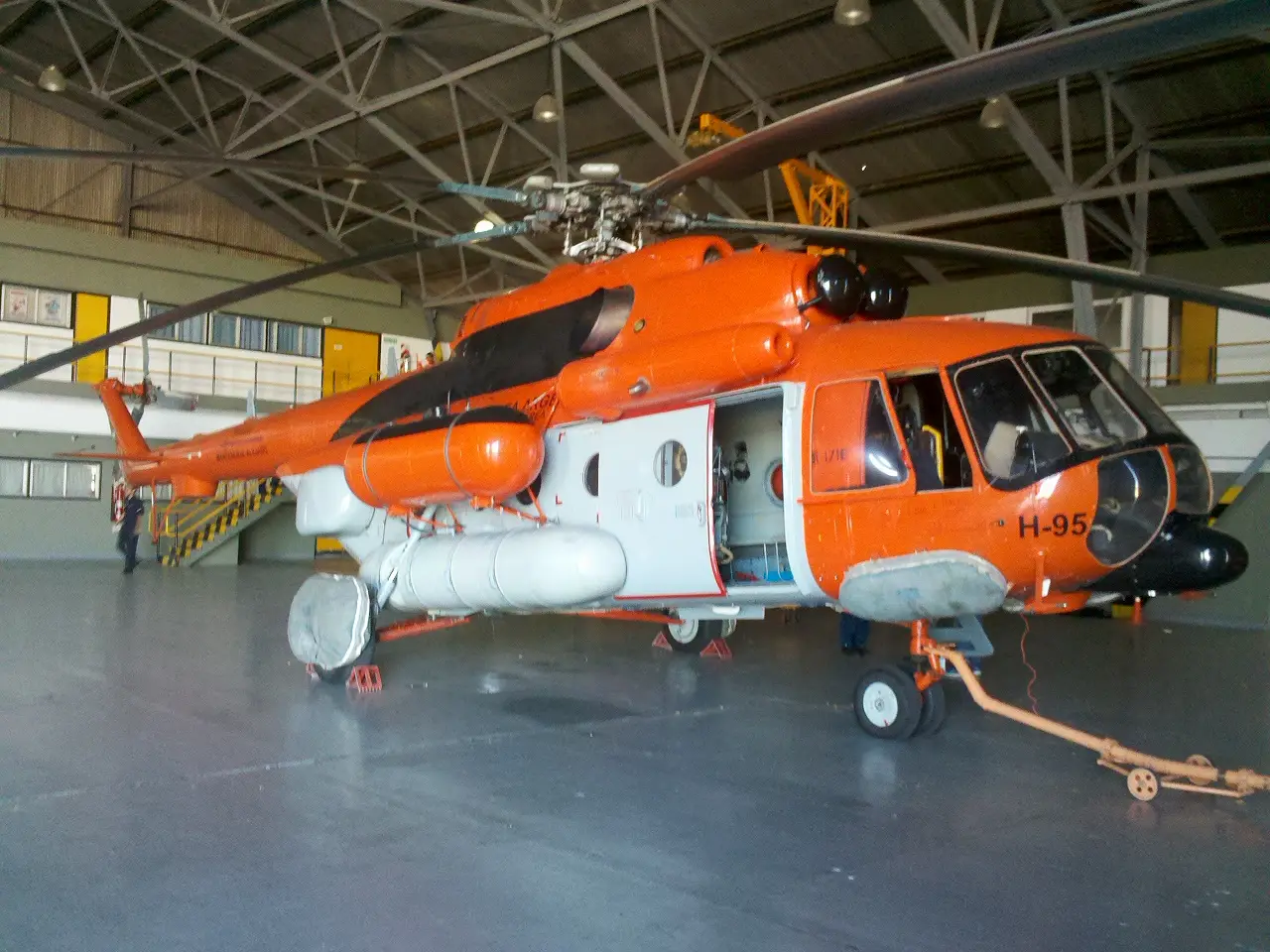
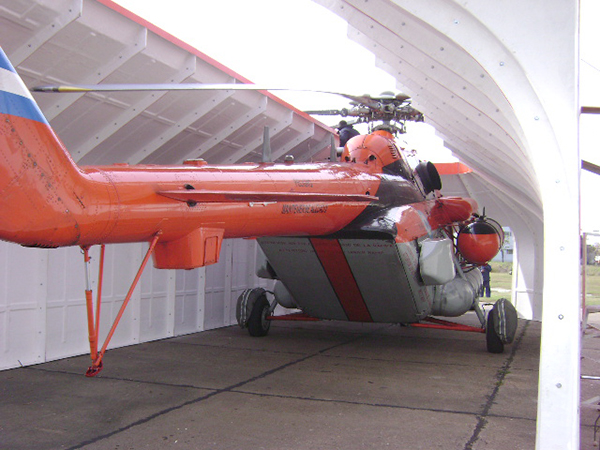
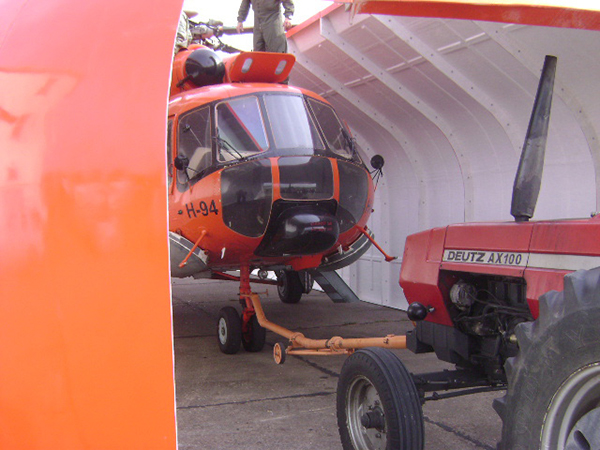
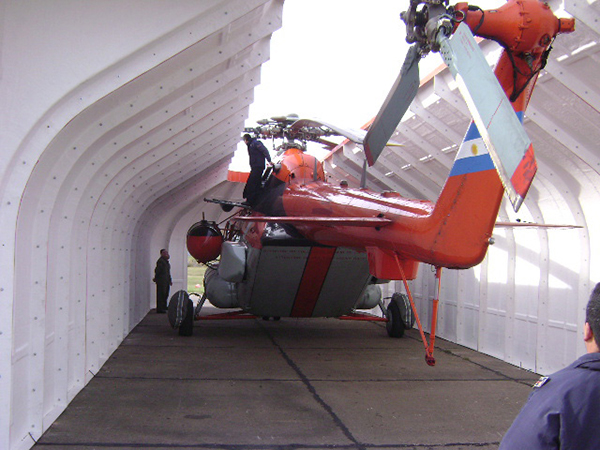
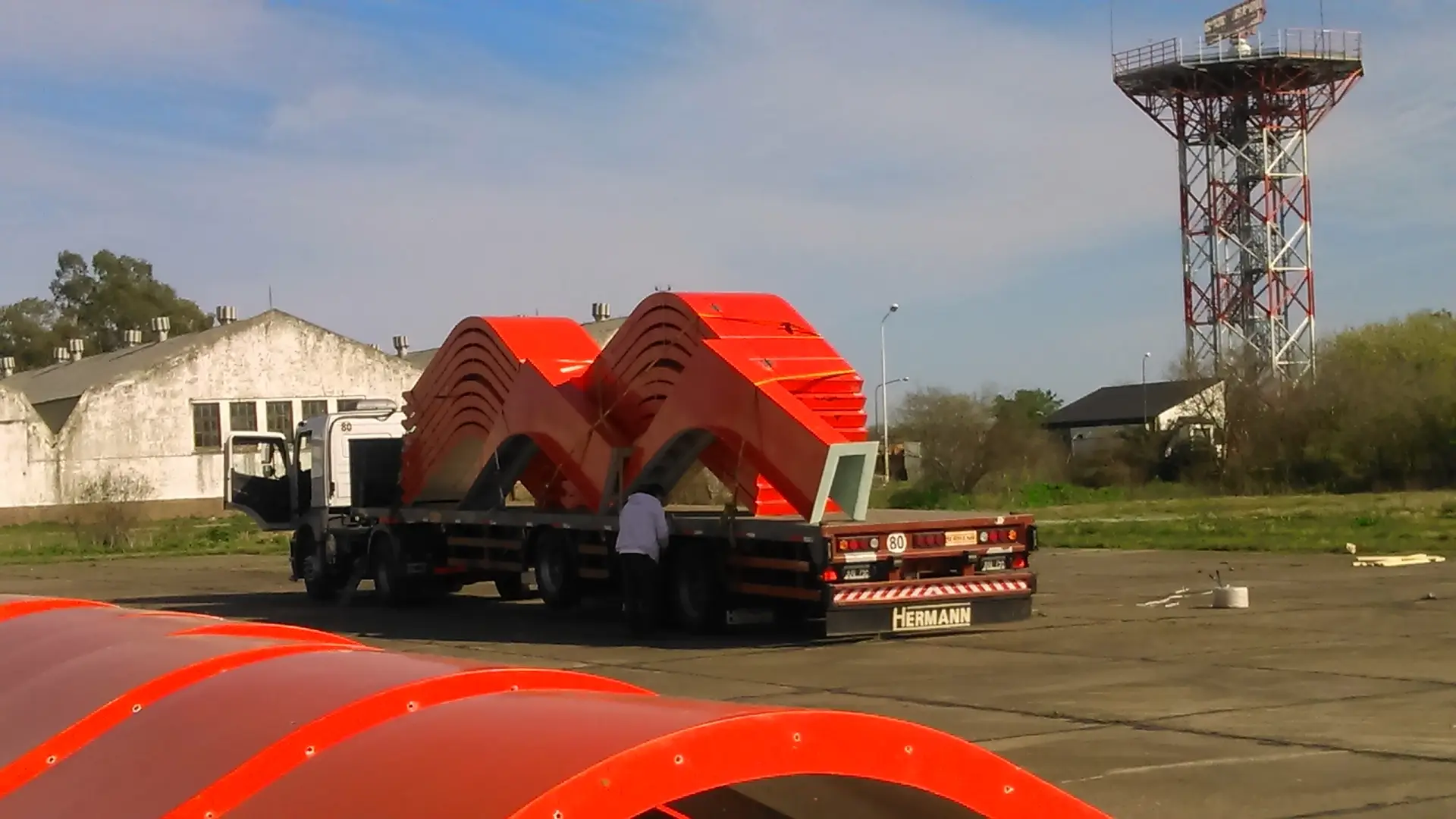
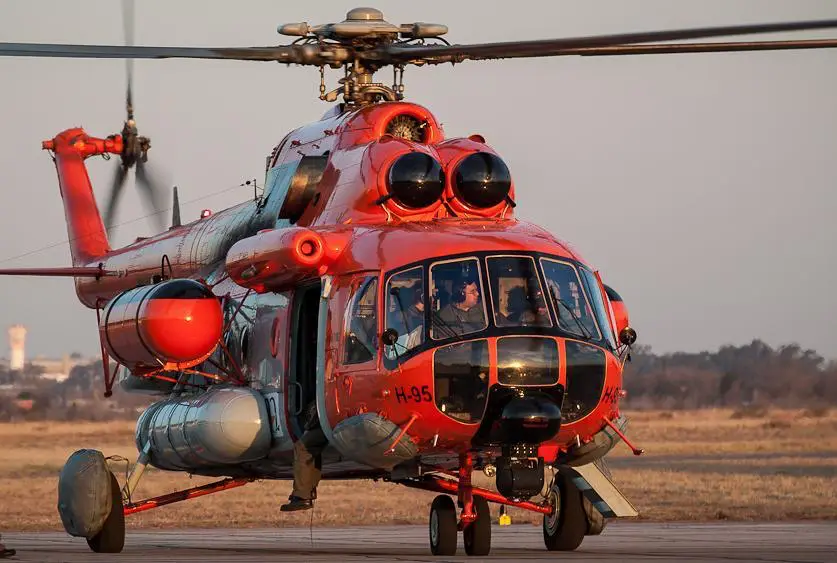
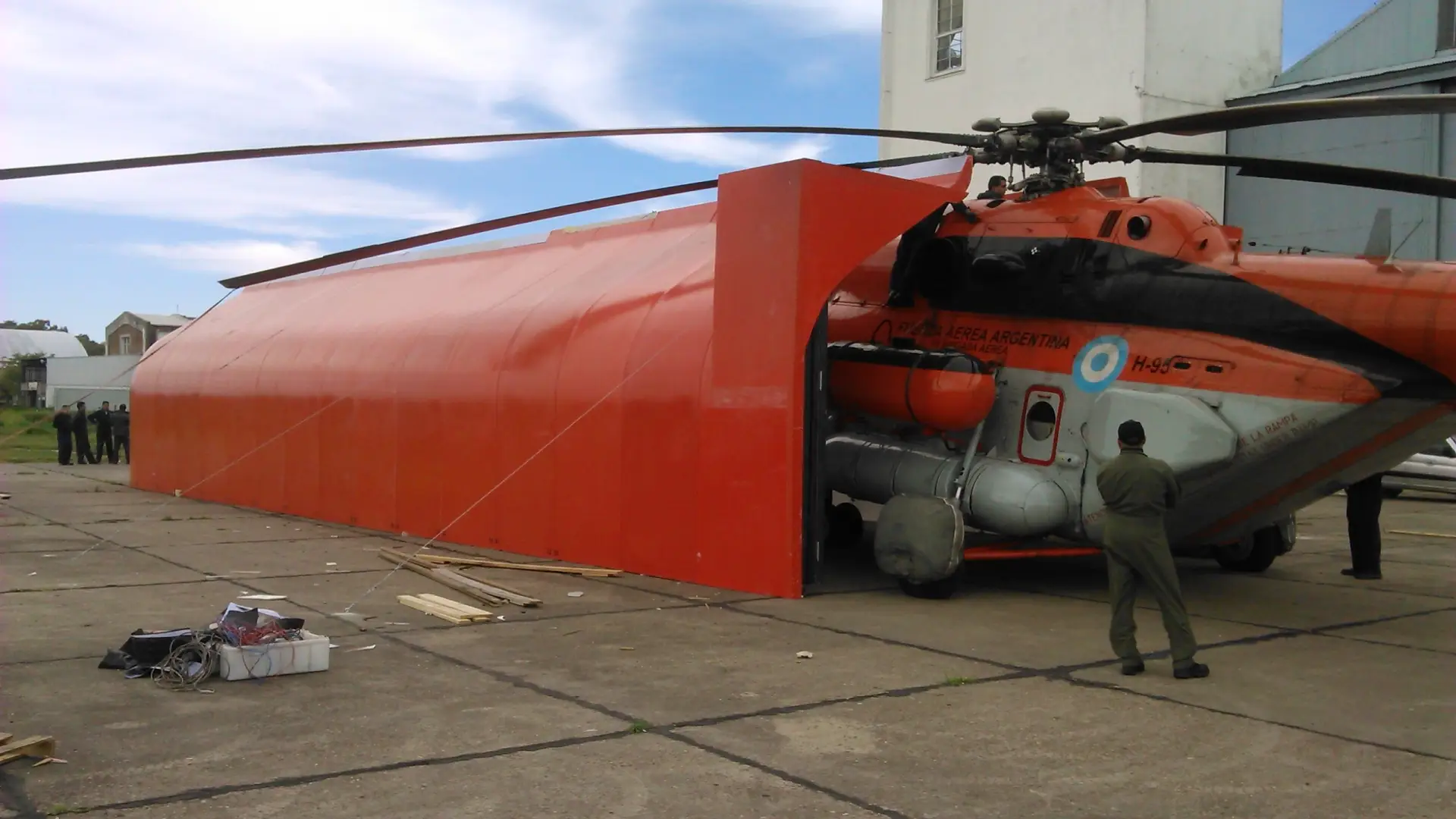
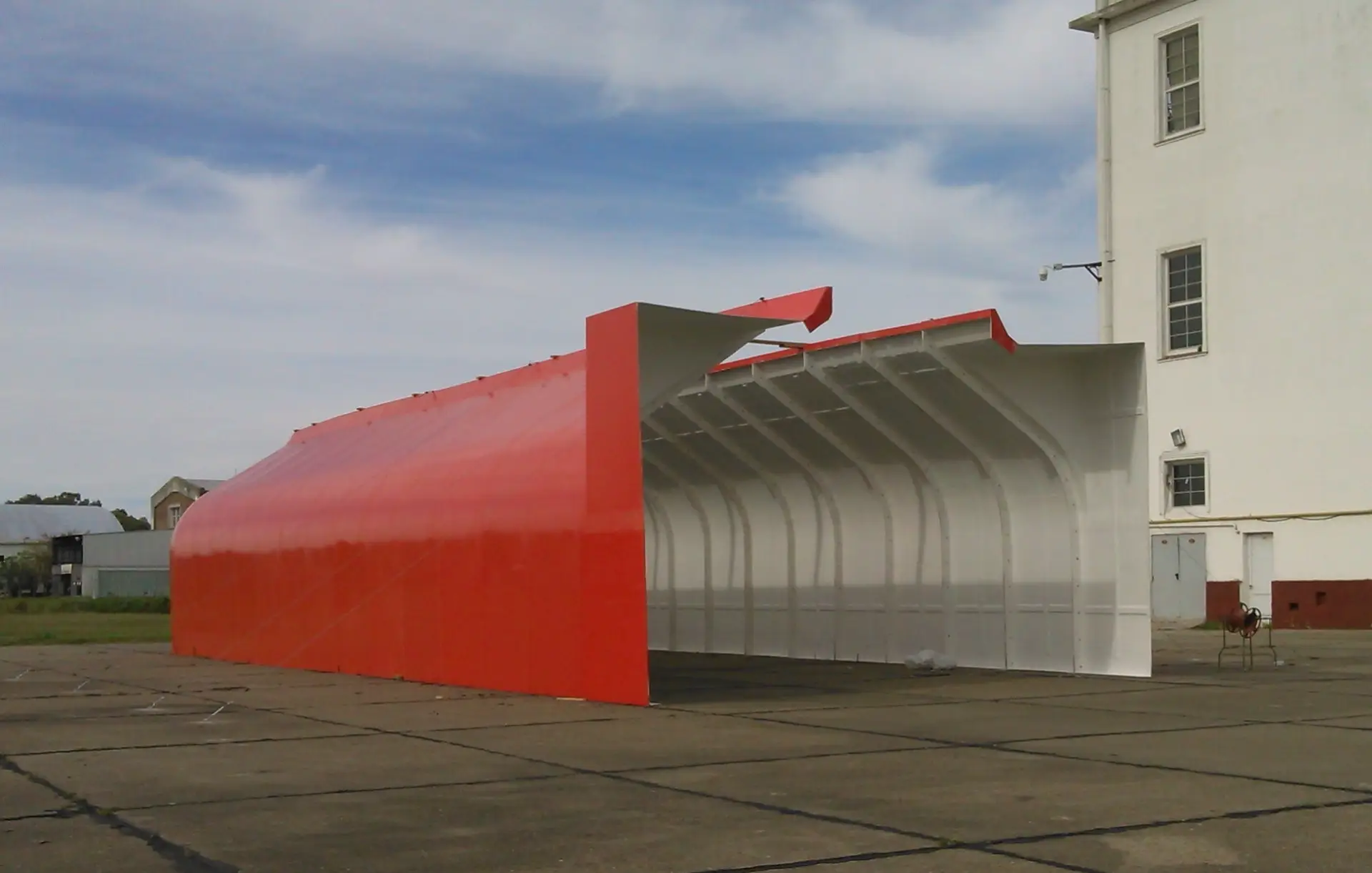
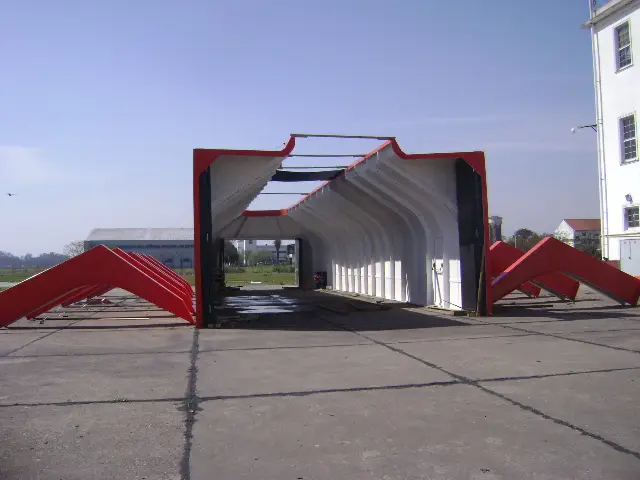
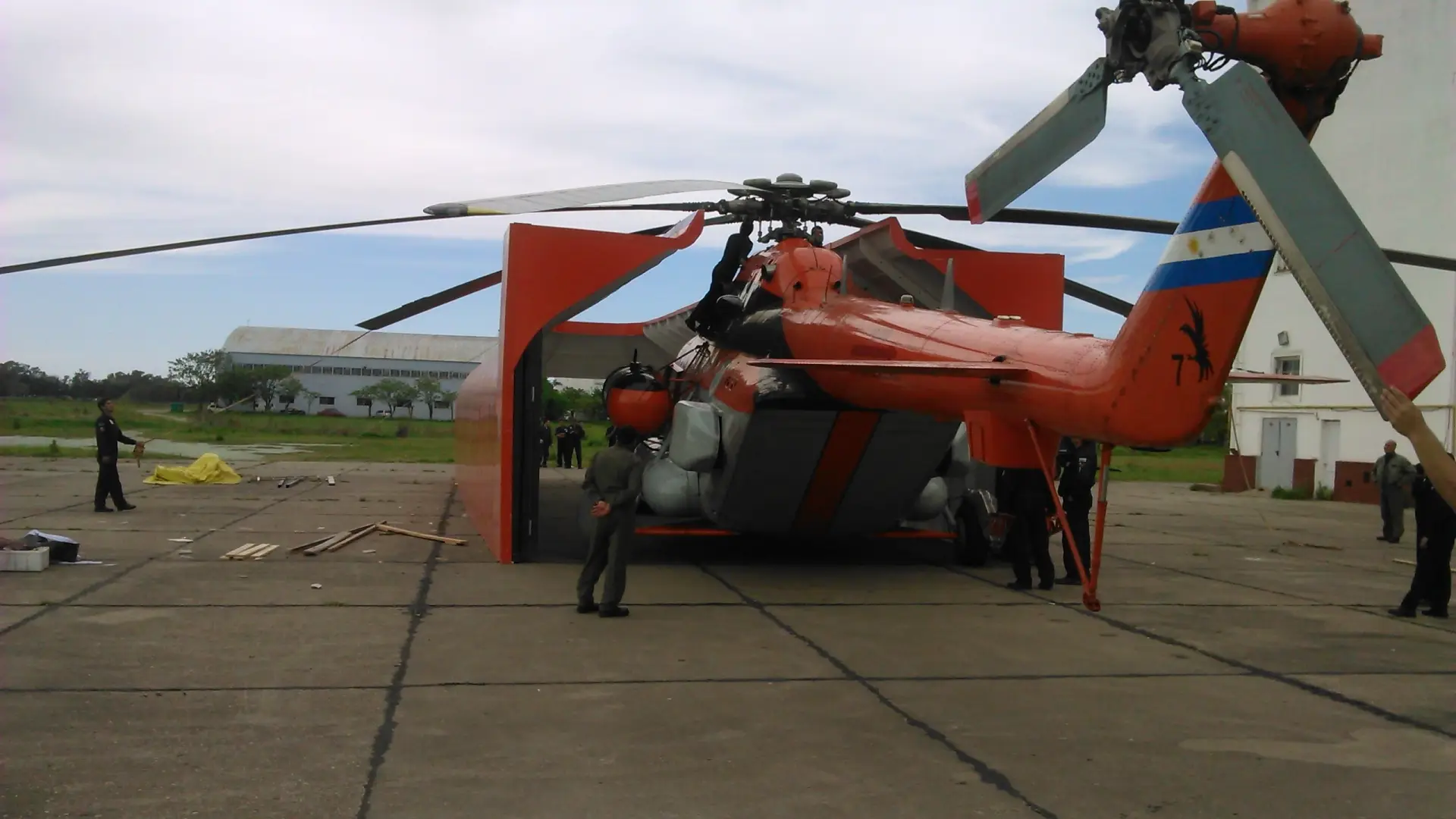
Antarctic cover for MI-17 helicopters
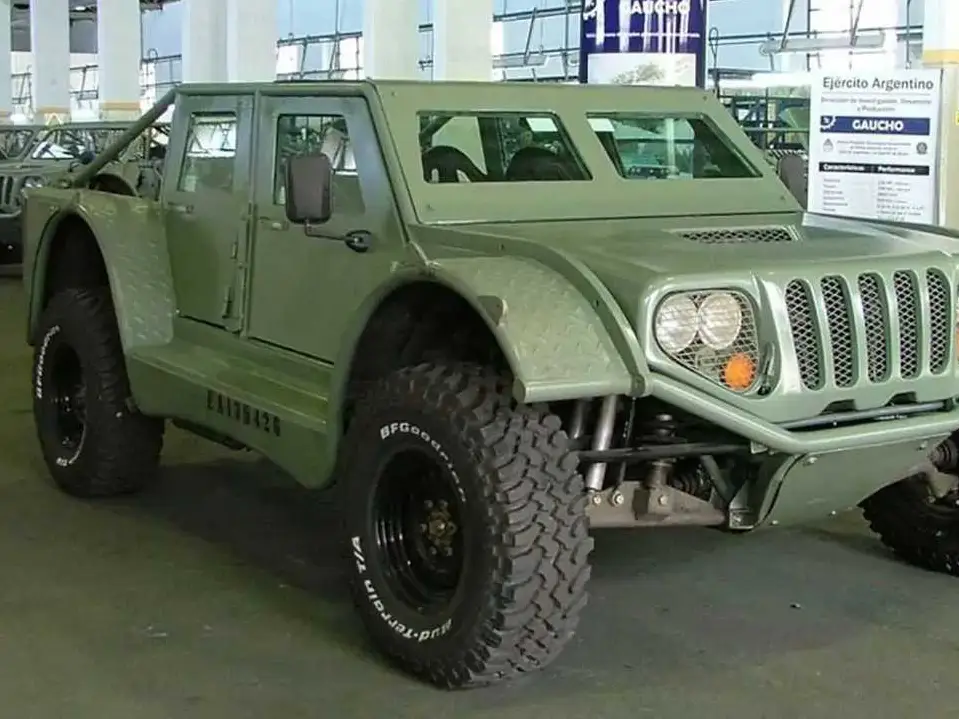
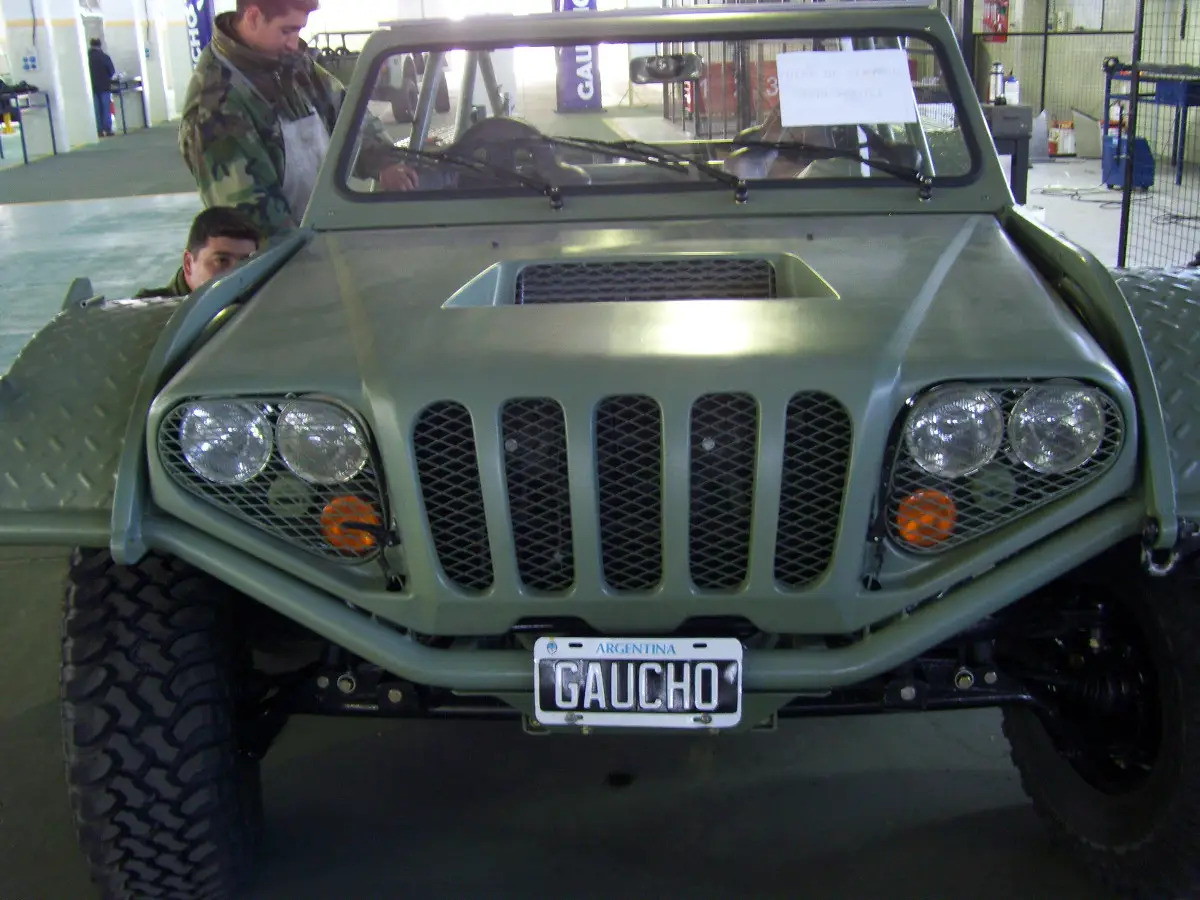
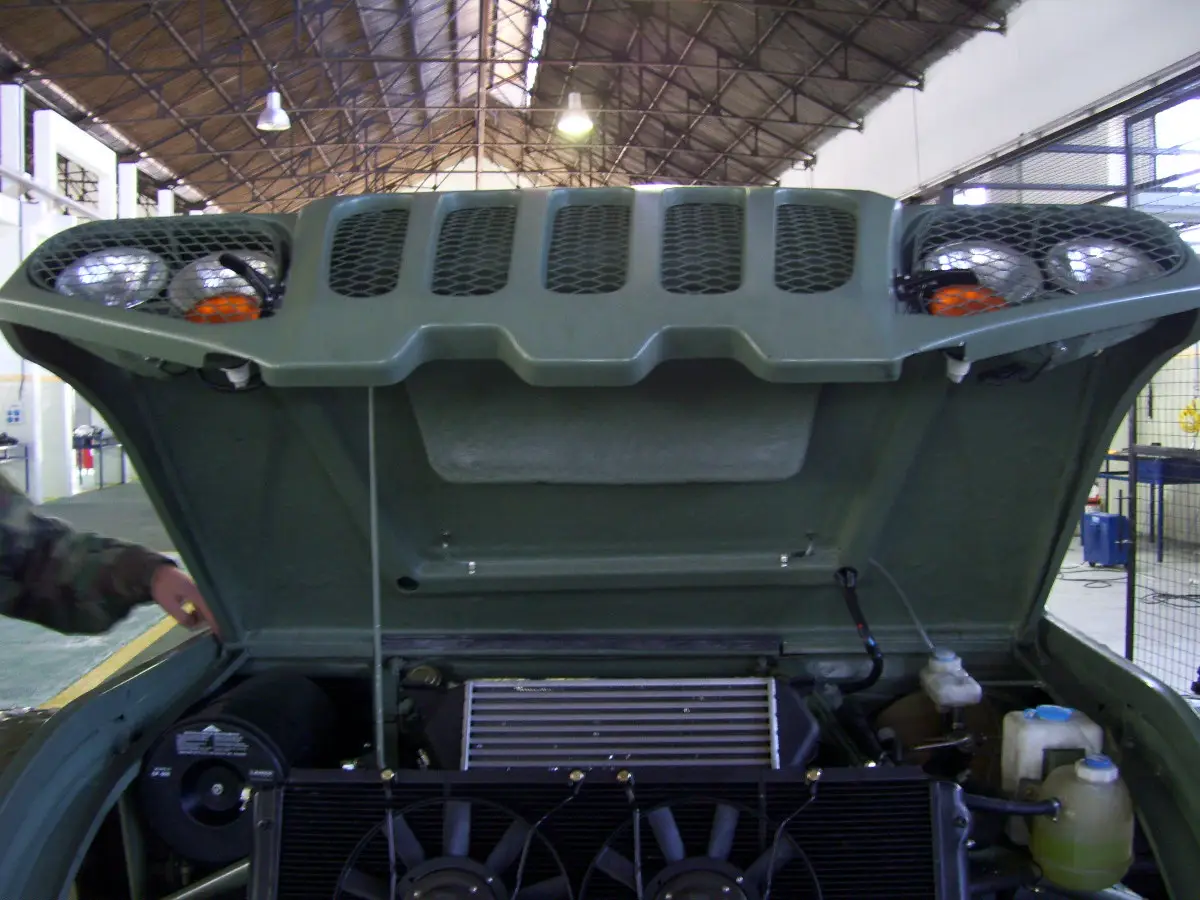
Auto parts for Gaucho military vehicle
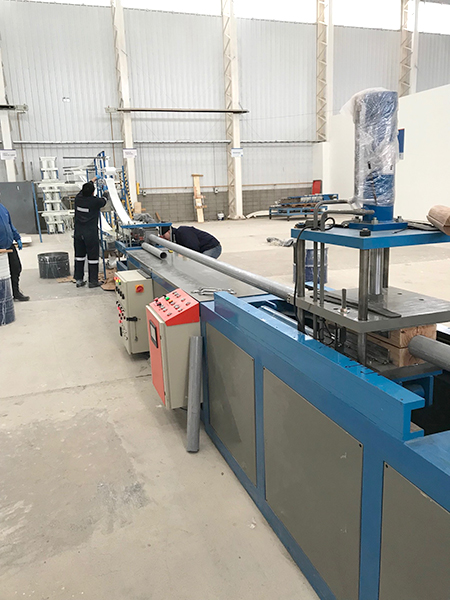
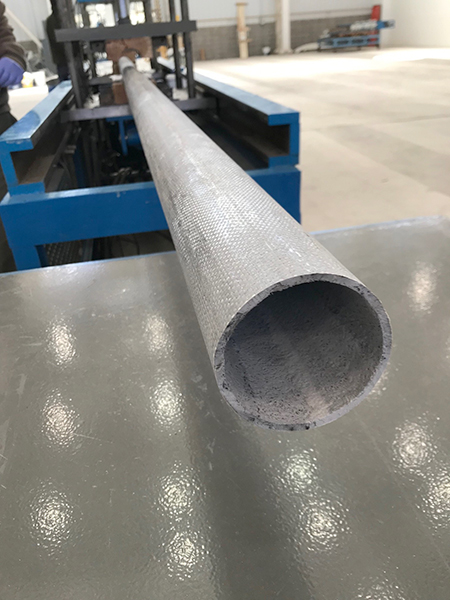
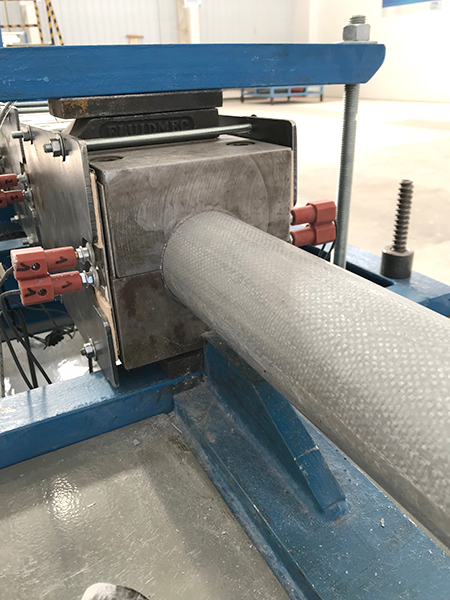
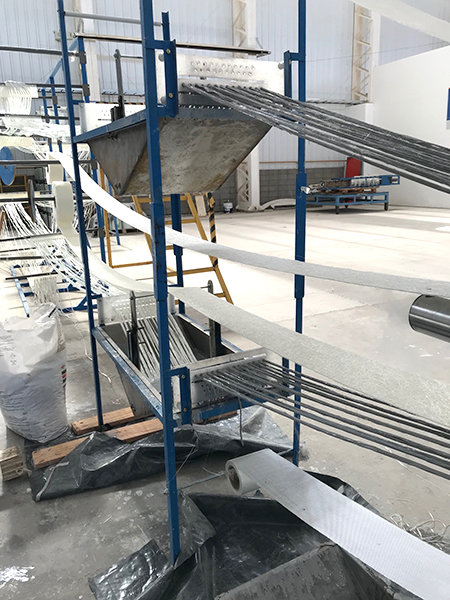
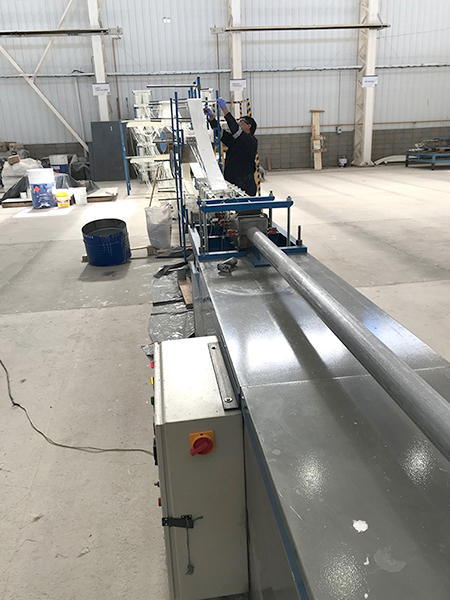
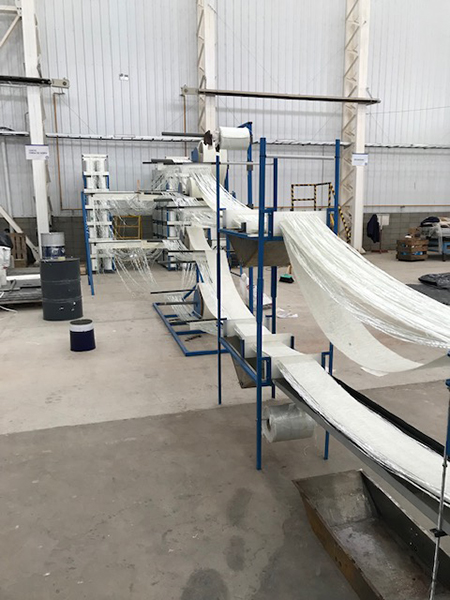
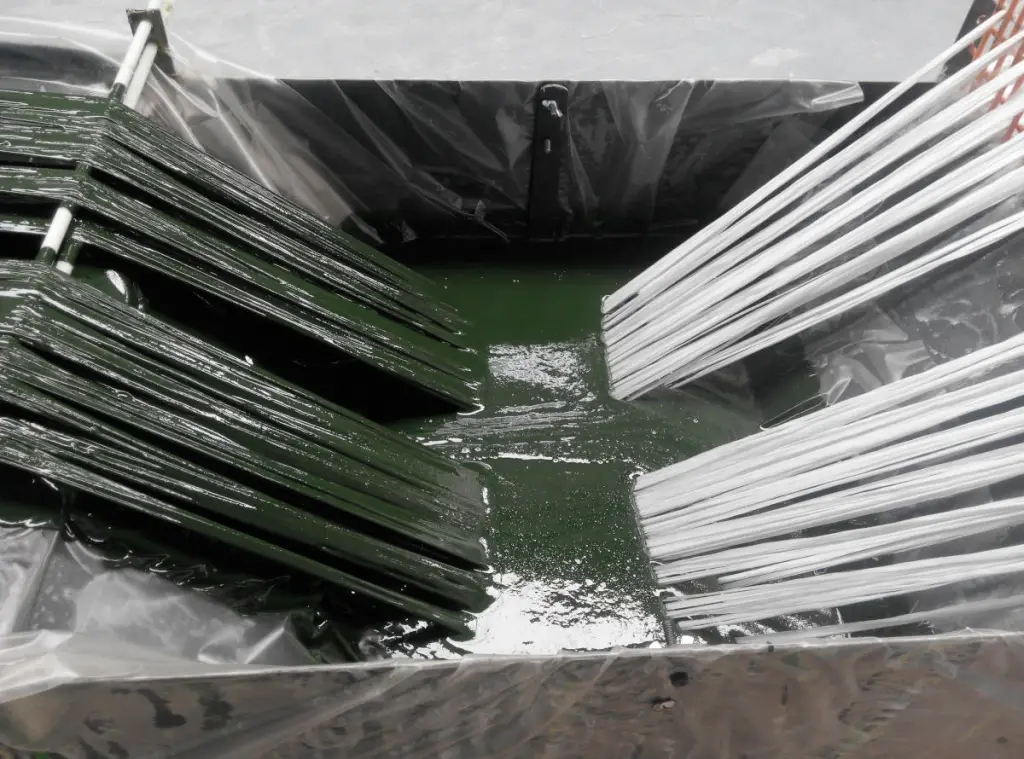
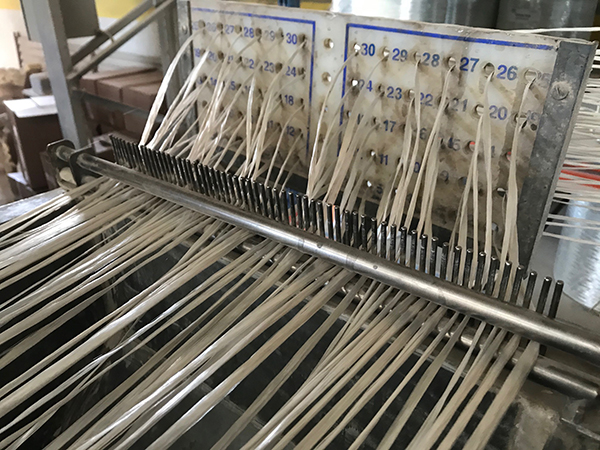
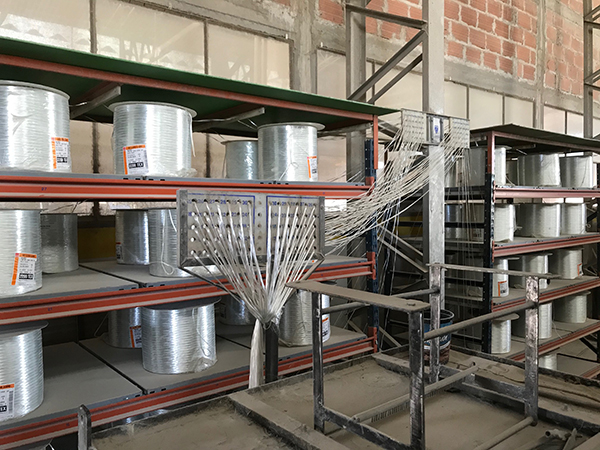
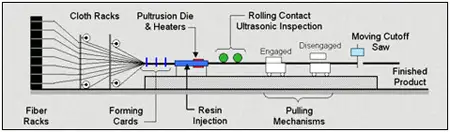
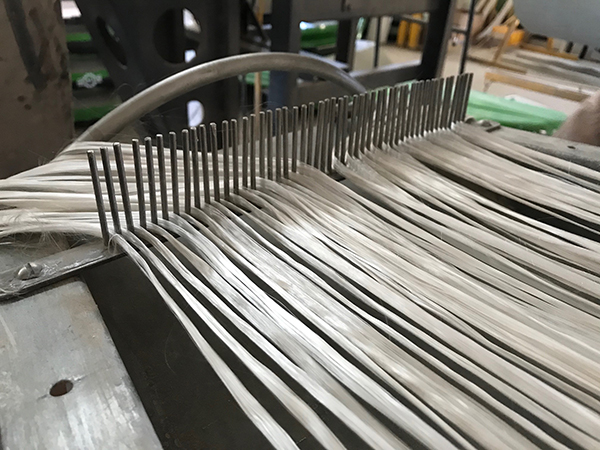
Pultrusion
Pultrusion is a continuous production process used to create linear structural profiles with no thickness variation (e.g., square, round, or rectangular hollow profiles, double “T” profiles, “U” profiles, among others). One of the most remarkable qualities of this process is the fiber-to-resin ratio that can be achieved in the final piece, which can range from 35% to 70%, depending on the profile being manufactured and its mechanical requirements.
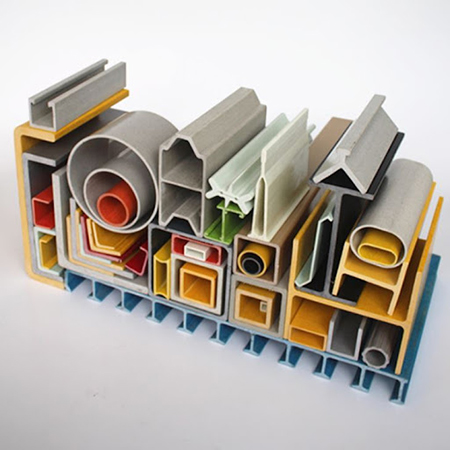
Completed Works
Profiles and Structures
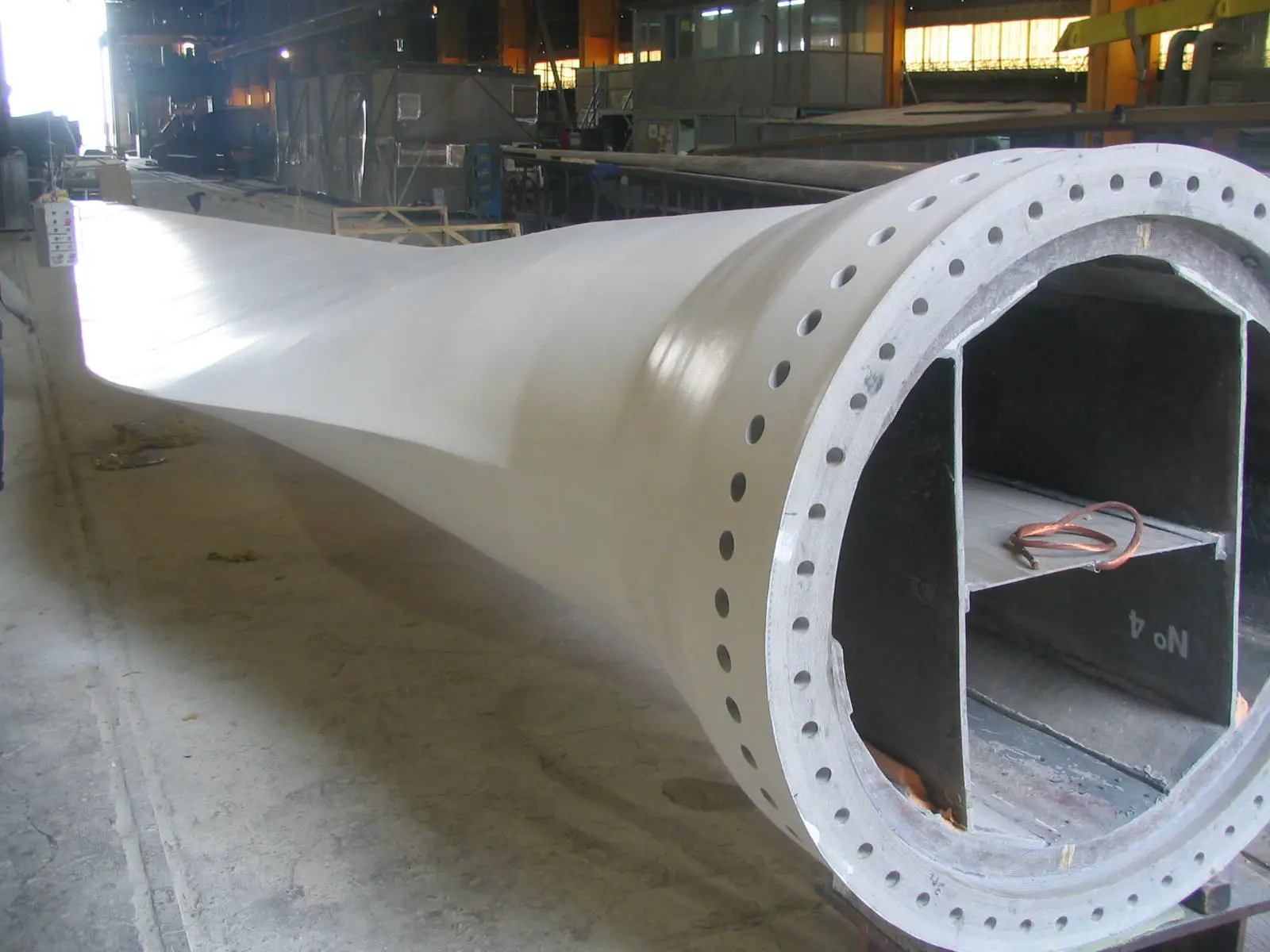
Filament Winding
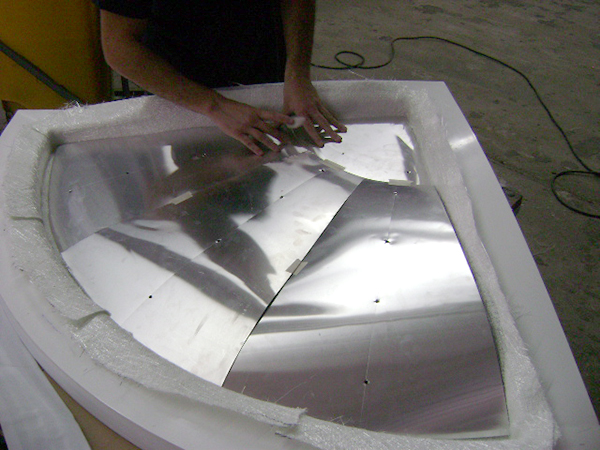
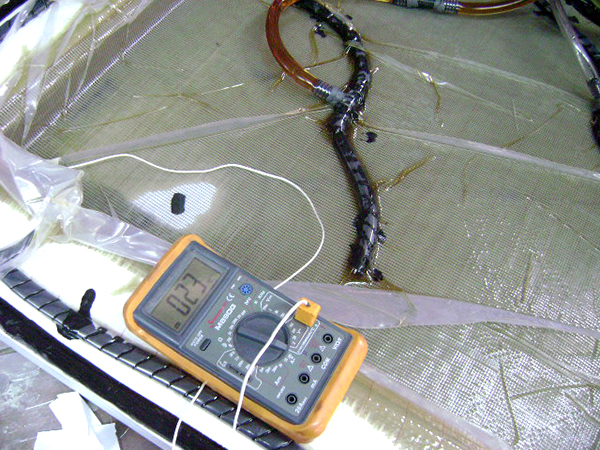
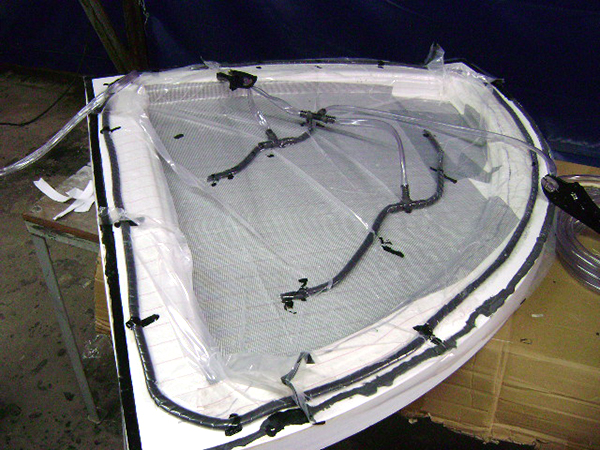
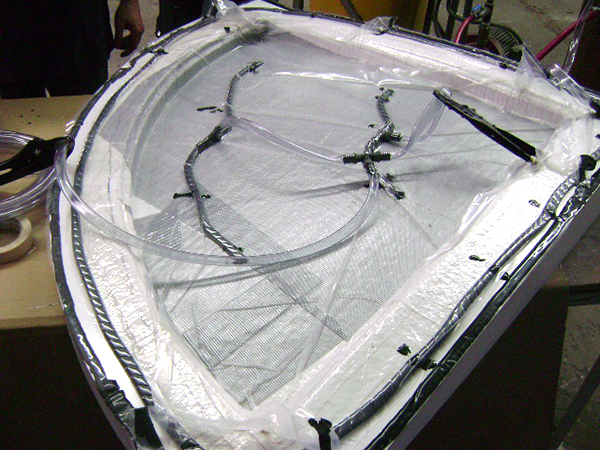
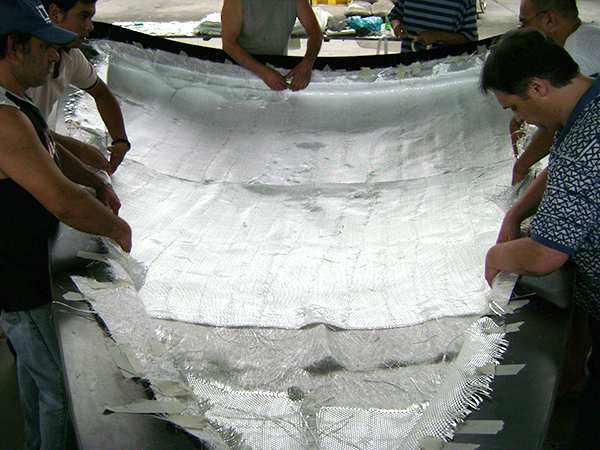
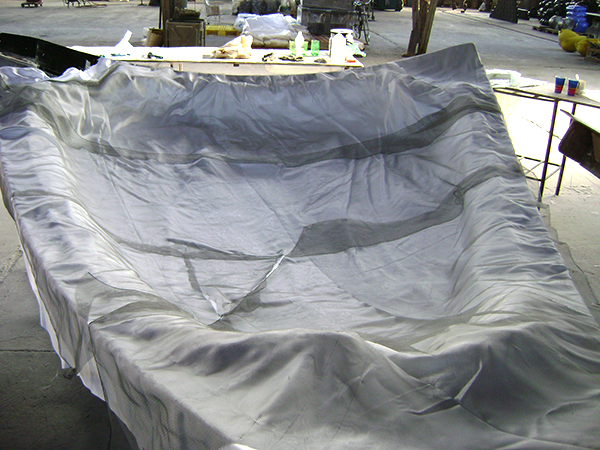
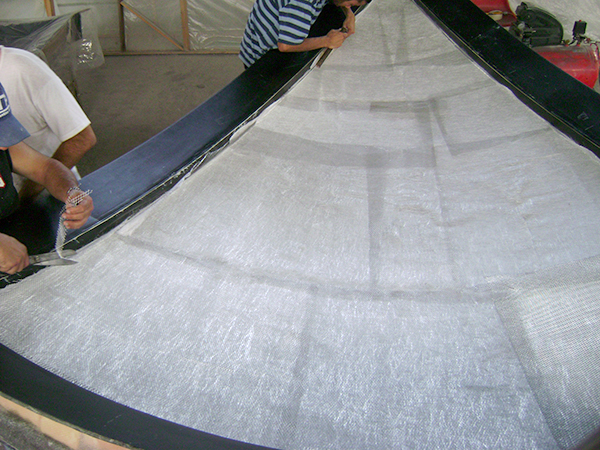
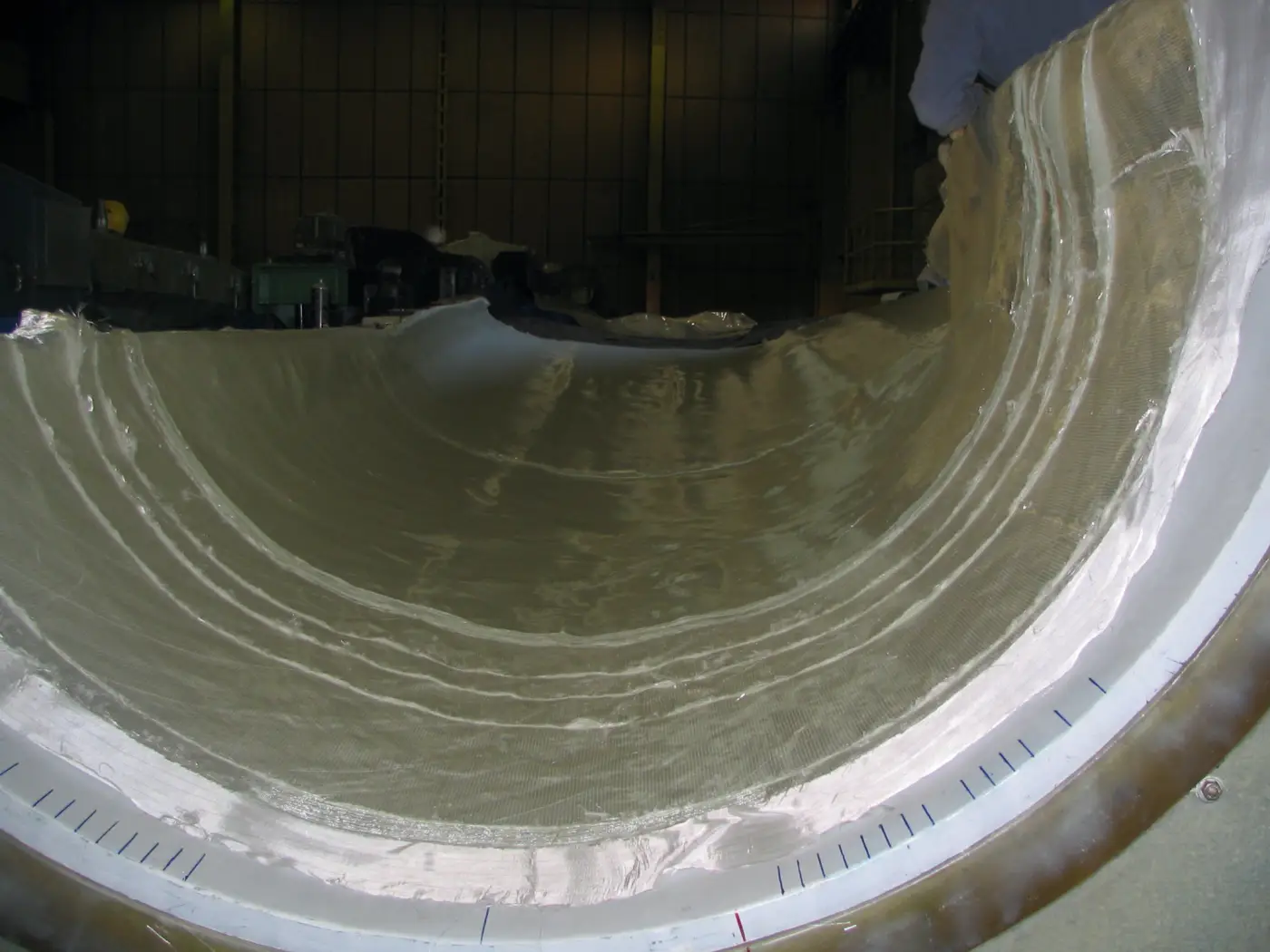
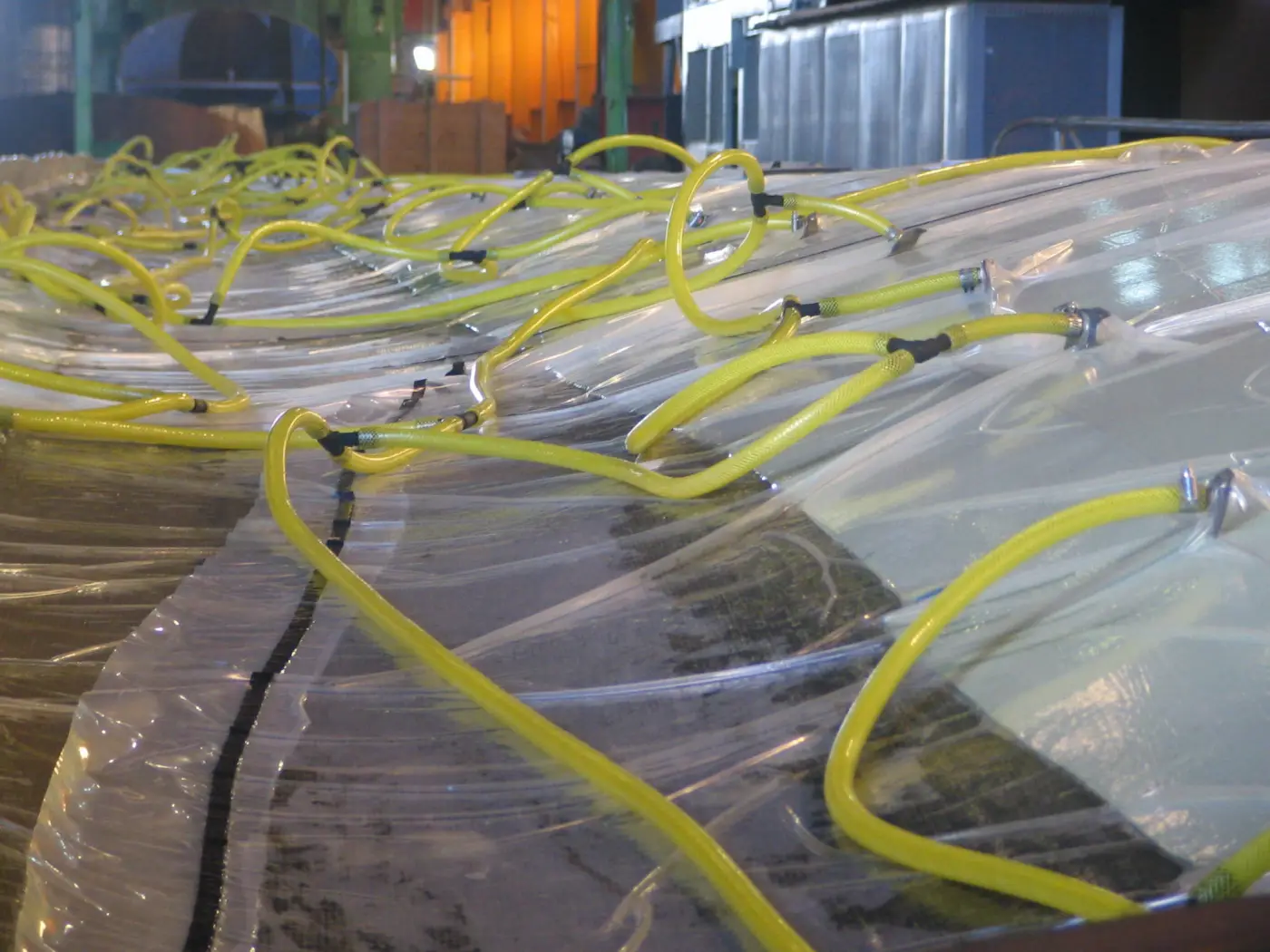
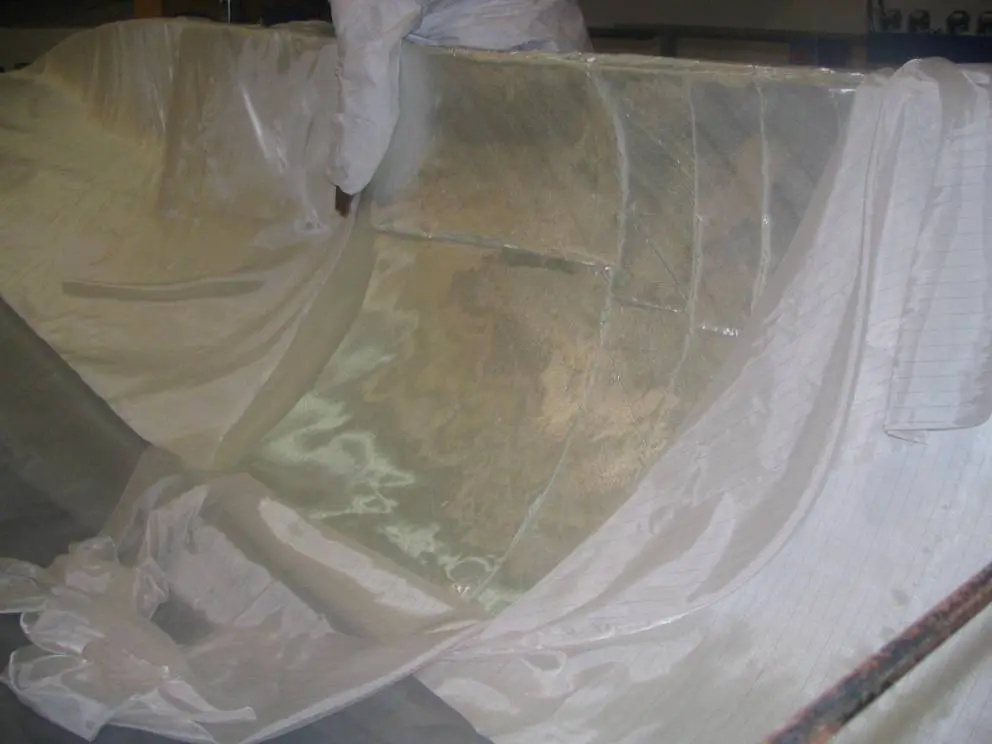
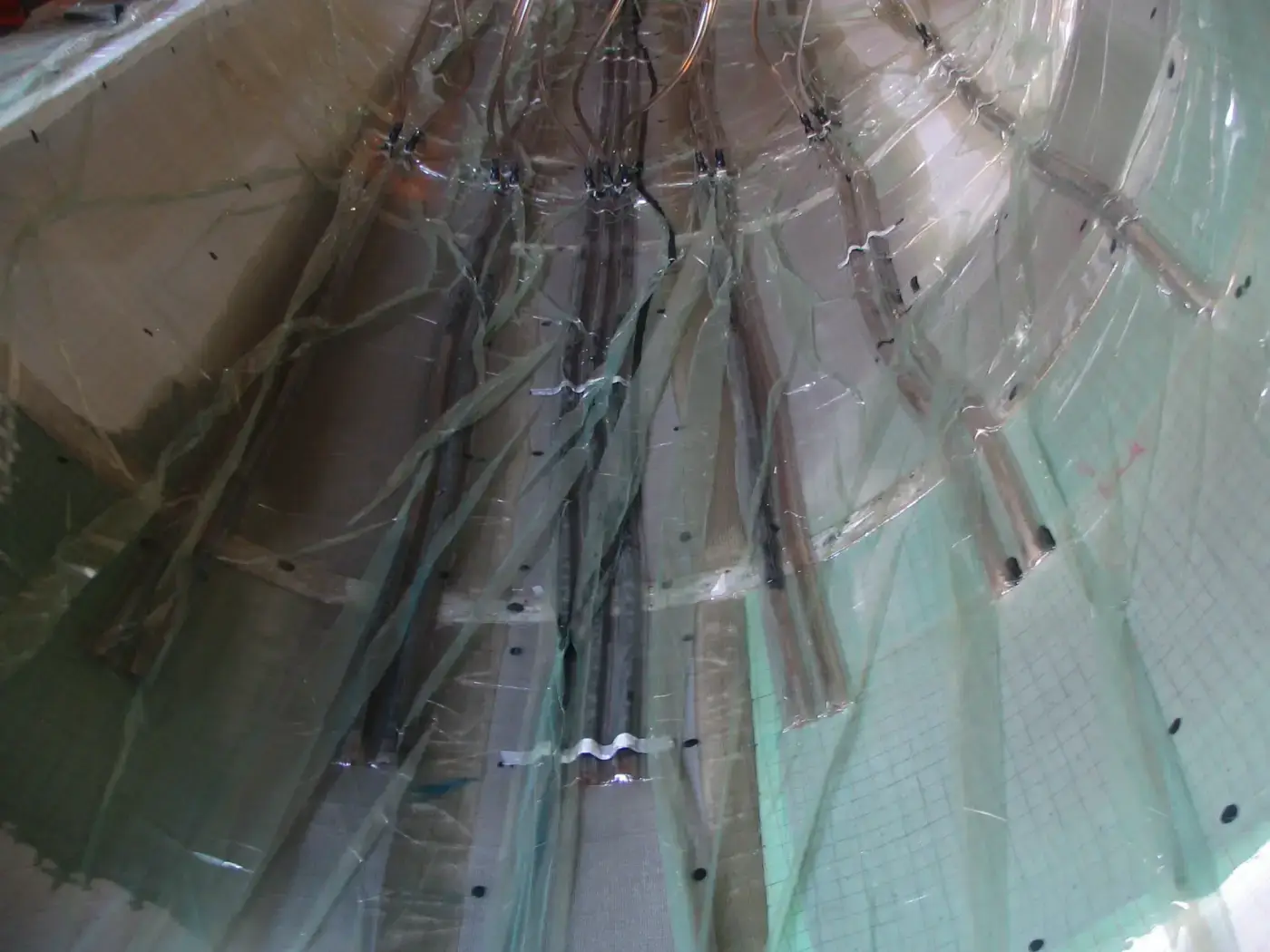
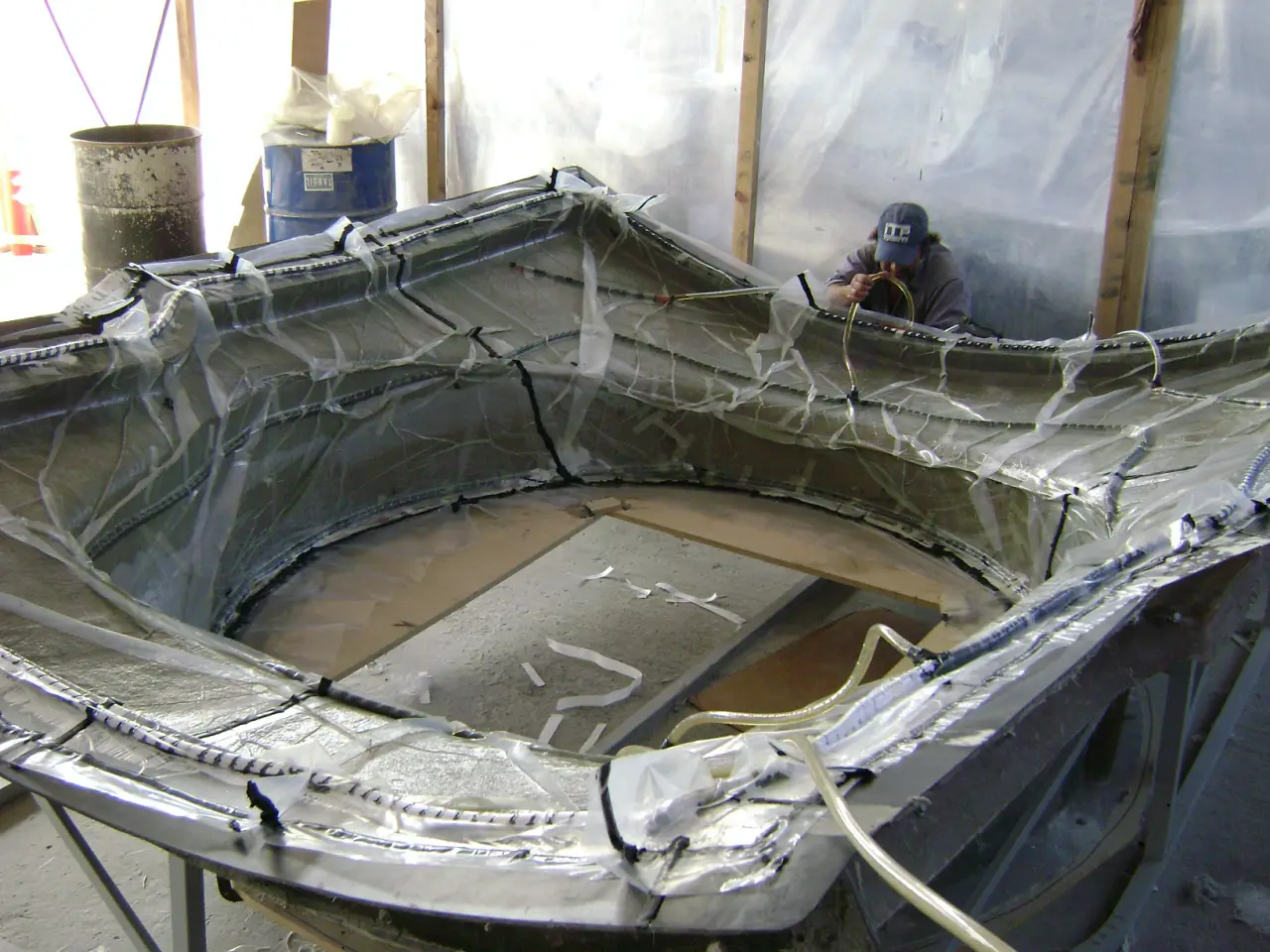
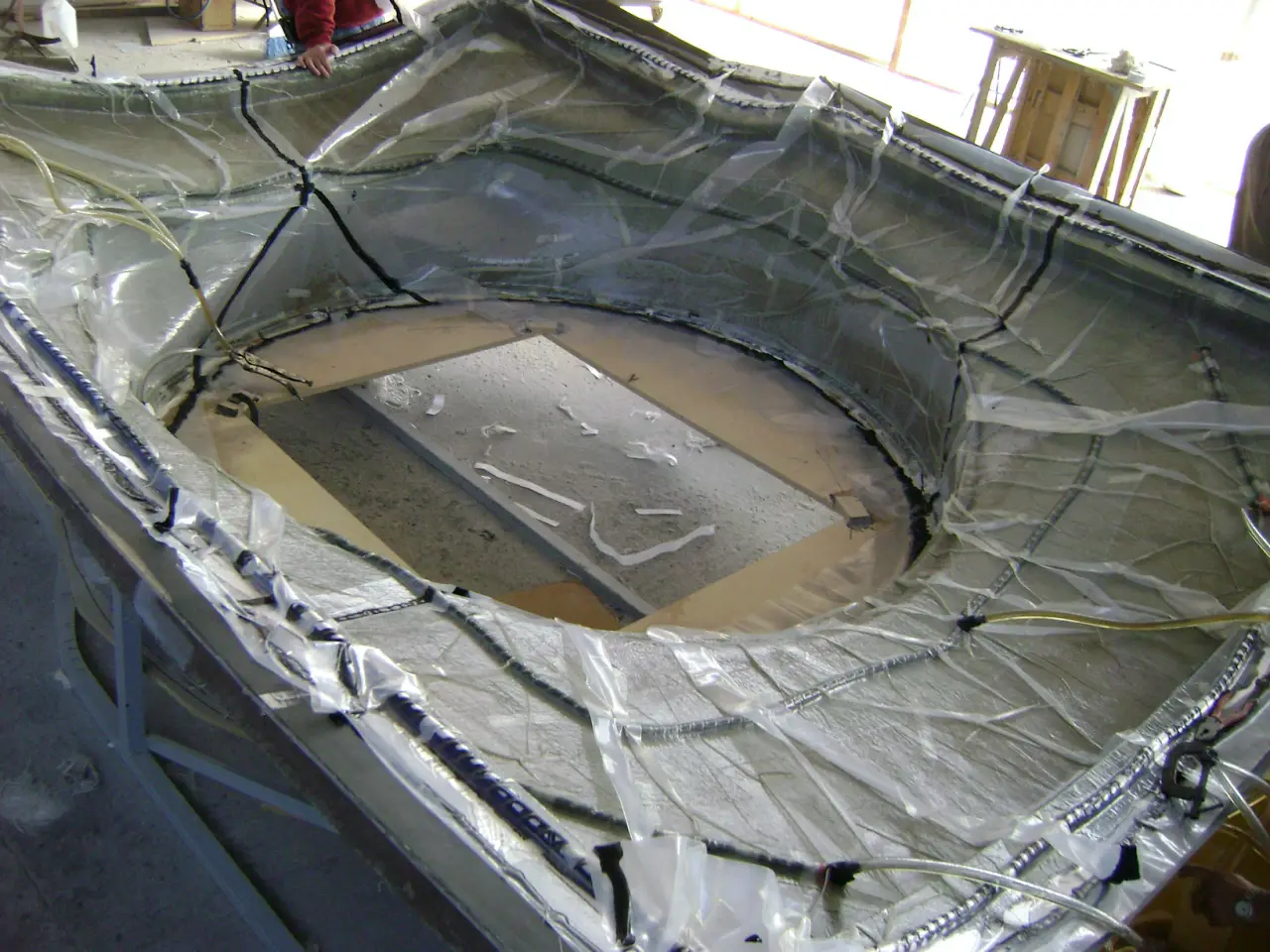
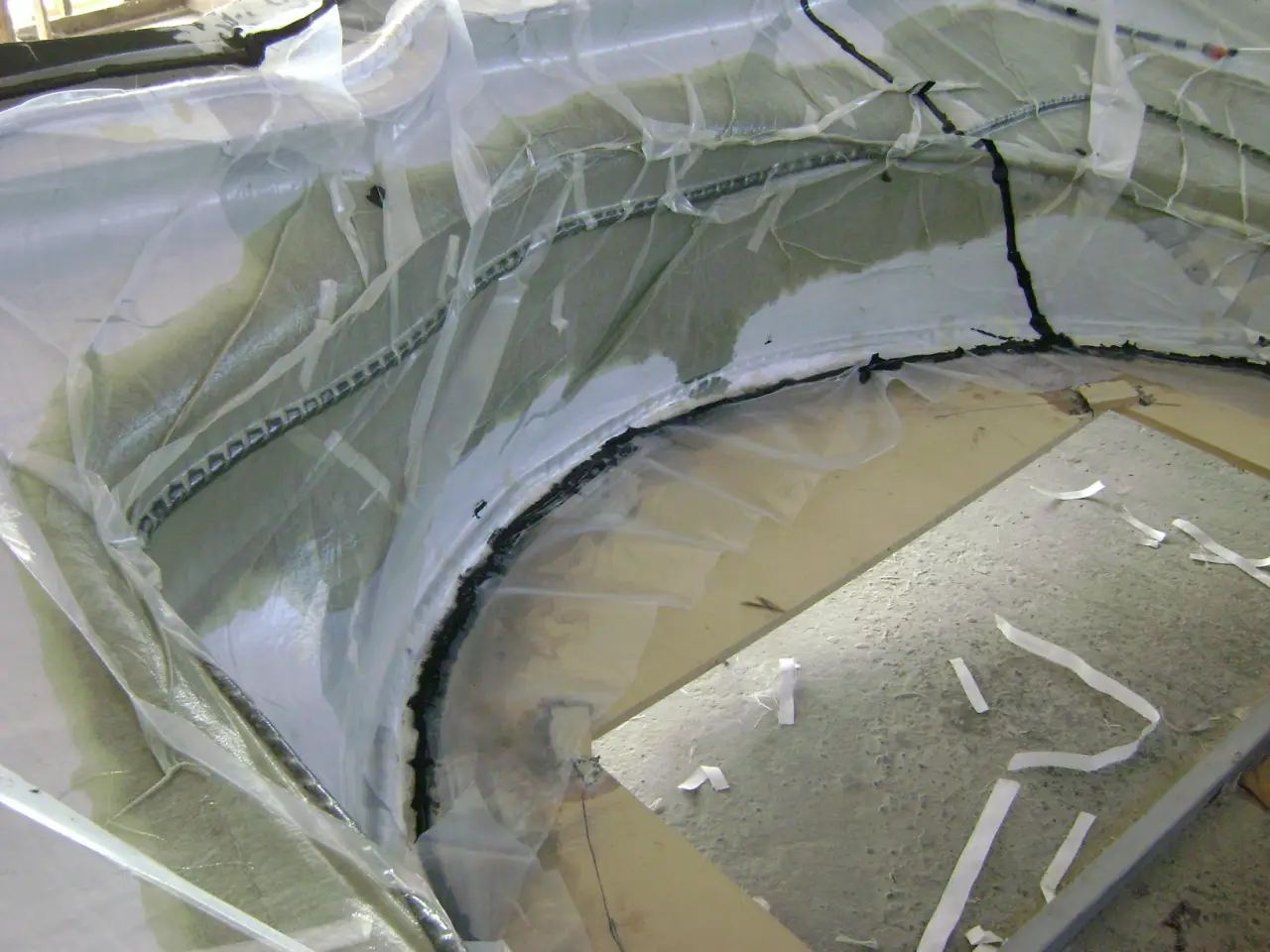
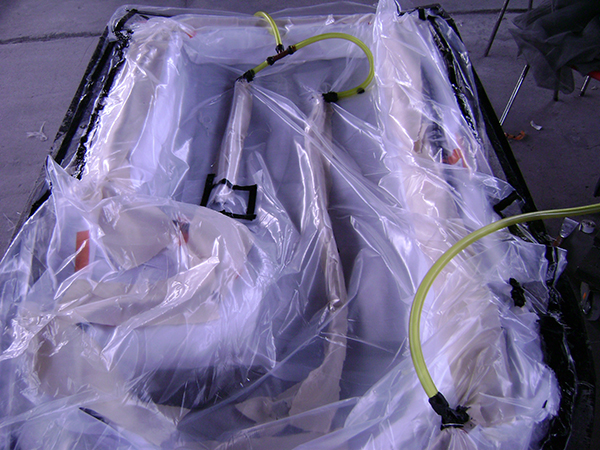
Vacuum Infusion
Resin infusion is a process where vacuum pressure draws resin into a dry fiber laminate within a one-sided mold. A rigid or flexible film membrane is placed over the top and sealed around the mold’s perimeter.
Resin infusion is considered a “closed mold process.” The main characteristics of this process include a higher fiber-to-resin ratio and improved mechanical properties.